Nervous System Ch 10 Notes - Reading Community Schools
... threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
... threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
Nervous System I
... Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System. Central Nervous System (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) composed of the nervous (cranial and spinal) that connects the CNS to other body parts. Together these systems provide three general functio ...
... Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System. Central Nervous System (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) composed of the nervous (cranial and spinal) that connects the CNS to other body parts. Together these systems provide three general functio ...
File
... movements of the muscles, like walking or swinging the arms. • This means that the movement is smooth and controlled and you don’t fall over when you turn around. • Cerebrum has special areas, which receive messages about sight, touch, hearing and taste. Other areas control movement, speech, learnin ...
... movements of the muscles, like walking or swinging the arms. • This means that the movement is smooth and controlled and you don’t fall over when you turn around. • Cerebrum has special areas, which receive messages about sight, touch, hearing and taste. Other areas control movement, speech, learnin ...
2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks
... Based on a computational model of Basal ganglia-Thalamus-Cortex (BTC) circuit proposed for action selection, the task of associating a sensory stimulus with a desired action is realized on a humonoid robot. The computational model of BTC circuit, incorporates two different levels of modeling: point ...
... Based on a computational model of Basal ganglia-Thalamus-Cortex (BTC) circuit proposed for action selection, the task of associating a sensory stimulus with a desired action is realized on a humonoid robot. The computational model of BTC circuit, incorporates two different levels of modeling: point ...
D. Vertebrate Nervous Systems
... Effector cells carry out the body’s response to a stimulus. The central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for integration. The signals of the nervous system are conducted by nerves. ...
... Effector cells carry out the body’s response to a stimulus. The central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for integration. The signals of the nervous system are conducted by nerves. ...
Notes-Brain and Memory
... of memories. Brain neurons are specialized cells in your body that transfer messages, or impulses, through electrical signals ...
... of memories. Brain neurons are specialized cells in your body that transfer messages, or impulses, through electrical signals ...
Peripheral nervous system
... - the nerve with myelin can send an action potential at a speed of 100 meters/sec. - the nerve without myelin can send the action potential at a speed of 1 meter/sec ...
... - the nerve with myelin can send an action potential at a speed of 100 meters/sec. - the nerve without myelin can send the action potential at a speed of 1 meter/sec ...
Document
... The major structures of the basal ganglia (red-shaded areas) include the caudate nucleus, the subthalamic nucleus, the substantia nigra, the globus pallidus, and the putamen. The critical connections (inputs and outputs) of the basal ganglia are illustrated. ...
... The major structures of the basal ganglia (red-shaded areas) include the caudate nucleus, the subthalamic nucleus, the substantia nigra, the globus pallidus, and the putamen. The critical connections (inputs and outputs) of the basal ganglia are illustrated. ...
12-nervoussystemintro - Alexmac
... • Sensory receptors are structures in the skin and other tissues that detect changes in the internal or external environment. These receptors consist of specialized neuron endings or specialized cells in close contact with neurons that convert the energy of the stimulus (sound, color, odor, etc.) to ...
... • Sensory receptors are structures in the skin and other tissues that detect changes in the internal or external environment. These receptors consist of specialized neuron endings or specialized cells in close contact with neurons that convert the energy of the stimulus (sound, color, odor, etc.) to ...
Membrane potential
... • Sensory and motor neurons make direct reflex connections in the spinal cord • Spinal reflexes do not involve the brain ...
... • Sensory and motor neurons make direct reflex connections in the spinal cord • Spinal reflexes do not involve the brain ...
PDF
... connections of the approximately 300 neurons comprising the nervous system of a single simple worm C. elegans. Their Herculean cartographic effort has not been equaled since, but we think will soon become relatively commonplace. We believe that the payoff these maps will provide for neuroscience wil ...
... connections of the approximately 300 neurons comprising the nervous system of a single simple worm C. elegans. Their Herculean cartographic effort has not been equaled since, but we think will soon become relatively commonplace. We believe that the payoff these maps will provide for neuroscience wil ...
