Neuroscience, 4e
... Figure 9.3 Receptive fields and two-point discrimination threshold (Part 1) ...
... Figure 9.3 Receptive fields and two-point discrimination threshold (Part 1) ...
Lineage origins of GABAergic versus glutamatergic neurons in the
... a subset of Cux2+ RGCs are specified to generate Satb2+ callosal projection neurons in upper and deep layers of the neocortex, whereas lower-layer neurons that project to subcortical targets are produced from RGCs of the Cux2 lineage. In addition, subpopulations of interneurons that migrate into the ...
... a subset of Cux2+ RGCs are specified to generate Satb2+ callosal projection neurons in upper and deep layers of the neocortex, whereas lower-layer neurons that project to subcortical targets are produced from RGCs of the Cux2 lineage. In addition, subpopulations of interneurons that migrate into the ...
Acquisition of Box Pushing by Direct-Vision
... process that the robot notices such information is important to solve the task, and that it finds how the such information can be extracted from the image. These are based on the traditional idea that in order to make up high intelligence, the process from sensors to motors should be divided into som ...
... process that the robot notices such information is important to solve the task, and that it finds how the such information can be extracted from the image. These are based on the traditional idea that in order to make up high intelligence, the process from sensors to motors should be divided into som ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... and/or SNr must be suppressed for a period of time. 3. Pathways through the basal ganglia. These pathways provide the neural substrates that enable the basal ganglia to determine which action, thought or emotion will be facilitated, via a temporary suppression of its inhibitory output, or suppressed ...
... and/or SNr must be suppressed for a period of time. 3. Pathways through the basal ganglia. These pathways provide the neural substrates that enable the basal ganglia to determine which action, thought or emotion will be facilitated, via a temporary suppression of its inhibitory output, or suppressed ...
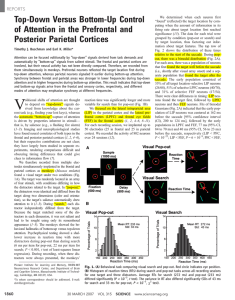
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization Primary Visual Cortex
... Many of them respond best to an oriented edge that is stopped, i.e., its end does not extend beyond a specific part of the receptive field. Neurons with such a pattern of response act as “angle detectors”. ...
... Many of them respond best to an oriented edge that is stopped, i.e., its end does not extend beyond a specific part of the receptive field. Neurons with such a pattern of response act as “angle detectors”. ...
Changes in Prefrontal Neuronal Activity after
... A neuron’s spike width was determined by calculating the distance between the 2 troughs of the average waveform. We distinguished between fast-spiking (FS—putative interneurons) and regular-spiking (RS—putative pyramidal) neurons based on previous analysis (Constantinidis and Goldman-Rakic 2002) whi ...
... A neuron’s spike width was determined by calculating the distance between the 2 troughs of the average waveform. We distinguished between fast-spiking (FS—putative interneurons) and regular-spiking (RS—putative pyramidal) neurons based on previous analysis (Constantinidis and Goldman-Rakic 2002) whi ...
KISHORE Aswathy - School of Computing
... representation’. Accordingly, different features of the object such as shape, texture and colour will be represented in different parts of the brain. Hence, in order to have a complete representation for the object, these individual localised representations have to be bound together to form a globa ...
... representation’. Accordingly, different features of the object such as shape, texture and colour will be represented in different parts of the brain. Hence, in order to have a complete representation for the object, these individual localised representations have to be bound together to form a globa ...
Chapter 12: Nervous System
... studied the brains of many deceased athletes, including hockey and football players. He has found that these players often suffered from chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), a degenerative brain disease caused by repeated blunt impact to the head. ...
... studied the brains of many deceased athletes, including hockey and football players. He has found that these players often suffered from chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), a degenerative brain disease caused by repeated blunt impact to the head. ...
Objectives
... a) Identify the parts of an animal cell and the role played by each. b) Identify the parts of a neuron and the role played by each. c) Discuss the different kinds of glial cells and the function of each. d) Identify the cells of the brain that can and cannot divide. e) Explain why the blood-brain ba ...
... a) Identify the parts of an animal cell and the role played by each. b) Identify the parts of a neuron and the role played by each. c) Discuss the different kinds of glial cells and the function of each. d) Identify the cells of the brain that can and cannot divide. e) Explain why the blood-brain ba ...
Document
... studied the brains of many deceased athletes, including hockey and football players. He has found that these players often suffered from chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), a degenerative brain disease caused by repeated blunt impact to the head. ...
... studied the brains of many deceased athletes, including hockey and football players. He has found that these players often suffered from chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), a degenerative brain disease caused by repeated blunt impact to the head. ...
