Chapter Two
... Connect words; they show the relationship of nouns or pronouns to other words in the sentence. about after at before behind ...
... Connect words; they show the relationship of nouns or pronouns to other words in the sentence. about after at before behind ...
Check 6 Answers - Tranmere Park Primary School
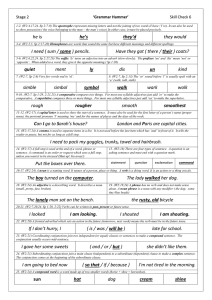
... 1-2. (W2:4,17,24. Sp 2:7-9) The apostrophe represents missing letters and not the joining of two words (I have / I’ve). It can also be used to show possession ( the voice belonging to the man – the man’s voice) In either case, it must be placed precisely. ...
... 1-2. (W2:4,17,24. Sp 2:7-9) The apostrophe represents missing letters and not the joining of two words (I have / I’ve). It can also be used to show possession ( the voice belonging to the man – the man’s voice) In either case, it must be placed precisely. ...
SE Cheat Codes
... Does anyone own those nouns? Do the nouns belong to anyone? Are they named? Are they given a “substitute” name? ...
... Does anyone own those nouns? Do the nouns belong to anyone? Are they named? Are they given a “substitute” name? ...
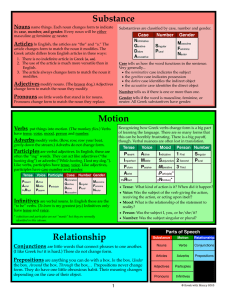
Substance Nouns
... • the genitive case indicates possession • the dative case identifies the indirect object • the accusative case identifies the direct object Number tells us if there is one or more than one. ...
... • the genitive case indicates possession • the dative case identifies the indirect object • the accusative case identifies the direct object Number tells us if there is one or more than one. ...
Unit 2: Verbs, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions and Interjections
... • Tip: if you can substitute “is, are, am” in for the linking verb and the sentence still makes sense, then the verb is linking ...
... • Tip: if you can substitute “is, are, am” in for the linking verb and the sentence still makes sense, then the verb is linking ...
seventh grade notes
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
Finite and Non-finite Verbs.p65
... a) He loves to dance and to sing. (gerund) b) It is no good to get upset. (gerund) c) The teacher told him that he should study hard. She further advised him that he should revise all the work done. (suitable infinite construction) d) Jim has decided that he is going to buy a car this summer. (suita ...
... a) He loves to dance and to sing. (gerund) b) It is no good to get upset. (gerund) c) The teacher told him that he should study hard. She further advised him that he should revise all the work done. (suitable infinite construction) d) Jim has decided that he is going to buy a car this summer. (suita ...
Nouns - Marlington Local Schools
... and, nor, but , or, yet, so (FANBOYS) These conjunctions connect words, phrases, and clauses of equal value. Clauses of equal value are called INDEPENDENT CLAUSES and can stand on their own as separate sentences. ...
... and, nor, but , or, yet, so (FANBOYS) These conjunctions connect words, phrases, and clauses of equal value. Clauses of equal value are called INDEPENDENT CLAUSES and can stand on their own as separate sentences. ...
Nouns Adjectives Verbs
... Using conjunctions Coordinating conjunctions: join items of equal importance You can have coffee or tea. Subordinating conjunctions: connect a subordinate clause to a main clause. I made a sandwich because I was hungry. ...
... Using conjunctions Coordinating conjunctions: join items of equal importance You can have coffee or tea. Subordinating conjunctions: connect a subordinate clause to a main clause. I made a sandwich because I was hungry. ...
Types of noun - Maiden Erlegh School
... Using conjunctions Coordinating conjunctions: join items of equal importance You can have coffee or tea. Subordinating conjunctions: connect a subordinate clause to a main clause. I made a sandwich because I was hungry. ...
... Using conjunctions Coordinating conjunctions: join items of equal importance You can have coffee or tea. Subordinating conjunctions: connect a subordinate clause to a main clause. I made a sandwich because I was hungry. ...
Grammar Cards - Word types(1) DOCX File
... Using conjunctions Coordinating conjunctions: join items of equal importance You can have coffee or tea. Subordinating conjunctions: connect a subordinate clause to a main clause. I made a sandwich because I was hungry. ...
... Using conjunctions Coordinating conjunctions: join items of equal importance You can have coffee or tea. Subordinating conjunctions: connect a subordinate clause to a main clause. I made a sandwich because I was hungry. ...
