Drug and Alcohol Abuse
... • (1) You will become familiar with the major parts of the brain and be able to describe their function. • (2) You will be able to explain how brain cells send and receive information. ...
... • (1) You will become familiar with the major parts of the brain and be able to describe their function. • (2) You will be able to explain how brain cells send and receive information. ...
Cultured Olfactory Interneurons From Limax maximus: Optical and
... increases in [ Ca]i into the 700- to 900-nM range with recovery of normal calcium levels after return to normal saline. This effect was quantified by measuring the 340/380-nm ratio and converting this to [ Ca]i for a number of individual PC cells before, during peak response to, and after recovery f ...
... increases in [ Ca]i into the 700- to 900-nM range with recovery of normal calcium levels after return to normal saline. This effect was quantified by measuring the 340/380-nm ratio and converting this to [ Ca]i for a number of individual PC cells before, during peak response to, and after recovery f ...
Lecture Slides - Austin Community College
... • Extensively branching from the cell body • Transmit electrical signals toward the cell body • Function as receptive sites for receiving signals from other neurons ...
... • Extensively branching from the cell body • Transmit electrical signals toward the cell body • Function as receptive sites for receiving signals from other neurons ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... - Adipose tissue: fat cells embedded in a small amount of extracellular matrix. - Blood: red and white blood cells and platelets suspended in a liquid matrix called plasma. - Cartilage: chondrocytes in a network of fine collagen fibers. - Bone: bone cells held within a matrix composed of collagen an ...
... - Adipose tissue: fat cells embedded in a small amount of extracellular matrix. - Blood: red and white blood cells and platelets suspended in a liquid matrix called plasma. - Cartilage: chondrocytes in a network of fine collagen fibers. - Bone: bone cells held within a matrix composed of collagen an ...
Sensory Cells and Transduction of Stimuli
... Sensory Receptors • When receptors are triggered, they open up Na+ and K+ channels to trigger an action potential ...
... Sensory Receptors • When receptors are triggered, they open up Na+ and K+ channels to trigger an action potential ...
Organization of the Nervous system. Physiology of neurons and glial
... about 20,000 genes (coding & regulatory DNA) 14,000 genes expressed in the developing/mature brain about 8,000 genes are expressed in all cells and tissues a great deal of “brain specific” genetic information resides in the regulatory DNA sequences that control timing, quantity, variability, and c ...
... about 20,000 genes (coding & regulatory DNA) 14,000 genes expressed in the developing/mature brain about 8,000 genes are expressed in all cells and tissues a great deal of “brain specific” genetic information resides in the regulatory DNA sequences that control timing, quantity, variability, and c ...
2014 nervous system ppt
... – Neurons have K+ and Na+ channels – Allow specific ions to diffuse down chemical and electrical gradient – Can be gated or ungated ion channels: • UNGATED = open all the time, no gradient established across membrane • GATED = open (or close) in response to chemical or electrical stimulus *Chemicall ...
... – Neurons have K+ and Na+ channels – Allow specific ions to diffuse down chemical and electrical gradient – Can be gated or ungated ion channels: • UNGATED = open all the time, no gradient established across membrane • GATED = open (or close) in response to chemical or electrical stimulus *Chemicall ...
Evolution and analysis of minimal neural circuits for klinotaxis in
... C. elegans chemotaxis specific predictions 1. Neck motor neurons need not be bistable. 2. Interneurons could be acting as passive conduits of activity. 3. Model suggests an antagonistic pathway between sensory and neck motor neurons. 4. ON/OFF cell activation during forward locomotion should reduce ...
... C. elegans chemotaxis specific predictions 1. Neck motor neurons need not be bistable. 2. Interneurons could be acting as passive conduits of activity. 3. Model suggests an antagonistic pathway between sensory and neck motor neurons. 4. ON/OFF cell activation during forward locomotion should reduce ...
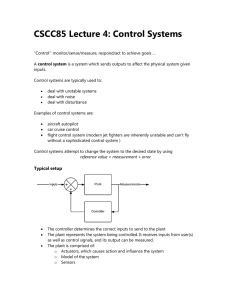
CSCC85 Lecture 4: Control Systems
... Greater number of neurons with different weights allows a greater range of functions to be approximated with increased accuracy ...
... Greater number of neurons with different weights allows a greater range of functions to be approximated with increased accuracy ...
Odor- and context dependent modulation of mitral cell
... The Olfactory Bulb Connected to everything else in the brain (according to Kay) Signals traveling to the olfactory bulb do not go through the thalamus Prone to disconnection in traumatic head injuries (sieve bone acts as guillotine) In rats, the olfactory bulb is very large, relatively much ...
... The Olfactory Bulb Connected to everything else in the brain (according to Kay) Signals traveling to the olfactory bulb do not go through the thalamus Prone to disconnection in traumatic head injuries (sieve bone acts as guillotine) In rats, the olfactory bulb is very large, relatively much ...
The Brain
... magnetic field that aligns the atoms that spin in the brain- Constructs images more detailed than PET or CAT C. FMRI- takes snapshots of the brain in action- studies both the function and structure of the human brain. D. PET scans- positron emission tomography- computerized image of the brain and ot ...
