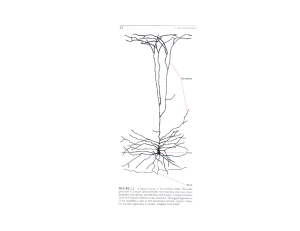
Nervous Systems
... body that RECEIVE signals from other neurons • Axon: a large extension from the cell body that TRANSMITS signals to other neurons or “effector” cells • Axon hillock: where the axon joins the cell body • Myelin sheath: a fatty layer of cells that “insulates” the axon (not present in most invertebrate ...
... body that RECEIVE signals from other neurons • Axon: a large extension from the cell body that TRANSMITS signals to other neurons or “effector” cells • Axon hillock: where the axon joins the cell body • Myelin sheath: a fatty layer of cells that “insulates” the axon (not present in most invertebrate ...
Brain Jokes (Questions)
... 2. What does a brain do when it sees a friend across the street? 3. Where does a brain go on vacation? 4. What did the hippocampus say during its retirement speech? 5. Why did the action potential cross the optic chiasm? 6. What did the right hemisphere say to the left hemisphere when they could not ...
... 2. What does a brain do when it sees a friend across the street? 3. Where does a brain go on vacation? 4. What did the hippocampus say during its retirement speech? 5. Why did the action potential cross the optic chiasm? 6. What did the right hemisphere say to the left hemisphere when they could not ...
File
... • Consists of the brain and the spinal cord • Pivotal in transferring messages to and from their environment. • Centre at which all the physiology of the individual is controlled • The Central Nervous System (CNS) is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The vertebrae of the spine encase and pro ...
... • Consists of the brain and the spinal cord • Pivotal in transferring messages to and from their environment. • Centre at which all the physiology of the individual is controlled • The Central Nervous System (CNS) is made up of the brain and the spinal cord. The vertebrae of the spine encase and pro ...
Slide 1
... The Sad Story of Phineas Gage Here’s a story that shows the different parts of our brain truly control separate aspects of how we function. In 1848, Phineas Gage was a foreman of a railway crew. He was a friendly, well-liked individual who could be trusted to treat the people in his life well and b ...
... The Sad Story of Phineas Gage Here’s a story that shows the different parts of our brain truly control separate aspects of how we function. In 1848, Phineas Gage was a foreman of a railway crew. He was a friendly, well-liked individual who could be trusted to treat the people in his life well and b ...
Chapter 3 Section 2 - 6th
... Chapter 3 Section 1 The Nervous System - Regulates our internal functions and is involved in how we react to the external world Two main parts: 1. central nervous system- consists of brain and spinal cord 2. peripheral nervous system- made up of nerve cells that send messages between the central ner ...
... Chapter 3 Section 1 The Nervous System - Regulates our internal functions and is involved in how we react to the external world Two main parts: 1. central nervous system- consists of brain and spinal cord 2. peripheral nervous system- made up of nerve cells that send messages between the central ner ...
The Nervous System - leavingcertbiology.net
... Mechanism of the Reflex Arc • Pain and temperature receptors at endings of sensory neurons in the skin are stimulated and generate nerve impulses • Nerve impulse travels the through the dendrite to the cell body of the sensory neuron located in the dorsal root ganglion and then travels the short se ...
... Mechanism of the Reflex Arc • Pain and temperature receptors at endings of sensory neurons in the skin are stimulated and generate nerve impulses • Nerve impulse travels the through the dendrite to the cell body of the sensory neuron located in the dorsal root ganglion and then travels the short se ...
Nervous system slides
... ¾ Somatosensory and motor areas of different lobes directly process info. and association areas integrate info. ¾ Our sensory perceptions are produced by a complicated interchange of signals among receiving centers and association centers. ...
... ¾ Somatosensory and motor areas of different lobes directly process info. and association areas integrate info. ¾ Our sensory perceptions are produced by a complicated interchange of signals among receiving centers and association centers. ...
Answers to Test Your Knowledge questions for
... the body over which some control is exerted by neurons in the associated regions of motor cortex. Some regions of the body have a relatively large amount of associated cortex. Regions with a large representation have a fine resolution of motor ability (e.g. fingers). Such areas are associated with f ...
... the body over which some control is exerted by neurons in the associated regions of motor cortex. Some regions of the body have a relatively large amount of associated cortex. Regions with a large representation have a fine resolution of motor ability (e.g. fingers). Such areas are associated with f ...
The Nervous System
... stimulated by the environment or by another neuron. It uses Sodium and Potassium Ions to move the impulse (action potential) ...
... stimulated by the environment or by another neuron. It uses Sodium and Potassium Ions to move the impulse (action potential) ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process. Neurons contain some very specialized structures (for example, synapses) and chemicals (for example, neurotransmitters) that enable one cell to communicate with another. ...
... Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process. Neurons contain some very specialized structures (for example, synapses) and chemicals (for example, neurotransmitters) that enable one cell to communicate with another. ...
Chapter 22 The Nervous System Nervous System - Function 6/1/2013
... stimulated by the environment or by another neuron. It uses Sodium and Potassium Ions to move the impulse (action potential) ...
... stimulated by the environment or by another neuron. It uses Sodium and Potassium Ions to move the impulse (action potential) ...
CHAPTER 13 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... to and going away from the CNS These two systems work together and are connected ...
... to and going away from the CNS These two systems work together and are connected ...
