The Nervous System
... Dendrites (from the Greek dendron = tree branch) are thin, branched processes that extend from the cytoplasm of the cell body. Dendrites provide a receptive area that transmits graded electrochemical impulses to the cell body. The axon is a longer process that conducts impulses, called action potent ...
... Dendrites (from the Greek dendron = tree branch) are thin, branched processes that extend from the cytoplasm of the cell body. Dendrites provide a receptive area that transmits graded electrochemical impulses to the cell body. The axon is a longer process that conducts impulses, called action potent ...
The Biology of Mind - American International School
... Neurons transmit messages when stimulated by signals from our senses or when triggered by chemical signals from neighboring neurons. In response, a neuron fires an impulse, called the action potential—a brief electrical charge that travels down its axon. Depending on the type of fiber, a neural impu ...
... Neurons transmit messages when stimulated by signals from our senses or when triggered by chemical signals from neighboring neurons. In response, a neuron fires an impulse, called the action potential—a brief electrical charge that travels down its axon. Depending on the type of fiber, a neural impu ...
Life span chapter 3-1 File
... The major principles of growth are the cephalocaudal principle, the proximodistal principle, the principle of hierarchical integration, and the principle of the independence of systems. The development of the nervous system first entails the development of billions of neurons and interconnections a ...
... The major principles of growth are the cephalocaudal principle, the proximodistal principle, the principle of hierarchical integration, and the principle of the independence of systems. The development of the nervous system first entails the development of billions of neurons and interconnections a ...
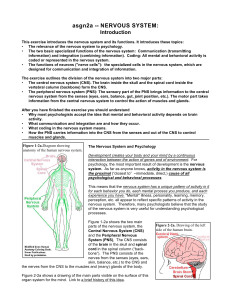
asgn2a -- NERVOUS SYSTEM - Indiana University Bloomington
... (nerve cell), illustrated in Figure 10-2a, has three specialized parts, in addition to the cell body (or soma), which carries out the basic life processes. These three parts are: 1. Several dendrites, which form the receiving end of a neuron. Most Figure 10-2a. The main parts of a neurons have many, ...
... (nerve cell), illustrated in Figure 10-2a, has three specialized parts, in addition to the cell body (or soma), which carries out the basic life processes. These three parts are: 1. Several dendrites, which form the receiving end of a neuron. Most Figure 10-2a. The main parts of a neurons have many, ...
Before and below `theory of mind`: embodied
... recent evidence by Subiaul et al. (2004) shows that they are capable of cognitive imitation—the study by Paukner et al. (2005) nevertheless shows that macaque monkeys do entertain the capacity to discriminate between very similar goal-related actions on the basis of their degree of similarity with t ...
... recent evidence by Subiaul et al. (2004) shows that they are capable of cognitive imitation—the study by Paukner et al. (2005) nevertheless shows that macaque monkeys do entertain the capacity to discriminate between very similar goal-related actions on the basis of their degree of similarity with t ...
Cortical Plasticity - Lund University Publications
... is divided into six layers, L-I-VI. The sensory input arrives first and foremost to L-IV and to some extent to L-VI and L-III and are, as mentioned above, arising from thalamus via thalamocortical axons. Output to other cortical and subcortical regions proceeds primarily via pyramidal cells in LV an ...
... is divided into six layers, L-I-VI. The sensory input arrives first and foremost to L-IV and to some extent to L-VI and L-III and are, as mentioned above, arising from thalamus via thalamocortical axons. Output to other cortical and subcortical regions proceeds primarily via pyramidal cells in LV an ...
the biological perspective
... layer of fatty substances called myelin. Oligodendrocytes produce myelin for the neurons in the brain and spinal cord (the central nervous system); Schwann cells produce myelin for the neurons of the body (the peripheral nervous system). Myelin wraps around the shaft of the axons, forming an insulat ...
