Nervous System - Phoenix Union High School District
... 1. Neuroglia of the CNS a) astrocytes - star shaped cells that connect neurons together and to their ...
... 1. Neuroglia of the CNS a) astrocytes - star shaped cells that connect neurons together and to their ...
The Nervous System
... • To identify the basic structure of a neuron. • To explain the main components of the nervous system. • To compare and contrast the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • To differentiate between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. ...
... • To identify the basic structure of a neuron. • To explain the main components of the nervous system. • To compare and contrast the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. • To differentiate between the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. ...
Neurotransmitters - Woodridge High School
... mood, appetite, and sleep. Research shows that people with depression often have lower than normal levels of serotonin. _______________________—mainly involved in controlling movement and aiding the flow of information to the front of the brain, which is linked to thought and emotion. It is also lin ...
... mood, appetite, and sleep. Research shows that people with depression often have lower than normal levels of serotonin. _______________________—mainly involved in controlling movement and aiding the flow of information to the front of the brain, which is linked to thought and emotion. It is also lin ...
Unit 3 Study Guide
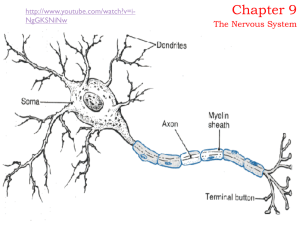
... 1. Neuroanatomy a. Neuroanatomy i. The study of the parts and functions of nerves ii. Neurons 1. individual nerve cells b. Parts of the Neuron i. Dendrites 1. root like parts of the cell 2. stretch out from the cell body 3. grow to make synaptic connections with other neurons ii. Cell body (soma) 1. ...
... 1. Neuroanatomy a. Neuroanatomy i. The study of the parts and functions of nerves ii. Neurons 1. individual nerve cells b. Parts of the Neuron i. Dendrites 1. root like parts of the cell 2. stretch out from the cell body 3. grow to make synaptic connections with other neurons ii. Cell body (soma) 1. ...
Neural Networks
... A neuron is a cell in the brain that collects, processes and disseminates electric signals On their own, neurons are not particularly complex Much of the brain’s information-processing capacity is thought to stem from the number of and interrelationships between the neurons. As such is an emergent p ...
... A neuron is a cell in the brain that collects, processes and disseminates electric signals On their own, neurons are not particularly complex Much of the brain’s information-processing capacity is thought to stem from the number of and interrelationships between the neurons. As such is an emergent p ...
biology lecture notes chapter 2
... that a neuron has to work with. Action Potential has the following characteristics: 1. THRESHOLD (enough neurotransmitters are received to send a message to take action): depolarization is needed to trigger. 2. It occurs “ALL OR NONE” principle (Neuron either fires completely or it does not fire at ...
... that a neuron has to work with. Action Potential has the following characteristics: 1. THRESHOLD (enough neurotransmitters are received to send a message to take action): depolarization is needed to trigger. 2. It occurs “ALL OR NONE” principle (Neuron either fires completely or it does not fire at ...
Part 2 of Unit Test 4
... Written portion Directions: Answer the following short answer questions using complete sentences. (5 points each) ...
... Written portion Directions: Answer the following short answer questions using complete sentences. (5 points each) ...
Brain - People
... Ability of the brain to continuously adapt its micro-morphology and function in response to new experiences (Nicolelis & Cicurel, The Relativistic Brain, (2015) ...
... Ability of the brain to continuously adapt its micro-morphology and function in response to new experiences (Nicolelis & Cicurel, The Relativistic Brain, (2015) ...
the physiological approach
... Na+ channels inactivate (absolute refractory period) – completely unresponsive to a second stimulus Potassium flows out of the axon ...
... Na+ channels inactivate (absolute refractory period) – completely unresponsive to a second stimulus Potassium flows out of the axon ...
Digit Recognition Using Machine Learning
... neural network machine learning algorithms with back propagation to develop a program which will recognize handwritten letters and numbers. ...
... neural network machine learning algorithms with back propagation to develop a program which will recognize handwritten letters and numbers. ...
here - CNC
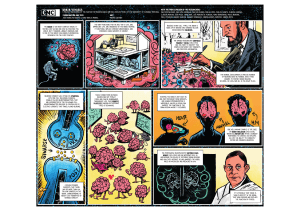
... The Portuguese Neuroscientist António Egas Moniz (1874-1955) had an important role in uncovering the roles of difFerent brain regions and how they interact. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1949. ...
... The Portuguese Neuroscientist António Egas Moniz (1874-1955) had an important role in uncovering the roles of difFerent brain regions and how they interact. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1949. ...
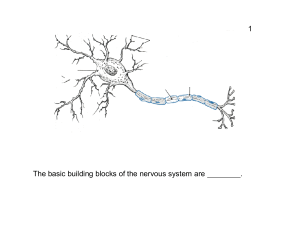
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... brief electrical charge that travels down the axon ...
