Chapter 10: Nervous System I: Basic Structure and Function
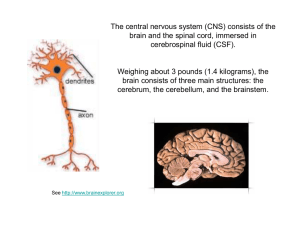
... A. The nervous system is composed predominately of nervous tissue but also includes some blood vessels and connective tissue. B. Two cell types of nervous tissue are neurons and neuroglial cells. C. Neurons are specialized to react to physical and chemical changes in their surroundings. D. Dendrites ...
... A. The nervous system is composed predominately of nervous tissue but also includes some blood vessels and connective tissue. B. Two cell types of nervous tissue are neurons and neuroglial cells. C. Neurons are specialized to react to physical and chemical changes in their surroundings. D. Dendrites ...
File
... • Multiple sclerosis: interferes with muscle control (as message to muscles is impeded..) ...
... • Multiple sclerosis: interferes with muscle control (as message to muscles is impeded..) ...
File
... protein to replace worn out CELL BODY structures and are important in PNS neuron regeneration. DENDRITES receive impulses and take them to the CELL BODY for processing. To make the DENDRITES, cut all the licorice (not the rope) in half (not lengthwise). Using five of the halves, tear the licorice al ...
... protein to replace worn out CELL BODY structures and are important in PNS neuron regeneration. DENDRITES receive impulses and take them to the CELL BODY for processing. To make the DENDRITES, cut all the licorice (not the rope) in half (not lengthwise). Using five of the halves, tear the licorice al ...
Stereological estimates of neuronal loss in the primary motor cortex
... whole central nervous systems of pwPMS we investigate whether a tract specific pattern of neurodegeneration contributes to the loss of motor function in pwPMS. Here, we present preliminary data on stereological estimates of neuronal cell loss in limb specific areas of the MS primary motor cortex (PM ...
... whole central nervous systems of pwPMS we investigate whether a tract specific pattern of neurodegeneration contributes to the loss of motor function in pwPMS. Here, we present preliminary data on stereological estimates of neuronal cell loss in limb specific areas of the MS primary motor cortex (PM ...
1. If a significant amount of Cl - entered the body of a motor neuron
... 11. The number of axons in a multipolar neuron is ___________________ the number of axons in a bipolar neuron. a. Greater than b. Fewer than c. The same as 12. Sensory neurons are considered to be efferent neurons because they take information from organs to the brain and the spinal cord. a. True b. ...
... 11. The number of axons in a multipolar neuron is ___________________ the number of axons in a bipolar neuron. a. Greater than b. Fewer than c. The same as 12. Sensory neurons are considered to be efferent neurons because they take information from organs to the brain and the spinal cord. a. True b. ...
Nervous System
... alpha waves (8-13 cycles per second) are produced when a person is a wake but resting, with eyes closed. beta waves (13 cps ) are produced when a person is actively engaged in mental activity. Theta waves (4-7 cps ) are normally produced by children; in adults, these may be related to early st ...
... alpha waves (8-13 cycles per second) are produced when a person is a wake but resting, with eyes closed. beta waves (13 cps ) are produced when a person is actively engaged in mental activity. Theta waves (4-7 cps ) are normally produced by children; in adults, these may be related to early st ...
Hailee Denson Biology 1090 Mark Radandt Taking Sides Analysis
... meaningful information from all the signaling that goes on within it. The two of us and others, however, have recently made exciting progress by focusing new attention on how the brain can efficiently use the timing of spikes to encode information and rapidly solve difficult computational problems. ...
... meaningful information from all the signaling that goes on within it. The two of us and others, however, have recently made exciting progress by focusing new attention on how the brain can efficiently use the timing of spikes to encode information and rapidly solve difficult computational problems. ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
... then the dendrites; information-sender Myelin: sheath-insulating material covering the axons; speed up communication in the neuron Presynaptic terminal: the point on the axon that releases chemicals ...
... then the dendrites; information-sender Myelin: sheath-insulating material covering the axons; speed up communication in the neuron Presynaptic terminal: the point on the axon that releases chemicals ...
PPT
... Human reaction times ~ 100 milliseconds Neural signaling time ~ 1 millisecond Simple messages between neurons Long connections are rare No new connections during learning Developmentally plausible ...
... Human reaction times ~ 100 milliseconds Neural signaling time ~ 1 millisecond Simple messages between neurons Long connections are rare No new connections during learning Developmentally plausible ...
Nervous System - Cloudfront.net
... Impulse is received by the dendrites from the environment or another neuron, then gets rapidly channeled through the cell body to the axon Axon branches out into axon terminals, which contain tiny vesicles filled with neurotransmitters, which are chemicals used by a neuron to transmit an impulse to ...
... Impulse is received by the dendrites from the environment or another neuron, then gets rapidly channeled through the cell body to the axon Axon branches out into axon terminals, which contain tiny vesicles filled with neurotransmitters, which are chemicals used by a neuron to transmit an impulse to ...
Unimodal or Bimodal Distribution of Synaptic Weights?
... Other plasticity models, however, that exhibit always [2] or for certain inputs [3] a unimodal distribution of synaptic weights have the problem that they do not lead to long-term stability of the weights. In particular, if, after learing, the input pattern changes back to ‘weak’ correlations, the n ...