... layer of fatty substances called myelin. Oligodendrocytes produce myelin for the neurons in the brain and spinal cord (the central nervous system); Schwann cells produce myelin for the neurons of the body (the peripheral nervous system). Myelin wraps around the shaft of the axons, forming an insulat ...
Expert systems - Plymouth State College
... Claude Shannon’s comparison of the human brain and the computer: Difference in size: The brain has a million more parts. Difference in structural organization: The seemingly random local structure of nerve networks differ vastly from the precise wiring of a computer. Differences in reliabili ...
... Claude Shannon’s comparison of the human brain and the computer: Difference in size: The brain has a million more parts. Difference in structural organization: The seemingly random local structure of nerve networks differ vastly from the precise wiring of a computer. Differences in reliabili ...
Nissl substance and cellular structures involved in the intraneuronal
... cells capture an extracellular material by means of endocytosis. In MRN, however, the vesicular transport between perikarion and the neuronal membrane is restricted by the fibrillar envelope surrounding the cell body. Rather few vesicles are observed within this fibrillar layer. Vesicles approach th ...
... cells capture an extracellular material by means of endocytosis. In MRN, however, the vesicular transport between perikarion and the neuronal membrane is restricted by the fibrillar envelope surrounding the cell body. Rather few vesicles are observed within this fibrillar layer. Vesicles approach th ...
Hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in cultured Aplysia sensory
... of cell death in various organisms [15,26,27]. By producing free radicals, H 2 O 2 , a reactive oxygen species also causes depolarization [10,14,31] or hyperpolarization [3,8,20] of the resting membrane potential of various cells in many organisms. Though numerous studies have been carried out in th ...
... of cell death in various organisms [15,26,27]. By producing free radicals, H 2 O 2 , a reactive oxygen species also causes depolarization [10,14,31] or hyperpolarization [3,8,20] of the resting membrane potential of various cells in many organisms. Though numerous studies have been carried out in th ...
Total number and volume of Von Economo neurons in the cerebral
... wide pyramidal layer III; a relatively thin pyramidal layer V containing large pyramidal cells usually distributed in small clusters; and a multiform layer VI (Morgane et al., 1988; Glezer and Morgane, 1990; Hof and Sherwood, 2005; Hof and Van der Gucht, 2007). This cortical lamination pattern with ...
... wide pyramidal layer III; a relatively thin pyramidal layer V containing large pyramidal cells usually distributed in small clusters; and a multiform layer VI (Morgane et al., 1988; Glezer and Morgane, 1990; Hof and Sherwood, 2005; Hof and Van der Gucht, 2007). This cortical lamination pattern with ...
Uygar Sümbül - Department of Statistics
... BRIEF DESCRIPTIONS OF MAJOR PROJECTS • Whole cell analysis of synapse distributions (with Prof. Liam Paninski and Prof. Franck Polleux) All excitatory and inhibitory synapses on the dendritic arbors of cortical pyramidal neurons are identified using structural and molecular information. Statistical ...
... BRIEF DESCRIPTIONS OF MAJOR PROJECTS • Whole cell analysis of synapse distributions (with Prof. Liam Paninski and Prof. Franck Polleux) All excitatory and inhibitory synapses on the dendritic arbors of cortical pyramidal neurons are identified using structural and molecular information. Statistical ...
Brain and Behavior
... Learning Objective 2.1.2 – Describe an action potential, including why it is an all-ornothing event, the function of the myelin layer within the process of saltatory conduction, why an action potential is considered an electrical event, and the definitions of the following terms: resting potential, ...
... Learning Objective 2.1.2 – Describe an action potential, including why it is an all-ornothing event, the function of the myelin layer within the process of saltatory conduction, why an action potential is considered an electrical event, and the definitions of the following terms: resting potential, ...
Chapter Two: Brain and Behavior
... Learning Objective 2.1.2 – Describe an action potential, including why it is an all-ornothing event, the function of the myelin layer within the process of saltatory conduction, why an action potential is considered an electrical event, and the definitions of the following terms: resting potential, ...
