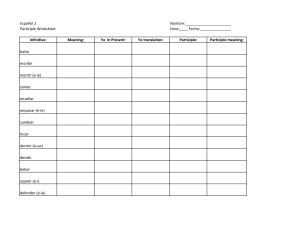
Past participle (solved, run) - Unit Operations Lab @ Brigham Young
... • Aristotle taught that matter comprised earth, wind, fire, and water. (not comprises earth, wind, fire, and water – further note the use of comprise here). ...
... • Aristotle taught that matter comprised earth, wind, fire, and water. (not comprises earth, wind, fire, and water – further note the use of comprise here). ...
Noun Clauses - 2 - Binus Repository
... • If the reporting verb (e.g. said) is in the past, the verb in the noun clause will usually also be in a past form: She said she watched TV every day. • Sometimes in spoken English, no change is made in the noun clause verb, especially if the speaker is reporting something immediately or soon after ...
... • If the reporting verb (e.g. said) is in the past, the verb in the noun clause will usually also be in a past form: She said she watched TV every day. • Sometimes in spoken English, no change is made in the noun clause verb, especially if the speaker is reporting something immediately or soon after ...
Parts of Speech - University of Central Missouri
... Kolln says that we can think of the words in the form classes as bricks and words in the structure classes as the mortar which holds the bricks together. Pronouns don't fit into either class but are part of both. Handouts included in this collection cover verbs and auxiliaries, adverbs, prepositions ...
... Kolln says that we can think of the words in the form classes as bricks and words in the structure classes as the mortar which holds the bricks together. Pronouns don't fit into either class but are part of both. Handouts included in this collection cover verbs and auxiliaries, adverbs, prepositions ...
Morphology and Syntax - University of Edinburgh
... That painting is beautiful. The door is locked. or attributively an ill person a pregnant woman a beautiful painting the locked door ...
... That painting is beautiful. The door is locked. or attributively an ill person a pregnant woman a beautiful painting the locked door ...
Ron`s Rules for Good Writing
... Rule #4: Use the Verb NOT the Noun In English, many words have two forms: a verb form and a noun form. Often a noun can be generated from a verb by adding a suffix such as ion. For example: Verbs create construct derive demonstrate solve ...
... Rule #4: Use the Verb NOT the Noun In English, many words have two forms: a verb form and a noun form. Often a noun can be generated from a verb by adding a suffix such as ion. For example: Verbs create construct derive demonstrate solve ...
16 Mar 09 - Pegasus @ UCF
... common and proper nouns – What are the rules for capitalizing a noun in English? count and noncount nouns – When do I use much/many, few/little? Why can’t I say much persons (In Spanish it’s "muchas personas")? Why do I say many cars but much/a lot of traffic (not many traffics)? singular and plural ...
... common and proper nouns – What are the rules for capitalizing a noun in English? count and noncount nouns – When do I use much/many, few/little? Why can’t I say much persons (In Spanish it’s "muchas personas")? Why do I say many cars but much/a lot of traffic (not many traffics)? singular and plural ...
How to determine the part of speech of a word
... These introduce subordinate clauses (sentences inside sentences). Examples: She said that she was going, I wonder if you are going, I wonder whether you are going. Pronouns Nominative I you he she it we they ...
... These introduce subordinate clauses (sentences inside sentences). Examples: She said that she was going, I wonder if you are going, I wonder whether you are going. Pronouns Nominative I you he she it we they ...
Common noun - Ms. Guggenheimer`s Education Connection
... use a comma before the conjunction. ◦ Note: If the sentences are very short, you can sometimes leave out the comma. ...
... use a comma before the conjunction. ◦ Note: If the sentences are very short, you can sometimes leave out the comma. ...
A brief revision on basics of Grammar
... doing the ‘watching’ action (Subject)? ‘She’ is, thus the subject. So the answer cannot be C or D because they describe Objects. For example, She ‘was watched by…’ This tells us that someone else is doing the watching, not ‘she’. ...
... doing the ‘watching’ action (Subject)? ‘She’ is, thus the subject. So the answer cannot be C or D because they describe Objects. For example, She ‘was watched by…’ This tells us that someone else is doing the watching, not ‘she’. ...