... magnetic field that aligns the atoms that spin in the brain- Constructs images more detailed than PET or CAT C. FMRI- takes snapshots of the brain in action- studies both the function and structure of the human brain. D. PET scans- positron emission tomography- computerized image of the brain and ot ...
Luis V. Colom, MD, PhD VP of Research Center for Biomedical Studies
... Damaged hippocampal axon terminals lead to altered somatic functions and subsequent death of cholinergic and glutamatergic septal neurons (injured cortical axons will lead to neuronal death in additional basal forebrain structures). Altered properties of the surviving septal neurons Oxidative Stress ...
... Damaged hippocampal axon terminals lead to altered somatic functions and subsequent death of cholinergic and glutamatergic septal neurons (injured cortical axons will lead to neuronal death in additional basal forebrain structures). Altered properties of the surviving septal neurons Oxidative Stress ...
Neuronal cell types
... (A) Projection neurons; (B) intrinsic neurons. The projection neurons of the cortex are pyramidal cells, and the intrinsic cells are simply called interneurons. The projection neuron of the cerebellum is the Purkinje cell, and the intrinsic cells are the granule, basket, stellate and Golgi cells. Th ...
... (A) Projection neurons; (B) intrinsic neurons. The projection neurons of the cortex are pyramidal cells, and the intrinsic cells are simply called interneurons. The projection neuron of the cerebellum is the Purkinje cell, and the intrinsic cells are the granule, basket, stellate and Golgi cells. Th ...
Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
Types of neurons
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
... But new dendrites can grow Provides room for more connections to other neurons New connections are basis for learning ...
The Nervous System - Hartland High School
... Cells on the outside of the axons outside of the CNS that produce the myelin sheath by wrapping themselves tightly around the axon in a jelly-roll like fashion. Related to Schwann cells are three other structures of a neuron. i. Myelin Sheath – Myelin cover that encloses the axon ii. Neurilemma – pa ...
... Cells on the outside of the axons outside of the CNS that produce the myelin sheath by wrapping themselves tightly around the axon in a jelly-roll like fashion. Related to Schwann cells are three other structures of a neuron. i. Myelin Sheath – Myelin cover that encloses the axon ii. Neurilemma – pa ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Coast Colleges Home Page
... Schwann Cells (Neurolemmocytes) - Form Myelin Sheath Satellite Cells - Protect, Cushion Ganglia ...
... Schwann Cells (Neurolemmocytes) - Form Myelin Sheath Satellite Cells - Protect, Cushion Ganglia ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Schwann Cells (Neurolemmocytes) - Form Myelin Sheath Satellite Cells - Protect, Cushion Ganglia ...
... Schwann Cells (Neurolemmocytes) - Form Myelin Sheath Satellite Cells - Protect, Cushion Ganglia ...
Ch. 48 - 49
... Name the three types of neurons and their functions. Which make up the CNS and the PNS? Describe the main parts of a neuron. Describe what happens in a Reflex Arc. How are Nodes of Ranvier and Saltatory conduction related? What occurs at the synapse? ...
... Name the three types of neurons and their functions. Which make up the CNS and the PNS? Describe the main parts of a neuron. Describe what happens in a Reflex Arc. How are Nodes of Ranvier and Saltatory conduction related? What occurs at the synapse? ...
MCB 163: Mammalian Neuroanatomy
... 11. ANTERIOR THALAMIC NUCLEI These nuclei are related to the limbic system and receive projections from the amygdala, and in turn project to the frontal lobes and especially the lateral prefrontal cortex. This circuit appears to be important for modulating emotionality and for socially acceptable be ...
... 11. ANTERIOR THALAMIC NUCLEI These nuclei are related to the limbic system and receive projections from the amygdala, and in turn project to the frontal lobes and especially the lateral prefrontal cortex. This circuit appears to be important for modulating emotionality and for socially acceptable be ...
The Nervous System funtions and neuron
... Long, thin processes with uniform diameter carry impulses away from cell body Many fine extensions at end called collaterals Axon ending= at ends of collaterals contain synaptic knob (comes in contact with receptive surface of another cell) ...
... Long, thin processes with uniform diameter carry impulses away from cell body Many fine extensions at end called collaterals Axon ending= at ends of collaterals contain synaptic knob (comes in contact with receptive surface of another cell) ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... 1. The membrane of a resting neuron is polarized, and the potential difference of this polarity (approximately –70 mV) is called the resting membrane potential. The resting membrane potential exists only across the membrane and is mostly due to two factors: differences in ionic makeup of intracellul ...
... 1. The membrane of a resting neuron is polarized, and the potential difference of this polarity (approximately –70 mV) is called the resting membrane potential. The resting membrane potential exists only across the membrane and is mostly due to two factors: differences in ionic makeup of intracellul ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... 1. The membrane of a resting neuron is polarized, and the potential difference of this polarity (approximately –70 mV) is called the resting membrane potential. The resting membrane potential exists only across the membrane and is mostly due to two factors: differences in ionic makeup of intracellul ...
... 1. The membrane of a resting neuron is polarized, and the potential difference of this polarity (approximately –70 mV) is called the resting membrane potential. The resting membrane potential exists only across the membrane and is mostly due to two factors: differences in ionic makeup of intracellul ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.