... Learning Objective 2.1.2 – Describe an action potential, including why it is an all-ornothing event, the function of the myelin layer within the process of saltatory conduction, why an action potential is considered an electrical event, and the definitions of the following terms: resting potential, ...
Acetylcholine (ACh)
... Action Potential – An electric nerve impulse that travels through a neuron, changing the cell’s charge from negative to positive ...
... Action Potential – An electric nerve impulse that travels through a neuron, changing the cell’s charge from negative to positive ...
1From neuronal activity to scalp potential fields - Assets
... Figure 1.2. Closely folded brain structures only generate “closed fields” which cancel within a few millimeters due to nearby sources with random or opposite orientations. Although some structures like the cerebellum were historically considered to generate only closed fields and no EEG, recent MEG ...
... Figure 1.2. Closely folded brain structures only generate “closed fields” which cancel within a few millimeters due to nearby sources with random or opposite orientations. Although some structures like the cerebellum were historically considered to generate only closed fields and no EEG, recent MEG ...
Brain Tumor Classification Using Wavelet and Texture
... cerebral MR images. Their future work is to classify brain tumors into benign and malignant brain tumors. From the literature survey, firstly, it can be concluded that, various research works have been performed in classifying MR brain images into normal and abnormal [1], [2]. Whereas, classifying M ...
... cerebral MR images. Their future work is to classify brain tumors into benign and malignant brain tumors. From the literature survey, firstly, it can be concluded that, various research works have been performed in classifying MR brain images into normal and abnormal [1], [2]. Whereas, classifying M ...
Motor and cognitive functions of the ventral premotor cortex
... of F5. These studies showed that most F5 neurons code specific actions, rather than the single movements that form them. F5 neurons were thus subdivided into several action classes, for example, ‘grasping’, ‘holding’ or ‘tearing’ neurons [30]. Many F5 neurons respond to the presentation of visual st ...
... of F5. These studies showed that most F5 neurons code specific actions, rather than the single movements that form them. F5 neurons were thus subdivided into several action classes, for example, ‘grasping’, ‘holding’ or ‘tearing’ neurons [30]. Many F5 neurons respond to the presentation of visual st ...
as a PDF
... regions (Fig. 1) known to contain preganglionic parasympathetic neurons in experimental animals. Medium-sized neurons were located in a region bordered by the spinal trigeminal nucleus laterally, the facial nucleus medially and the medial vestibular nucleus dorsally. Rostrally, these neurons were sc ...
... regions (Fig. 1) known to contain preganglionic parasympathetic neurons in experimental animals. Medium-sized neurons were located in a region bordered by the spinal trigeminal nucleus laterally, the facial nucleus medially and the medial vestibular nucleus dorsally. Rostrally, these neurons were sc ...
Ch 8 (Student MCQs etc)
... For example, the deployment of attention to locate a target is generated internally rather than externally, and is therefore considered to be ‘top-down’ (in contrast to, say, the sudden appearance of an object in peripheral vision, which will capture the observer’s attention in an automatic ‘bottom- ...
... For example, the deployment of attention to locate a target is generated internally rather than externally, and is therefore considered to be ‘top-down’ (in contrast to, say, the sudden appearance of an object in peripheral vision, which will capture the observer’s attention in an automatic ‘bottom- ...
ANS Jeopardy
... • Nicotinic receptors are always _________ when stimulated by acetylcholine. • Answer: excitatory ...
... • Nicotinic receptors are always _________ when stimulated by acetylcholine. • Answer: excitatory ...
The mind-body problem - BECS / CoE in
... • a simple definition of plant intelligence can be coined as adaptively variable growth and development during the lifetime of the individual. • Learning, memory, goal-directedness, choice etc. ...
... • a simple definition of plant intelligence can be coined as adaptively variable growth and development during the lifetime of the individual. • Learning, memory, goal-directedness, choice etc. ...