A brief revision on basics of Grammar
... doing the ‘watching’ action (Subject)? ‘She’ is, thus the subject. So the answer cannot be C or D because they describe Objects. For example, She ‘was watched by…’ This tells us that someone else is doing the watching, not ‘she’. ...
... doing the ‘watching’ action (Subject)? ‘She’ is, thus the subject. So the answer cannot be C or D because they describe Objects. For example, She ‘was watched by…’ This tells us that someone else is doing the watching, not ‘she’. ...
The Parts of Speech
... Recognition Tools: -Adverbs answer: How? When? Where? To what extent? How often? How much? How long? -by ending “-ly” ...
... Recognition Tools: -Adverbs answer: How? When? Where? To what extent? How often? How much? How long? -by ending “-ly” ...
Grammar Review - cloudfront.net
... Demonstrative pronouns – points specific things out (this, that, these, those) Indefinite pronouns – not referring to a specific person or thing (anyone, each) Reflexive pronouns – self, selves forms (myself, himself, ourselves, etc.) Possessive Pronouns – Caution – These words can act as ad ...
... Demonstrative pronouns – points specific things out (this, that, these, those) Indefinite pronouns – not referring to a specific person or thing (anyone, each) Reflexive pronouns – self, selves forms (myself, himself, ourselves, etc.) Possessive Pronouns – Caution – These words can act as ad ...
Parts of Speech Definitions
... Verb: (describes action taken by a noun) run, swim, think, eat, hate, love, tease, help Transitive – need to be followed by something that receives the action(a direct object); hit, sawed, helped, painted Intransitive – verbs that can stand alone; ran, thought, shopped, swam Helping/Linking/verbs of ...
... Verb: (describes action taken by a noun) run, swim, think, eat, hate, love, tease, help Transitive – need to be followed by something that receives the action(a direct object); hit, sawed, helped, painted Intransitive – verbs that can stand alone; ran, thought, shopped, swam Helping/Linking/verbs of ...
Chapter 4 - Tony Morris
... o Pronouns: stand in for nouns, usually so that we can avoid cumbersome repetition: Cristina is class president. She was elected last Month. Christina is the noun and the antecedent of the pronoun she. A pronoun must always agree in number with its antecedent. Pronouns include: personal (I/me, we/us ...
... o Pronouns: stand in for nouns, usually so that we can avoid cumbersome repetition: Cristina is class president. She was elected last Month. Christina is the noun and the antecedent of the pronoun she. A pronoun must always agree in number with its antecedent. Pronouns include: personal (I/me, we/us ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... intervening prepositional phrases. Do not make verbs agree with material that adds on to the subject without using “and” (usually surrounded by commas). When subjects are joined by or or nor the verb agrees with the noun closest to it (can be singular or plural). ...
... intervening prepositional phrases. Do not make verbs agree with material that adds on to the subject without using “and” (usually surrounded by commas). When subjects are joined by or or nor the verb agrees with the noun closest to it (can be singular or plural). ...
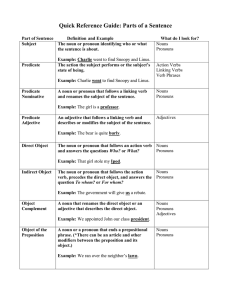
Parts of Speech and Parts of a Sentence
... Minnie asked Mickey, “Would you please carry in my suitcase for me?” Minnie told Daisy, “I would have gone to the party if Mickey had come home from work on time.” ...
... Minnie asked Mickey, “Would you please carry in my suitcase for me?” Minnie told Daisy, “I would have gone to the party if Mickey had come home from work on time.” ...
Slide 1
... which one? what kind of? how many? They usually precede the noun or pronoun that they modify. ...
... which one? what kind of? how many? They usually precede the noun or pronoun that they modify. ...
Parts of Speech
... Minnie asked Mickey, “Would you please carry in my suitcase for me?” Minnie told Daisy, “I would have gone to the party if Mickey had come home from work on time.” ...
... Minnie asked Mickey, “Would you please carry in my suitcase for me?” Minnie told Daisy, “I would have gone to the party if Mickey had come home from work on time.” ...