Introduction to Neural Networks
... • An NN is a network of many simple processors (“units, neurons”), each possibly having a small amount of local memory. The units are connected by communication channels (“connections”) which usually carry numeric data, encoded by any of various means. The units operate only on their local data and ...
... • An NN is a network of many simple processors (“units, neurons”), each possibly having a small amount of local memory. The units are connected by communication channels (“connections”) which usually carry numeric data, encoded by any of various means. The units operate only on their local data and ...
Nervous System Notes
... molecules causing ion channels to open This causes postsynaptic potential ...
... molecules causing ion channels to open This causes postsynaptic potential ...
Notes Outline I (Part I)
... 17. Clusters of cell bodies that accumulate in the CNS are called __________________ and in the PNS are called ___________________. 18. _____________________ receive imput from other neurons (axons). 19. Axons and dendrites are called ___________________ ________________. 20. Very long axons are oth ...
... 17. Clusters of cell bodies that accumulate in the CNS are called __________________ and in the PNS are called ___________________. 18. _____________________ receive imput from other neurons (axons). 19. Axons and dendrites are called ___________________ ________________. 20. Very long axons are oth ...
Ch.02 - Neuroscience
... Links central nervous system (spinal cord) to sense receptors, muscles and glands ...
... Links central nervous system (spinal cord) to sense receptors, muscles and glands ...
Computer Research II Drugs and Mind
... 4a. What is a special cell in the brain and what does it do? _____________________________ Click BACK and go to The Neuron and choose Millions and Billions of Cells http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/cells.html 1b. What is a neuron? ______________________ 2b. What does it do?_____________________ ...
... 4a. What is a special cell in the brain and what does it do? _____________________________ Click BACK and go to The Neuron and choose Millions and Billions of Cells http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/cells.html 1b. What is a neuron? ______________________ 2b. What does it do?_____________________ ...
Lab Report
... Objective: You will observe different cell types found in living organisms and compare the cell structure to its function. You will explain the similarities and differences amongst these cell types and describe how their structure relates to their function. Part One: Skeletal (Striated) Muscle There ...
... Objective: You will observe different cell types found in living organisms and compare the cell structure to its function. You will explain the similarities and differences amongst these cell types and describe how their structure relates to their function. Part One: Skeletal (Striated) Muscle There ...
Optogenetics in a transparent animal: circuit function in the larval
... Optogenetics in a transparent animal: circuit function in the larval zebrafish Ruben Portugues1, Kristen E Severi2, Claire Wyart2 and Misha B Ahrens3 Optogenetic tools can be used to manipulate neuronal activity in a reversible and specific manner. In recent years, such methods have been applied to ...
... Optogenetics in a transparent animal: circuit function in the larval zebrafish Ruben Portugues1, Kristen E Severi2, Claire Wyart2 and Misha B Ahrens3 Optogenetic tools can be used to manipulate neuronal activity in a reversible and specific manner. In recent years, such methods have been applied to ...
Nervous System - Effingham County Schools
... Huntington’s Disease- genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and causes involuntary twitching. Tourette’s Syndrome- irregular movements of the head, neck, or shoulders. They also may be more complex motor behaviors such as snorting, sniffing, and involuntary vocalization ...
... Huntington’s Disease- genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and causes involuntary twitching. Tourette’s Syndrome- irregular movements of the head, neck, or shoulders. They also may be more complex motor behaviors such as snorting, sniffing, and involuntary vocalization ...
Traffic Sign Recognition Using Artificial Neural Network
... processing – one processing unit, many operations in one second. Neural networks are based on the parallel architecture of animal brains-slow ,parallel and complicated-good for pattern matching. Pattern matching can solve many problems to which algorithms are not exist or very complicated. ...
... processing – one processing unit, many operations in one second. Neural networks are based on the parallel architecture of animal brains-slow ,parallel and complicated-good for pattern matching. Pattern matching can solve many problems to which algorithms are not exist or very complicated. ...
UNIT 3
... or hyperpolarizing (more negative than the resting level), whose strength is directly proportional to the strength of the triggering event. A large stimulus will cause a strong graded potential, and a small stimulus will result in a weak graded potential. Graded potentials lose strength as they move ...
... or hyperpolarizing (more negative than the resting level), whose strength is directly proportional to the strength of the triggering event. A large stimulus will cause a strong graded potential, and a small stimulus will result in a weak graded potential. Graded potentials lose strength as they move ...
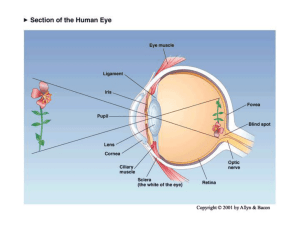
Blue= rods Green = Cones
... (thalamus), and then visual association cortex: orienting eyes to things we see and hear – the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and then the primary visual cortex (V1, area 17): more to come… ...