Slide ()
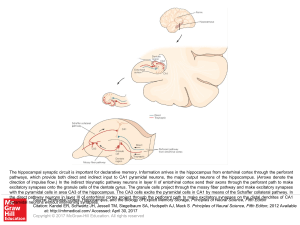
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
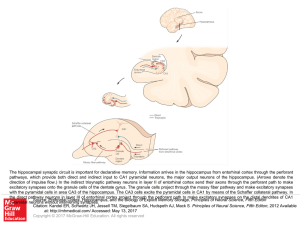
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Final Exam Review Part II 1) The entire nervous system is divided
... 42) Which of the following characteristics is the same for the nervous and endocrine systems: a) target cells affected b) time to onset of actions c) duration of actions d) mechanism of signalling and communication e) none of the above 43. Why do hormones cause changes only in specific body organs? ...
... 42) Which of the following characteristics is the same for the nervous and endocrine systems: a) target cells affected b) time to onset of actions c) duration of actions d) mechanism of signalling and communication e) none of the above 43. Why do hormones cause changes only in specific body organs? ...
Anatomy and Physiology 241 Lecture Objectives The Nervous
... telodendria, synaptic terminal, node of Ranvier. Give function of each of these. Tell which cells myelinate axons in both the PNS and the CNS. Describe the synapse in detail. Define sensory neuron, motor neuron, interneuron and give the function and location of each. Know the difference, location an ...
... telodendria, synaptic terminal, node of Ranvier. Give function of each of these. Tell which cells myelinate axons in both the PNS and the CNS. Describe the synapse in detail. Define sensory neuron, motor neuron, interneuron and give the function and location of each. Know the difference, location an ...
Unit 4: Neuroscience The Neuron Soma (cell body): Contains
... Association Areas: Areas of the cortex not involved in sensory or motor functions. They are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, planning, and language. About 75-80% of the brain is composed of association areas. Hemispheres of the Brain Virtually all activiti ...
... Association Areas: Areas of the cortex not involved in sensory or motor functions. They are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, planning, and language. About 75-80% of the brain is composed of association areas. Hemispheres of the Brain Virtually all activiti ...
BCH 450 Nervous Tissues
... carrying signals from various parts of the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum cerebellum Its most clearly-understood function is to coordinate body movements. So the cerebellum appears to be a center for learning ...
... carrying signals from various parts of the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum cerebellum Its most clearly-understood function is to coordinate body movements. So the cerebellum appears to be a center for learning ...
CHAPTER 4 STRUCTURE AND CELL BIOLOGY OF THE NEURON
... The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles. It is the maintenance center of the neuron. It contains the cell's genetic material as well as the molecular machinery for synthesizing different chemical substances used for information transfer to other neurons, for maintenance and repair of ...
... The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles. It is the maintenance center of the neuron. It contains the cell's genetic material as well as the molecular machinery for synthesizing different chemical substances used for information transfer to other neurons, for maintenance and repair of ...
K - Cloudfront.net
... – Calcium and phosphorus, found in teeth and bones – Dissolved minerals found in urine – Sodium and potassium ions used for nerve impulses in the brain – Iron, found in hemoglobin, in the blood cells (this is what makes it red in color) ...
... – Calcium and phosphorus, found in teeth and bones – Dissolved minerals found in urine – Sodium and potassium ions used for nerve impulses in the brain – Iron, found in hemoglobin, in the blood cells (this is what makes it red in color) ...
histology of nervous tissue
... Support and brace neurons Anchor neurons to their nutrient supplies Guide migration of young neurons Control the chemical environment ...
... Support and brace neurons Anchor neurons to their nutrient supplies Guide migration of young neurons Control the chemical environment ...
Problems with Imbalance
... This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or part, of any images; any r ...
... This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or part, of any images; any r ...
Chapter 13
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...