Neurons, Synapses, the Nervous System
... Action potentials are the signals conducted by axons. An action potential (nerve impulse) is an all-or-none response to depolarization of the nerve cell. A stimulus opens voltage-gated sodium channels and Na+ ions enter the cell, bringing the membrane potential to a positive value. In order to gener ...
... Action potentials are the signals conducted by axons. An action potential (nerve impulse) is an all-or-none response to depolarization of the nerve cell. A stimulus opens voltage-gated sodium channels and Na+ ions enter the cell, bringing the membrane potential to a positive value. In order to gener ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes the membrane to become more positive. This starts an action potential, or nerve impulse. They follow the all or none law!!! • The membrane will repolarize when K+ ...
... depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes the membrane to become more positive. This starts an action potential, or nerve impulse. They follow the all or none law!!! • The membrane will repolarize when K+ ...
M.learning.hccs.edu
... postsynaptic neuron will have an Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP) when A) chemically-regulated potassium channels are open and potassium is diffusing out of the cell. B) more calcium ions than usual diffuse into the neuron. C) chemically-regulated sodium channels are open and sodium is diffu ...
... postsynaptic neuron will have an Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP) when A) chemically-regulated potassium channels are open and potassium is diffusing out of the cell. B) more calcium ions than usual diffuse into the neuron. C) chemically-regulated sodium channels are open and sodium is diffu ...
Control_Systems11
... impulse travels up sensory neurons, to the spinal cord (interneuron), then immediately travels down motor neurons for a response. The pathway the impulse travels is called the reflex arc ...
... impulse travels up sensory neurons, to the spinal cord (interneuron), then immediately travels down motor neurons for a response. The pathway the impulse travels is called the reflex arc ...
Developer Notes
... messages. These “messages” are actually electrical. We can use our knowledge of physics to understand how they are transmitted! Different types of neurons respond to different stimuli. A stimulus is anything that generates a nerve response. For example, light is a stimulus that generates a response ...
... messages. These “messages” are actually electrical. We can use our knowledge of physics to understand how they are transmitted! Different types of neurons respond to different stimuli. A stimulus is anything that generates a nerve response. For example, light is a stimulus that generates a response ...
The Biological Perspective - Klicks-IBPsychology-Wiki
... • Act like a wire passing an electric signal called a nerve impulse • Key components of neurons – Dendrites- small branches that receive and transmit info between neurons – Axon-cable like structure on which messages travel through neurons – Myelin- insulating sheath around the axon, made of tightly ...
... • Act like a wire passing an electric signal called a nerve impulse • Key components of neurons – Dendrites- small branches that receive and transmit info between neurons – Axon-cable like structure on which messages travel through neurons – Myelin- insulating sheath around the axon, made of tightly ...
Study Guide 1
... 16. What is the absolute refractory period of a neuron? The relative refractory period? 17. What is a neurotransmitter? Which neurotransmitters are excitatory and which are inhibitory? 18. What is depolarization? What is hyperpolarization? 19. Under what conditions does neurotransmitter release caus ...
... 16. What is the absolute refractory period of a neuron? The relative refractory period? 17. What is a neurotransmitter? Which neurotransmitters are excitatory and which are inhibitory? 18. What is depolarization? What is hyperpolarization? 19. Under what conditions does neurotransmitter release caus ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... contained wholly within one region of the nervous system are called intrinsic neurons or interneurons. Interneurons may not have an axon. ...
... contained wholly within one region of the nervous system are called intrinsic neurons or interneurons. Interneurons may not have an axon. ...
Week7
... • The human brain has an estimated 1011 tiny units called neurons • These neurons are interconnected with an estimated 1015 links (each neuron makes synapses with approximately 104 other neurons). • Massive parallelism allows for computational efficiency ...
... • The human brain has an estimated 1011 tiny units called neurons • These neurons are interconnected with an estimated 1015 links (each neuron makes synapses with approximately 104 other neurons). • Massive parallelism allows for computational efficiency ...
Nervous System
... Excitable cells communicate with each other by action potential (AP) for long distance and by graded potential for short distance. *Production of both types of potentials depend upon the existence of a resting membrane potential (RMP) and the presence of certain types of ion channel. *The RMP is an ...
... Excitable cells communicate with each other by action potential (AP) for long distance and by graded potential for short distance. *Production of both types of potentials depend upon the existence of a resting membrane potential (RMP) and the presence of certain types of ion channel. *The RMP is an ...
Ch10 Reading Guide
... 1. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across ______________________________ and react with ____________________ that form structures called _______________ in or on the______________________ neuron membrane. 2. Some neurotransmitters cause ion channels to _________________________ , some cause ion c ...
... 1. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across ______________________________ and react with ____________________ that form structures called _______________ in or on the______________________ neuron membrane. 2. Some neurotransmitters cause ion channels to _________________________ , some cause ion c ...
nervous system development and histology
... transmit information between neurons within the CNS; analyze inputs, • coordinate outputs are the most common type of neuron (20 billion)• are all multipolar• ...
... transmit information between neurons within the CNS; analyze inputs, • coordinate outputs are the most common type of neuron (20 billion)• are all multipolar• ...
The Nervous System
... and much of the cytoplasm Dendrites branched extensions that spread out from the cell body receive impulses from other neurons and carry impulses to the cell body Axon the long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body ends in a series of small swellings called axon terminals As an impul ...
