Grammar
... of popular democracy was based on their belief in the tendency of factions to further their self-interest at the expense of the common good. This sentence seems to be a struggle to get through. We can make it more understandable if we revise it to make its subjects characters and its verbs actions: ...
... of popular democracy was based on their belief in the tendency of factions to further their self-interest at the expense of the common good. This sentence seems to be a struggle to get through. We can make it more understandable if we revise it to make its subjects characters and its verbs actions: ...
Subjects – who or what a clause, phrase, or sentence is about
... the end of a word Ex: -s, -ly, - er, -est, -ed A prefix comes at the beginning of a word. Ex: dis-, pre-, re-, interArticles – a, an, the Prepositional Phrases Made up of a preposition plus its object and any modifiers. Common prepositions – about, above, according to, across, after, against, along, ...
... the end of a word Ex: -s, -ly, - er, -est, -ed A prefix comes at the beginning of a word. Ex: dis-, pre-, re-, interArticles – a, an, the Prepositional Phrases Made up of a preposition plus its object and any modifiers. Common prepositions – about, above, according to, across, after, against, along, ...
Fundamentals of English Grammar, Fourth Edition
... 5-3 Where, why, when, what time, how come, what . . . for . . . . . . . . . . . 117 5-4 Questions with who, who(m), and what . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119 5-5 Using what ⫹ a form of do . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121 5-6 Using which a ...
... 5-3 Where, why, when, what time, how come, what . . . for . . . . . . . . . . . 117 5-4 Questions with who, who(m), and what . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119 5-5 Using what ⫹ a form of do . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121 5-6 Using which a ...
Grammar wrap-up — Verbs, Adverbs, and Prepositions I realized
... Irish has only four tenses, one “mood” and one “voice”, those being: Present Habitual, Simple Past, Past Habitual, and Future tenses; Conditional Mood (if-then / would), and Subjunctive Voice (hope / curse). In our western dialect we only have a few personal pronoun endings to worry about when conju ...
... Irish has only four tenses, one “mood” and one “voice”, those being: Present Habitual, Simple Past, Past Habitual, and Future tenses; Conditional Mood (if-then / would), and Subjunctive Voice (hope / curse). In our western dialect we only have a few personal pronoun endings to worry about when conju ...
grammar notes powerpoint1
... A word used to describe a noun or pronoun to give more specific meaning. ...
... A word used to describe a noun or pronoun to give more specific meaning. ...
Year 2 - Crossley Fields
... speaker/writer by suggesting that you cannot be sure of a fact, or there may be some exceptions to the point being made. For example: ‘CO2 emissions are probably a major cause of global warming.’ Adverbs such as ‘also’, ‘however’ and ‘therefore’ are frequently used to make cohesive links between sen ...
... speaker/writer by suggesting that you cannot be sure of a fact, or there may be some exceptions to the point being made. For example: ‘CO2 emissions are probably a major cause of global warming.’ Adverbs such as ‘also’, ‘however’ and ‘therefore’ are frequently used to make cohesive links between sen ...
Courtney Wolfberg
... that introduces a dependent clause, joining it to a main clause. Also called a subordinator after, although, as, because, before, even if, even though, if, in order that once, provided that, rather than, since, so that, than, that, though, unless until, when, whenever, where, whereas, wherever, wh ...
... that introduces a dependent clause, joining it to a main clause. Also called a subordinator after, although, as, because, before, even if, even though, if, in order that once, provided that, rather than, since, so that, than, that, though, unless until, when, whenever, where, whereas, wherever, wh ...
Appendices (Spanish Grammar Book, Enrique Yepes, Bowdoin) http
... Object [objeto o complemento]. Part of the sentence that undergoes the action expressed by the verb. Examples: She wrote a letter to Pedro. → the letter is the direct object (what did she write?) → Pedro is the indirect object (to whom did she write?) She told him the secret. → the secret is the dir ...
... Object [objeto o complemento]. Part of the sentence that undergoes the action expressed by the verb. Examples: She wrote a letter to Pedro. → the letter is the direct object (what did she write?) → Pedro is the indirect object (to whom did she write?) She told him the secret. → the secret is the dir ...
Table of Contents – Overview
... A verb or noun is highlighted in a sentence and students have to sort it (ID it) as a verb or noun. *Use Supplemental Practice Activity 1 (still would use the direct teach in the re-teach unit, but would use these student pages). P2: Action and Linking Verbs Given an action verb (not in a sentence e ...
... A verb or noun is highlighted in a sentence and students have to sort it (ID it) as a verb or noun. *Use Supplemental Practice Activity 1 (still would use the direct teach in the re-teach unit, but would use these student pages). P2: Action and Linking Verbs Given an action verb (not in a sentence e ...
An introduction to Traditional Grammar
... your patience would be so fretted that you would hang yourself. Had we but world enough and time, / This coyness, lady, were no crime. Be that as it may . . .). Apart from the dropped -s ending in the present tense of verbs (as in that he leave), which tends in any case to be an American rather than ...