Understanding Neurotransmission and the Disease of Addiction
... and muscle cells. A typical neuron has four morphologically defined regions: the cell body, dendrites, axons, and presynaptic terminals. ...
... and muscle cells. A typical neuron has four morphologically defined regions: the cell body, dendrites, axons, and presynaptic terminals. ...
Brain - American Museum of Natural History
... stronger they become. And unused connections weaken and fade away. The adolescent brain is still strengthening connections between its reasoning and emotion-related regions. In addition, the reward center of the brain is more active during adolescence than in adulthood. These findings would explain w ...
... stronger they become. And unused connections weaken and fade away. The adolescent brain is still strengthening connections between its reasoning and emotion-related regions. In addition, the reward center of the brain is more active during adolescence than in adulthood. These findings would explain w ...
nips2.frame - /marty/papers/drotdil
... rotations and dilations seen by MT are apparently noise-like enough that any second order selectivity is averaged out. A larger (unrealistic) divergence allows a few units to solve the aperture problem and detect rotation and dilation in one step. Training sets that contain many pure-translation sti ...
... rotations and dilations seen by MT are apparently noise-like enough that any second order selectivity is averaged out. A larger (unrealistic) divergence allows a few units to solve the aperture problem and detect rotation and dilation in one step. Training sets that contain many pure-translation sti ...
Biology 211 Anatomy & Physiology I
... axons & dendrites. Nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of myelinated axons & dendrites and their supporting glia ...
... axons & dendrites. Nervous tissue of the CNS consisting of myelinated axons & dendrites and their supporting glia ...
Full text PDF - Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences
... myelin depositing, which is formed from repeated coiling of Schwan cells membrane around the axon. Myelin sheath which surrounds nerve fibres in spinal-cord has a very different origin, as it is formed from oligodentroglial cells. Although myelinisation of nerve fibres in spinal-cord starts approximat ...
... myelin depositing, which is formed from repeated coiling of Schwan cells membrane around the axon. Myelin sheath which surrounds nerve fibres in spinal-cord has a very different origin, as it is formed from oligodentroglial cells. Although myelinisation of nerve fibres in spinal-cord starts approximat ...
Electronic Realization of Human Brain`s Neo
... The neuron is the basic functional block of the nervous system. It is a highly specialized cellular unit for information processing and transmission of electrochemical signals. With diameters ranging from 4 to 100 microns, each neuron contains millions of electrochemical pumping stations that shift ...
... The neuron is the basic functional block of the nervous system. It is a highly specialized cellular unit for information processing and transmission of electrochemical signals. With diameters ranging from 4 to 100 microns, each neuron contains millions of electrochemical pumping stations that shift ...
Cation-Chloride Cotransporters and Neuronal Function
... GABAA and glycine receptors, CCCs also show close interactions with glutamatergic signaling. A crosstalk among CCCs and trophic factors is important in short-term and long-term modification of neuronal properties. CCCs appear to be multifunctional proteins that are also involved in shaping neuronal ...
... GABAA and glycine receptors, CCCs also show close interactions with glutamatergic signaling. A crosstalk among CCCs and trophic factors is important in short-term and long-term modification of neuronal properties. CCCs appear to be multifunctional proteins that are also involved in shaping neuronal ...
Document
... CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control
... firing rate about target location first reached significance (13). The data for each trial were grouped by condition (pop-out or search) and by target location, thus factoring out information about target features. The top row of Fig. 2 shows the distribution of these times relative to the start of ...
... firing rate about target location first reached significance (13). The data for each trial were grouped by condition (pop-out or search) and by target location, thus factoring out information about target features. The top row of Fig. 2 shows the distribution of these times relative to the start of ...
THE PEDAL NEURONS OF APLYSIA PUNCTATA
... There are no detailed accounts of the connexions and branching of the axons of neurons in the pedal ganglia of opisthobranchs. Most of the experiments on these ganglia have been limited to cutting and stimulating nerve trunks, and using these techniques, Frohlich (1910) demonstrated the role of the ...
... There are no detailed accounts of the connexions and branching of the axons of neurons in the pedal ganglia of opisthobranchs. Most of the experiments on these ganglia have been limited to cutting and stimulating nerve trunks, and using these techniques, Frohlich (1910) demonstrated the role of the ...
Saliency, switching, attention and control
... human brain, providing a link between stimulus-driven processing and brain regions involved in monitoring the internal milieu (Craig 2009). We suggest that in order to comprehend insula function it is important to not only understand cognitive and affective tasks which modulate activity in this regi ...
... human brain, providing a link between stimulus-driven processing and brain regions involved in monitoring the internal milieu (Craig 2009). We suggest that in order to comprehend insula function it is important to not only understand cognitive and affective tasks which modulate activity in this regi ...