... and much of the cytoplasm Dendrites branched extensions that spread out from the cell body receive impulses from other neurons and carry impulses to the cell body Axon the long fiber that carries impulses away from the cell body ends in a series of small swellings called axon terminals As an impul ...
The effect of neural synchronization on information transmission
... tuned to 16 orientations and projected nonspecifically to 20% of the neurons in the receiver layer. We assumed that the stimulus was a sequence of drifting gratings with random orientations. In response to stimuli, the network displayed transiently synchronized responses. Because similarly tuned LNP ...
... tuned to 16 orientations and projected nonspecifically to 20% of the neurons in the receiver layer. We assumed that the stimulus was a sequence of drifting gratings with random orientations. In response to stimuli, the network displayed transiently synchronized responses. Because similarly tuned LNP ...
Slide 1
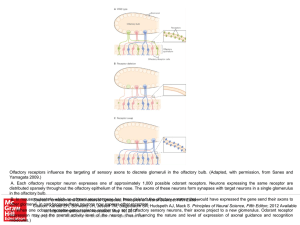
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Slide ()
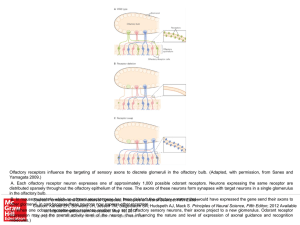
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Objective 1 | Explain why psychologists are concerned with human
... study of neural processes in other mammals and in relatively simple animals because humans and other animals have similar neural systems. Page: 54 Objective 3| Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. The body’s circuitry, the nervous system, consists of billions o ...
... study of neural processes in other mammals and in relatively simple animals because humans and other animals have similar neural systems. Page: 54 Objective 3| Describe the parts of a neuron, and explain how its impulses are generated. The body’s circuitry, the nervous system, consists of billions o ...
Chapter 13 - Los Angeles City College
... Action potentials pass directly from one neuron to another. 2. Chemical Synapse: Found in CNS, muscles, and most other organs. Require neurotransmitters: Chemicals that convey messages from one neuron to another. Transmitting neuron releases neurotransmitters which cross synapse and cause an ...
... Action potentials pass directly from one neuron to another. 2. Chemical Synapse: Found in CNS, muscles, and most other organs. Require neurotransmitters: Chemicals that convey messages from one neuron to another. Transmitting neuron releases neurotransmitters which cross synapse and cause an ...
HERE
... Click on the “Other Cells in the Brain” link and answer the following questions: 5. There are about ______________ neurons in the brain as well as ______________ of support cells called _____________________. 6. There are 3 types of glial cells. Name each of the 3 and explain their function: 1. ____ ...
... Click on the “Other Cells in the Brain” link and answer the following questions: 5. There are about ______________ neurons in the brain as well as ______________ of support cells called _____________________. 6. There are 3 types of glial cells. Name each of the 3 and explain their function: 1. ____ ...
O`Kane
... 9. Which of the following receives information from the peripheral nervous system? A. Effector B. Receptor C. Control center D. A and B are correct. E. A and C are correct. 10. Complex activities require one or more ______________ within the integrative center. A. afferent nerves B. sensory neurons ...
... 9. Which of the following receives information from the peripheral nervous system? A. Effector B. Receptor C. Control center D. A and B are correct. E. A and C are correct. 10. Complex activities require one or more ______________ within the integrative center. A. afferent nerves B. sensory neurons ...
Study Guide
... your heart, breathing, and digestion is called the medulla. The cerebellum controls balance and coordination and makes sure your muscles work in the right order. Nerves are long threads of specialized cells. Jumping across the space between two neurons is called a synapse. The spinal cord is the lar ...
... your heart, breathing, and digestion is called the medulla. The cerebellum controls balance and coordination and makes sure your muscles work in the right order. Nerves are long threads of specialized cells. Jumping across the space between two neurons is called a synapse. The spinal cord is the lar ...
Chapter 3
... environment 2. motor neurons – send information from brain to parts of body 3. interneurons – intermediaries between motor and sensory neurons; receive and send information b. parts of the neuron (diagram p. 48) c. glial cells – hold neurons in place; care and feeding of neurons ...
... environment 2. motor neurons – send information from brain to parts of body 3. interneurons – intermediaries between motor and sensory neurons; receive and send information b. parts of the neuron (diagram p. 48) c. glial cells – hold neurons in place; care and feeding of neurons ...
Development & Neuroplasticity - U
... young brain may contribute to its greater plasticity (capability for functions to be mediated by other neurons not originally involved) ...
... young brain may contribute to its greater plasticity (capability for functions to be mediated by other neurons not originally involved) ...
The Nervous System (Chapter 7)
... 27. The faster type of impulse propagation occurs in myelinated fibers and is called _________________________. 28. List a few of the factors that can impair the conduction of impulses. ...
... 27. The faster type of impulse propagation occurs in myelinated fibers and is called _________________________. 28. List a few of the factors that can impair the conduction of impulses. ...
Nerve Flash Cards
... and transmit sensory information, and there are several different types of them, with receptors for touch, light, smell, etc). Motor neurons transmit signals for muscle contraction, etc. What characteristics do all neurons share? They all share certain characteristics. They have longevity (can last ...
... and transmit sensory information, and there are several different types of them, with receptors for touch, light, smell, etc). Motor neurons transmit signals for muscle contraction, etc. What characteristics do all neurons share? They all share certain characteristics. They have longevity (can last ...