110 ~W~U~~ ~~~\W(Q)(UJ~
... When your hand jerks back suddenly and involuntarily from a hot stove before you are even aware that you have burned yourself, you are using a neural pathway called a "spinal reflex arc." It includes a receptor, a sensory neuron, at least one synapse in the spinal cord, and a motor neuron. Each sens ...
... When your hand jerks back suddenly and involuntarily from a hot stove before you are even aware that you have burned yourself, you are using a neural pathway called a "spinal reflex arc." It includes a receptor, a sensory neuron, at least one synapse in the spinal cord, and a motor neuron. Each sens ...
What is Psychology? - Weber State University
... How Neurons Communicate • Synapse: Site where a nerve impulse is transmitted from one neuron to another; includes the axon terminal, synaptic cleft, and receptor sites on receiving cell. • Neurotransmitter: Chemical substance that is released by transmitting neuron at the synapse and alters the act ...
... How Neurons Communicate • Synapse: Site where a nerve impulse is transmitted from one neuron to another; includes the axon terminal, synaptic cleft, and receptor sites on receiving cell. • Neurotransmitter: Chemical substance that is released by transmitting neuron at the synapse and alters the act ...
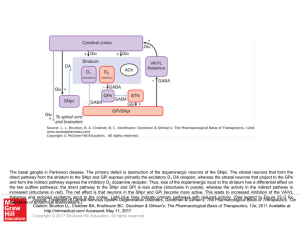
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
... direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differentia ...
... direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differentia ...
A- A- A- K+ A - How Your Brain Works
... • The brainstem connects the brain to the body via the spinal cord and a number of cranial nerves. • The cerebellum is involved in motor learning and balance. It is connected to the brainstem via the Pons. Cerebellum, pons and brainstem make up the hindbrain. • The midbrain links hindbrain to forebr ...
... • The brainstem connects the brain to the body via the spinal cord and a number of cranial nerves. • The cerebellum is involved in motor learning and balance. It is connected to the brainstem via the Pons. Cerebellum, pons and brainstem make up the hindbrain. • The midbrain links hindbrain to forebr ...
Anatomy of the Basal Ganglia
... eye movements. Types of Neurons in the Striatum Medium spiny neurons—make up 95% of the total. Use GABA as a transmitter. Are the output neurons of the striatum. Large aspiny neurons—interneurons that use ACh as a transmitter. Medium aspiny cells—interneurons that use somatostatin as a neurotransmit ...
... eye movements. Types of Neurons in the Striatum Medium spiny neurons—make up 95% of the total. Use GABA as a transmitter. Are the output neurons of the striatum. Large aspiny neurons—interneurons that use ACh as a transmitter. Medium aspiny cells—interneurons that use somatostatin as a neurotransmit ...
Neural Networks - School of Computer Science
... The dendrites can be regarded as the inputs to the neuron and the axon can be regarded as the neuron’s output. In the brain axons (outputs) from many neurons will connect to the dendrites (inputs) of many other neurons. ...
... The dendrites can be regarded as the inputs to the neuron and the axon can be regarded as the neuron’s output. In the brain axons (outputs) from many neurons will connect to the dendrites (inputs) of many other neurons. ...
Nervous System Bookwork—KEY
... Nervous System Bookwork—KEY Ch 7: S/A # 6, 9, 12, 14 Clinic # 2, 5, 10 Short answer 6. A threshold stimulus causes a change in membrane permeability that allows Na + to enter the neuron through sodium gates. This causes local depolarization and generates the action potential, which is then self-prop ...
... Nervous System Bookwork—KEY Ch 7: S/A # 6, 9, 12, 14 Clinic # 2, 5, 10 Short answer 6. A threshold stimulus causes a change in membrane permeability that allows Na + to enter the neuron through sodium gates. This causes local depolarization and generates the action potential, which is then self-prop ...
Artificial intelligence neural computing and
... Extending from the cell body is a single long fiber called the axon, which eventually branches into strands and substrands, and are connected to other neurons through synaptic terminals or synapses. The transmission of signals from one neuron to another at synapses is a complex chemical process in w ...
... Extending from the cell body is a single long fiber called the axon, which eventually branches into strands and substrands, and are connected to other neurons through synaptic terminals or synapses. The transmission of signals from one neuron to another at synapses is a complex chemical process in w ...
We are investigating the use of novel stimulus
... determine whether they can provide more precise control over the temporal and spatial pattern of elicited activity as compared to conventional pulsatile stimulation. To study this, we measured the response of retinal ganglion cells to both sinusoidal and white noise waveforms. The use of cell-attach ...
... determine whether they can provide more precise control over the temporal and spatial pattern of elicited activity as compared to conventional pulsatile stimulation. To study this, we measured the response of retinal ganglion cells to both sinusoidal and white noise waveforms. The use of cell-attach ...
Step back and look at the Science
... Imaging Scans have limited accuracy Patient’s age very relevant ...
... Imaging Scans have limited accuracy Patient’s age very relevant ...
Homework 5
... Problem 7. How many action potentials can neurons fire at the peak of beta wave? Problem 8. How many action potentials can neurons fire at the peak of theta wave? Problem 9. How many action potentials can neurons fire at the peak of delta wave? Problem 10. Draw a spectrogram (time frequency graph) o ...
... Problem 7. How many action potentials can neurons fire at the peak of beta wave? Problem 8. How many action potentials can neurons fire at the peak of theta wave? Problem 9. How many action potentials can neurons fire at the peak of delta wave? Problem 10. Draw a spectrogram (time frequency graph) o ...