... brief electrical charge that travels down the axon ...
the neural impulse
... Neurons' specialized structures allow them to transmit messages throughout the nervous system. The sending of a message from one neuron to the next is called the neural impulse. Figure 2 is a series of simplified diagrams meant to familiarize you with the steps involved in the neural impulse. Refer ...
... Neurons' specialized structures allow them to transmit messages throughout the nervous system. The sending of a message from one neuron to the next is called the neural impulse. Figure 2 is a series of simplified diagrams meant to familiarize you with the steps involved in the neural impulse. Refer ...
Nervous System - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... Nervous System: receives and responds to information gotten both inside and outside of the body; also helps to maintain homeostasis. Stimulus: an environmental signal that an organism reacts to. Response: what the body does in reaction to a stimulus. Neuron (nerve cell): specialized cell that carrie ...
... Nervous System: receives and responds to information gotten both inside and outside of the body; also helps to maintain homeostasis. Stimulus: an environmental signal that an organism reacts to. Response: what the body does in reaction to a stimulus. Neuron (nerve cell): specialized cell that carrie ...
The Nervous System
... The neurotransmitter serotonin is vital in regulating many of our basic functions. Serotonin is, among other things, the feel good neurotransmitter and helps to regulate body temp. Our brain cells are constantly trying to bring some amount of serotonin back into the cells and out of the ...
... The neurotransmitter serotonin is vital in regulating many of our basic functions. Serotonin is, among other things, the feel good neurotransmitter and helps to regulate body temp. Our brain cells are constantly trying to bring some amount of serotonin back into the cells and out of the ...
Lecture #19 - Suraj @ LUMS
... The Hind and Midbrain • The brain stem is the smallest and from an evolutionary viewpoint, the oldest and most primitive part of the brain. • The brain stem is continuous with the spinal cord, and is composed of the parts of the hindbrain and midbrain. • The medulla oblongata and pons control heart ...
... The Hind and Midbrain • The brain stem is the smallest and from an evolutionary viewpoint, the oldest and most primitive part of the brain. • The brain stem is continuous with the spinal cord, and is composed of the parts of the hindbrain and midbrain. • The medulla oblongata and pons control heart ...
13.2 part 2
... synapse is called the presynaptic neuron. The neuron leaving the synapse is called the postsynaptic neuron. The neurotransmitters that carry the impulse across the synapse are contained in small vesicles located in the end plates of axons. ...
... synapse is called the presynaptic neuron. The neuron leaving the synapse is called the postsynaptic neuron. The neurotransmitters that carry the impulse across the synapse are contained in small vesicles located in the end plates of axons. ...
The Nervous System
... Types of synapses Excitatory synapses—neurotransmitter causes Na+ to enter and K+ to exit, which depolarizes the cell. If enough “excitation” occurs action potential is the result. Inhibitory synapses—causes membrane to be more permeable to K+ and Cl-, hyperpolarizing the cell. If enough “inhibitio ...
... Types of synapses Excitatory synapses—neurotransmitter causes Na+ to enter and K+ to exit, which depolarizes the cell. If enough “excitation” occurs action potential is the result. Inhibitory synapses—causes membrane to be more permeable to K+ and Cl-, hyperpolarizing the cell. If enough “inhibitio ...
The Nervous System
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
Nervous Tissue - MrsSconyersAnatomy
... List the structures and basic functions of the nervous system. Describe the organization of the nervous system. ...
... List the structures and basic functions of the nervous system. Describe the organization of the nervous system. ...
6 BIO Neurotransmitters - Appoquinimink High School
... neuron has a pre-set level of stimulation that needs to be met or exceeded in order for it to pass the received impulses on to the next neuron. This is called a neuron’s threshold. ...
... neuron has a pre-set level of stimulation that needs to be met or exceeded in order for it to pass the received impulses on to the next neuron. This is called a neuron’s threshold. ...
36.1: The Nervous System
... body’s responses to changes in the environment HOW: Stimulus: a change in the external or internal environment which initiates an impulse Impulse~ an electro-chemical charge generated along a neuron Receptors~ structures specialized to detect certain stimuli Response~ a reaction to a stimulus Effect ...
... body’s responses to changes in the environment HOW: Stimulus: a change in the external or internal environment which initiates an impulse Impulse~ an electro-chemical charge generated along a neuron Receptors~ structures specialized to detect certain stimuli Response~ a reaction to a stimulus Effect ...
Study Concepts for Exam V - Nervous System
... Motor pathways that descend the spinal cord to the PNS The specialized cells, location, and function associated with vision, taste buds, olfaction, hearing, static equilibrium, and dynamic equilibrium. The wrappings of a nerve Nervous system defects arising during pregnancy Divisions of the CNS and ...
... Motor pathways that descend the spinal cord to the PNS The specialized cells, location, and function associated with vision, taste buds, olfaction, hearing, static equilibrium, and dynamic equilibrium. The wrappings of a nerve Nervous system defects arising during pregnancy Divisions of the CNS and ...