... your patience would be so fretted that you would hang yourself. Had we but world enough and time, / This coyness, lady, were no crime. Be that as it may . . .). Apart from the dropped -s ending in the present tense of verbs (as in that he leave), which tends in any case to be an American rather than ...
Document
... The verb you are about to learn, “ir” is IRREGULAR. It means “to go” in English. It is often followed by the word a: Voy al cine. ...
... The verb you are about to learn, “ir” is IRREGULAR. It means “to go” in English. It is often followed by the word a: Voy al cine. ...
TAM seminar I
... the part of speech noun in English is inflected for case and number, the primary and most characteristic use is to express substances; the secondary use of the nouns as regards their meaning is to express attributes and phenomena....The primary grammatical function is to serve as head nouns; melting ...
... the part of speech noun in English is inflected for case and number, the primary and most characteristic use is to express substances; the secondary use of the nouns as regards their meaning is to express attributes and phenomena....The primary grammatical function is to serve as head nouns; melting ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... There and here are never considered subjects. In sentences that begin with these words, the subject is usually found after the verb. ...
... There and here are never considered subjects. In sentences that begin with these words, the subject is usually found after the verb. ...
Nouns
... 2. It is hard for her to get up in the morning. 3. Where is the world’s largest amusement park? 4. The music folder was found underneath the old piano. 5. Some people are very superstitious; they do not like black cats or broken mirrors. 6. She seems happy about her high grade on the math test. ...
... 2. It is hard for her to get up in the morning. 3. Where is the world’s largest amusement park? 4. The music folder was found underneath the old piano. 5. Some people are very superstitious; they do not like black cats or broken mirrors. 6. She seems happy about her high grade on the math test. ...
Subject
... • Several of the women are pilots. • A few in the crowd were rowdy. • Have both tried harder? ...
... • Several of the women are pilots. • A few in the crowd were rowdy. • Have both tried harder? ...
Lexical words - ملتقى طلاب وطالبات جامعة الملك فيصل,جامعة الدمام
... Lexical Verbs Words such as admit, build, choose, write are lexical verbs. They are distinct from Auxiliary verbs like can and will, which we treat as function words. The primary verbs be, have and do ( the most common verbs in English) occur as both lexical verbs and auxiliaries. Lexical verbs are ...
... Lexical Verbs Words such as admit, build, choose, write are lexical verbs. They are distinct from Auxiliary verbs like can and will, which we treat as function words. The primary verbs be, have and do ( the most common verbs in English) occur as both lexical verbs and auxiliaries. Lexical verbs are ...
basics - La Salle University
... Reflexives pronouns only after named: I, myself, agree. Not: Bill and myself. Pronoun case as above: Is it subjective (nominative), objective (whom-him). Give advice to whoever asked. [Did him ask or did he ask? He asked, so it’s whoever] Jones, who I always thought was uneducated, gave the correct ...
... Reflexives pronouns only after named: I, myself, agree. Not: Bill and myself. Pronoun case as above: Is it subjective (nominative), objective (whom-him). Give advice to whoever asked. [Did him ask or did he ask? He asked, so it’s whoever] Jones, who I always thought was uneducated, gave the correct ...
The Sentence Page 4-5
... Learning Objective: To identify verbs that agree with their subject in a sentence. ...
... Learning Objective: To identify verbs that agree with their subject in a sentence. ...
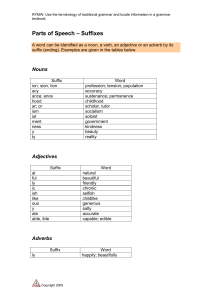
Parts of Speech – Suffixes
... Adding suffixes to words can change or add to their meaning, but most importantly they show how a word will be used in a sentence and what part of speech (e.g. noun, verb, adjective) the word belongs to. Creating words banks is one way of helping learners build their vocabulary base. Look at the exa ...
... Adding suffixes to words can change or add to their meaning, but most importantly they show how a word will be used in a sentence and what part of speech (e.g. noun, verb, adjective) the word belongs to. Creating words banks is one way of helping learners build their vocabulary base. Look at the exa ...
Nouns
... places or things without specifying which one 3 types: singular, plural or both Singular – use with “is” ...
... places or things without specifying which one 3 types: singular, plural or both Singular – use with “is” ...
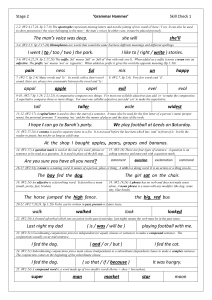
Stage 2 Check 1 – Answers
... 1-2. (W2:4,17,24. Sp 2:7-9) The apostrophe represents missing letters and not the joining of two words (I have / I’ve). It can also be used to show possession ( the voice belonging to the man – the man’s voice) In either case, it must be placed precisely. ...
... 1-2. (W2:4,17,24. Sp 2:7-9) The apostrophe represents missing letters and not the joining of two words (I have / I’ve). It can also be used to show possession ( the voice belonging to the man – the man’s voice) In either case, it must be placed precisely. ...