... (thalamus), and then visual association cortex: orienting eyes to things we see and hear – the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) and then the primary visual cortex (V1, area 17): more to come… ...
Nervous System Guided Notes
... 1) _______________________________or sensory neurons - bring stimuli to CNS -- affect the body by internal or external information 2) _______________________________or motor neurons -- cause muscles or glands to respond -- effect a change / response ...
... 1) _______________________________or sensory neurons - bring stimuli to CNS -- affect the body by internal or external information 2) _______________________________or motor neurons -- cause muscles or glands to respond -- effect a change / response ...
B4 B5 B6 Revision B6 Growth and Development
... cells are identical and could produce any sort of cell required by the organism (embryonic stem cells); After this point the cells become specialised and form different types of tissue. Adult and embryonic stem cells have the potential to produce cells needed to replace damaged tissues. In carefully ...
... cells are identical and could produce any sort of cell required by the organism (embryonic stem cells); After this point the cells become specialised and form different types of tissue. Adult and embryonic stem cells have the potential to produce cells needed to replace damaged tissues. In carefully ...
Lecture3
... – Neurons are “charged” like batteries and have the ability to send electrical messages over long distances to other cells. • Sensory neurons carry information from sense organs to the central nervous system. • Motor neurons carry information from the CNS to muscles ...
... – Neurons are “charged” like batteries and have the ability to send electrical messages over long distances to other cells. • Sensory neurons carry information from sense organs to the central nervous system. • Motor neurons carry information from the CNS to muscles ...
Axon Outgrowth in the Developing Cerebral
... transcription factors have any role in this process? Using visualization of cortical neurons through electroporation and organotypic slice culture, it was identified that significant axon growth begins a long time prior to the end of radial migration during neuronal development. Combining this metho ...
... transcription factors have any role in this process? Using visualization of cortical neurons through electroporation and organotypic slice culture, it was identified that significant axon growth begins a long time prior to the end of radial migration during neuronal development. Combining this metho ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... presynaptic neuron into the intersynaptic space. Neurotransmitters determine the opening of ion channels in the postsynaptic neuron. This causes the depolarisation of the postsynaptic neuron membrane and the initiation of nerve impulses. ...
... presynaptic neuron into the intersynaptic space. Neurotransmitters determine the opening of ion channels in the postsynaptic neuron. This causes the depolarisation of the postsynaptic neuron membrane and the initiation of nerve impulses. ...
Parts of the Neuron 45
... also convey messages to your glands, causing them to release hormones, chemical substances that help regulate bodily processes. Interneurons (also called associative neurons) are the most common type of neuron in the nervous system. They connect neurons to neurons. In the spinal cord, they connect s ...
... also convey messages to your glands, causing them to release hormones, chemical substances that help regulate bodily processes. Interneurons (also called associative neurons) are the most common type of neuron in the nervous system. They connect neurons to neurons. In the spinal cord, they connect s ...
Neuroanatomy Part 2
... photopigments). Nyctalopia: night blindness (inability to see well in low light) causes by a deficiency in Vitamin A. Light immediately begins to degrade the photopigments which causes visual stimulation. Step Two: When light stimulates the photoreceptors, the impulse causes the rods and cones to re ...
... photopigments). Nyctalopia: night blindness (inability to see well in low light) causes by a deficiency in Vitamin A. Light immediately begins to degrade the photopigments which causes visual stimulation. Step Two: When light stimulates the photoreceptors, the impulse causes the rods and cones to re ...
Nervous System
... • This tissue is made up entirely of specialized cells called neurons – Brain, spinal cord, nerves = nervous tissue ...
... • This tissue is made up entirely of specialized cells called neurons – Brain, spinal cord, nerves = nervous tissue ...
file - Athens Academy
... responsible for ridding the brain of debris and foreign substances – it acts as an immune system for the nervous system. ...
... responsible for ridding the brain of debris and foreign substances – it acts as an immune system for the nervous system. ...
Sensory Systems
... Balance is maintained by mechanoreceptors in the _________ semicircular canals of the inner ear. These canals are filled with fluid and the interiors are lined with ___________ cells that have tiny particles of calcium carbonate on top of them. When the head moves, the hair cells bend on the calcium ...
... Balance is maintained by mechanoreceptors in the _________ semicircular canals of the inner ear. These canals are filled with fluid and the interiors are lined with ___________ cells that have tiny particles of calcium carbonate on top of them. When the head moves, the hair cells bend on the calcium ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.