... Other plasticity models, however, that exhibit always [2] or for certain inputs [3] a unimodal distribution of synaptic weights have the problem that they do not lead to long-term stability of the weights. In particular, if, after learing, the input pattern changes back to ‘weak’ correlations, the n ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... summarize how impulses begin and continue. • F. Summarize the relationship between the nervous system parts. ...
... summarize how impulses begin and continue. • F. Summarize the relationship between the nervous system parts. ...
Readings to Accompany “Nerves” Worksheet (adapted from France
... Types of Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is composed of two main cell types: neurons and neuroglial cells. Neurons transmit nerve messages. Neuroglial cells are in direct contact with neurons and often surround them. They serve to insulate, support and protect the neurons. The Neuron The neuron is the ...
... Types of Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is composed of two main cell types: neurons and neuroglial cells. Neurons transmit nerve messages. Neuroglial cells are in direct contact with neurons and often surround them. They serve to insulate, support and protect the neurons. The Neuron The neuron is the ...
Chapter 8 Nervous System
... internal and external conditions. In response, the NS can stimulate or inhibit the activities of other systems to maintain homeostasis. ...
... internal and external conditions. In response, the NS can stimulate or inhibit the activities of other systems to maintain homeostasis. ...
Neuroscience
... These composite MRI brain scans show the distribution of active areas in the brain of males (left) and females (right) during a verbal task involving rhyming. In males, activation is more lateralized, or confined, to the left hemisphere, whereas in females, activation is bilateralized, that is, occ ...
... These composite MRI brain scans show the distribution of active areas in the brain of males (left) and females (right) during a verbal task involving rhyming. In males, activation is more lateralized, or confined, to the left hemisphere, whereas in females, activation is bilateralized, that is, occ ...
Neuro1
... 2) Myelin is a lipid-rich layer surrounding nerve cells (making a myelin sheath). It insulates axons except at their initial and terminal segments and allows faster conductions of impulses through the nerve fiber. Myelin is secreted by Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS. 3) All ...
... 2) Myelin is a lipid-rich layer surrounding nerve cells (making a myelin sheath). It insulates axons except at their initial and terminal segments and allows faster conductions of impulses through the nerve fiber. Myelin is secreted by Schwann cells in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS. 3) All ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 9. Speculate about why synapses and neurotransmitters are beneficial adaptations to animal nervous systems, compared to direct connections between neurons. Direct connections between neurons, as in the nerve nets of cnidarians (see section 26.1), mean that a single nervous impulse spreads in all di ...
... 9. Speculate about why synapses and neurotransmitters are beneficial adaptations to animal nervous systems, compared to direct connections between neurons. Direct connections between neurons, as in the nerve nets of cnidarians (see section 26.1), mean that a single nervous impulse spreads in all di ...
consciousness
... by proposing that the division of labour is determined by the use to which visual information is to be put, once it has reached the striate cortex. They suggest that a ventral stream, terminating in the inferotemporal cortex, is involved in maintaining an enduring, viewpoint-independent, representat ...
... by proposing that the division of labour is determined by the use to which visual information is to be put, once it has reached the striate cortex. They suggest that a ventral stream, terminating in the inferotemporal cortex, is involved in maintaining an enduring, viewpoint-independent, representat ...
Slide ()
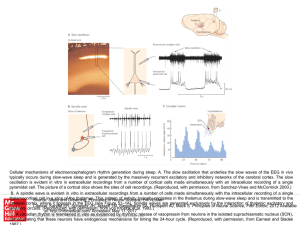
... oscillation is evident in vitro in extracellular recordings from a number of cortical cells made simultaneously with an intracellular recording of a single pyramidal cell. The picture of a cortical slice shows the sites of cell recordings. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanchez-Vives and McCormi ...
... oscillation is evident in vitro in extracellular recordings from a number of cortical cells made simultaneously with an intracellular recording of a single pyramidal cell. The picture of a cortical slice shows the sites of cell recordings. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanchez-Vives and McCormi ...
Chapter 3
... – depolarization = membrane becomes less negative inside – repolarization = restoration of RMP (-70 mV) – threshold potential = -55 mV • potential at which an action potential is generated • all-or-none principle: if stimulus causes depolarization to threshold, action potential is generated – no “la ...
... – depolarization = membrane becomes less negative inside – repolarization = restoration of RMP (-70 mV) – threshold potential = -55 mV • potential at which an action potential is generated • all-or-none principle: if stimulus causes depolarization to threshold, action potential is generated – no “la ...
Ch45--Neurons and Nervous Systems v2015
... widespread in brain lack of dopamine in brain associated with Parkinson’s disease excessive dopamine linked to schizophrenia pleasure & reward pathways ...
... widespread in brain lack of dopamine in brain associated with Parkinson’s disease excessive dopamine linked to schizophrenia pleasure & reward pathways ...
Organization of the Nervous system. Physiology of neurons and glial
... about 20,000 genes (coding & regulatory DNA) 14,000 genes expressed in the developing/mature brain about 8,000 genes are expressed in all cells and tissues a great deal of “brain specific” genetic information resides in the regulatory DNA sequences that control timing, quantity, variability, and c ...
... about 20,000 genes (coding & regulatory DNA) 14,000 genes expressed in the developing/mature brain about 8,000 genes are expressed in all cells and tissues a great deal of “brain specific” genetic information resides in the regulatory DNA sequences that control timing, quantity, variability, and c ...