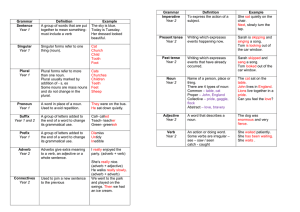
Subjects – who or what a clause, phrase, or sentence is about
... Prepositional Phrases Made up of a preposition plus its object and any modifiers. Common prepositions – about, above, according to, across, after, against, along, among, around, at , ...
... Prepositional Phrases Made up of a preposition plus its object and any modifiers. Common prepositions – about, above, according to, across, after, against, along, among, around, at , ...
Writing Practice – Simple Present Tense
... Directions: Write sentences with the verbs listed below. For each verb, make three sentences. For one sentence use the subject I. For the second sentence use one singular noun as the subject, such as my friend, my sister, my neighbor, this city, this college, or any other person, place, or thing you ...
... Directions: Write sentences with the verbs listed below. For each verb, make three sentences. For one sentence use the subject I. For the second sentence use one singular noun as the subject, such as my friend, my sister, my neighbor, this city, this college, or any other person, place, or thing you ...
notes as word document
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
... 1. A NOUN NAMES A PERSON, PLACE, THING, OR IDEA. IT CAN BE PROPER OR COMMON, COLLECTIVE, CONCRETE, OR ABSTRACT, SINGULAR OR PLURAL. NOUNS HAVE PERSON (first, second, third), NUMBER (singular/plural), GENDER (masculine, feminine, neuter), AND CASE (nominative, possessive, objective). 2. A VERB IS A W ...
Parts of Speech Powerpoint
... • As a closed class/function word, they can only be taken from a small set. These are always followed by a noun. This is the key factor in determining whether or not a lexeme is a preposition or an adverb. Verbs • There is only one lexeme that has been marked for tense i.e. past tense; to be + past ...
... • As a closed class/function word, they can only be taken from a small set. These are always followed by a noun. This is the key factor in determining whether or not a lexeme is a preposition or an adverb. Verbs • There is only one lexeme that has been marked for tense i.e. past tense; to be + past ...
Latin 101: How to Identify Grammatical Forms in Context
... b. infinitive: identify as infinitive, and supply the 1st singular of the verb example: Quīntus nōlēbat diūtius in lūdō Orbiliī studēre. studēre: infinitive of studeō c. imperative: identify as imperative sing. or pl.; supply the 1st sing. of the verb example: nolīte ludere, puerī, sed audīte. audīt ...
... b. infinitive: identify as infinitive, and supply the 1st singular of the verb example: Quīntus nōlēbat diūtius in lūdō Orbiliī studēre. studēre: infinitive of studeō c. imperative: identify as imperative sing. or pl.; supply the 1st sing. of the verb example: nolīte ludere, puerī, sed audīte. audīt ...
Study Guide for Grammar Test 2
... Learn the term Predicate. It’s useful when we talk about commas. A predicate is the completer of a sentence. The subject names the "do-er" or "be-er" of the sentence; the predicate does the rest of the work. A simple predicate consists of only a verb, verb string, or compound verb: ...
... Learn the term Predicate. It’s useful when we talk about commas. A predicate is the completer of a sentence. The subject names the "do-er" or "be-er" of the sentence; the predicate does the rest of the work. A simple predicate consists of only a verb, verb string, or compound verb: ...
- ESL101.com
... sentences. The goal here is to show how even the most complex sentences remain consistent with these essential grammatical features. In doing so we cill focus our attention on three types of subordinate clauses – adjective, noun, and adverb clauses. ...
... sentences. The goal here is to show how even the most complex sentences remain consistent with these essential grammatical features. In doing so we cill focus our attention on three types of subordinate clauses – adjective, noun, and adverb clauses. ...
The Eight Parts of Speech Poem
... All names of persons, places, ideas, and things Are nouns, such as Caesar, home, love and rings. Pronouns are used in place of nouns: I think, she sings, they work, he frowns. When the kind you wish to state Use an adjective, such as “great!” Next we have the verbs which tell Of action, being, state ...
... All names of persons, places, ideas, and things Are nouns, such as Caesar, home, love and rings. Pronouns are used in place of nouns: I think, she sings, they work, he frowns. When the kind you wish to state Use an adjective, such as “great!” Next we have the verbs which tell Of action, being, state ...
Grammar Definition Example Sentence Year 1 A group of words that
... A group of words that are put together to mean somethingmust include a verb ...
... A group of words that are put together to mean somethingmust include a verb ...