File
... A coating of fatty tissue along the axon which insulates the neuron and prevents information from spreading to other neurons. ...
... A coating of fatty tissue along the axon which insulates the neuron and prevents information from spreading to other neurons. ...
Scientific and Ethical Considerations in the Advancement of Stem
... Within the broad class of neurons, there are three categories of cells: receptors, interneurons, and effectors/motor neurons, that vary based on their functions. Receptors act to receive and encode sensory information. Through this action, receptors begin the process of sensation and perception. Int ...
... Within the broad class of neurons, there are three categories of cells: receptors, interneurons, and effectors/motor neurons, that vary based on their functions. Receptors act to receive and encode sensory information. Through this action, receptors begin the process of sensation and perception. Int ...
Receptive Field Properties of Single Neurons in Rat Primary Visual
... FIG. 1. Data obtained on-line from a single cell at 420-mm depth (layer 2–3). In all graphs, the y axis shows the response as impulse per second (imp/s). Spontaneous activity (SA; discharge rate with uniform field of average luminance) is presented to the right of each x axis as 2 horizontal lines: ...
... FIG. 1. Data obtained on-line from a single cell at 420-mm depth (layer 2–3). In all graphs, the y axis shows the response as impulse per second (imp/s). Spontaneous activity (SA; discharge rate with uniform field of average luminance) is presented to the right of each x axis as 2 horizontal lines: ...
neural plasticity
... common example is driving home from work in “auto-drive mode” while lost in thought about the events of the day, only to realize at some point along the way that you have been driving without any conscious attention, and that you have no idea where you are along your route. Finally, as Charles Leona ...
... common example is driving home from work in “auto-drive mode” while lost in thought about the events of the day, only to realize at some point along the way that you have been driving without any conscious attention, and that you have no idea where you are along your route. Finally, as Charles Leona ...
Station 1: Sensory Adaptation
... flag on p. 213 or go to Figure E on last page. of your book for one minute (have your partner time you). Immediately shift your gaze to a white paper or wall space. Draw what you see (in color) on your answer sheet. What you have just seen is called an afterimage. Opponentprocesses refer to any two ...
... flag on p. 213 or go to Figure E on last page. of your book for one minute (have your partner time you). Immediately shift your gaze to a white paper or wall space. Draw what you see (in color) on your answer sheet. What you have just seen is called an afterimage. Opponentprocesses refer to any two ...
Chapter 2
... dendrites. The next stage is for these neurons to connect up to each other, and to other structures, and form synapses. In order to do that, the axons and dendrites of various neurons need to grow towards each other. The tip of the developing axon or dendrite is referred to as the growth cone (Gordo ...
... dendrites. The next stage is for these neurons to connect up to each other, and to other structures, and form synapses. In order to do that, the axons and dendrites of various neurons need to grow towards each other. The tip of the developing axon or dendrite is referred to as the growth cone (Gordo ...
sensation - Warren County Schools
... become more sensitive (e.g., you cannot develop more rods and cones). Rather you do attend more to the other sensory cues and would notice things that you ...
... become more sensitive (e.g., you cannot develop more rods and cones). Rather you do attend more to the other sensory cues and would notice things that you ...
Maintenance and Regeneration of the Nerve Net in Hydra1 The
... stitial cells was initially assumed to be the answer (e.g., Bode and David, 1978), recent evidence indicates the second explanation is more probable. Both large and small interstitial cells are capable of migration as single cells, and possibly in pairs (Tardent and Morgenthaler, 1966; Campbell, 196 ...
... stitial cells was initially assumed to be the answer (e.g., Bode and David, 1978), recent evidence indicates the second explanation is more probable. Both large and small interstitial cells are capable of migration as single cells, and possibly in pairs (Tardent and Morgenthaler, 1966; Campbell, 196 ...
Assessing similarity to primary tissue and cortical layer identity in
... layer identity. We considered whether cells of mixed layer identity could be those with low expression of one set of canonical layer markers in combination with otherwise well-established layer identity. However, the level at which layer markers were expressed did not appear to differ between neuron ...
... layer identity. We considered whether cells of mixed layer identity could be those with low expression of one set of canonical layer markers in combination with otherwise well-established layer identity. However, the level at which layer markers were expressed did not appear to differ between neuron ...
Prof
... of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), which is the primary processing center for visual information received from the retina, in glaucoma patients. In experimental glaucoma monkeys, it was suggested that neuronal atrophy in LGN may occur in the early stage after IOP elevation, and that ...
... of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN), which is the primary processing center for visual information received from the retina, in glaucoma patients. In experimental glaucoma monkeys, it was suggested that neuronal atrophy in LGN may occur in the early stage after IOP elevation, and that ...
- Wiley Online Library
... by immunocytochemical and quantitative methods using discriminative antibodies specific for each enzyme. Nonlysosomal CE was barely detectable in these two brain tissues in the embryonic stages, whereas relatively high expression of lysosomal CD was observed in embryonic tissues. After birth, CE was ...
... by immunocytochemical and quantitative methods using discriminative antibodies specific for each enzyme. Nonlysosomal CE was barely detectable in these two brain tissues in the embryonic stages, whereas relatively high expression of lysosomal CD was observed in embryonic tissues. After birth, CE was ...
Review - Society for Developmental Biology
... retina in the mature animal is generated from a small zone of mitotically active cells at the peripheral margin of the retina. This zone has been called a variety of names in the literature, but we will use the term ciliary marginal zone (CMZ), due to its location at the junction between the ciliary ...
... retina in the mature animal is generated from a small zone of mitotically active cells at the peripheral margin of the retina. This zone has been called a variety of names in the literature, but we will use the term ciliary marginal zone (CMZ), due to its location at the junction between the ciliary ...
The neural basis for combinatorial coding in a cortical population response
... in which each cell responds independently to its sensory inputs. Mathematically, this means that the probability of responses from the population can be decomposed as a product of probabilities for each individual cell, as in Equation 1 below, where these single-cell properties have been estimated d ...
... in which each cell responds independently to its sensory inputs. Mathematically, this means that the probability of responses from the population can be decomposed as a product of probabilities for each individual cell, as in Equation 1 below, where these single-cell properties have been estimated d ...
Cerebral Cortex
... nonpyramidal neurons lack significant populations of dendritic spines, are found in all layers, and use GABA. They account for up to 30% of the total population of cortical neurons. They can be further divided into subpopulations based upon their production of one or other of three calcium-binding p ...
... nonpyramidal neurons lack significant populations of dendritic spines, are found in all layers, and use GABA. They account for up to 30% of the total population of cortical neurons. They can be further divided into subpopulations based upon their production of one or other of three calcium-binding p ...
NEUROCHEMISTRY & NEUROTRANSMITTERS
... THEIR RECEPTORS. AFTER BINDING TO THEIR RECEPTORS, NTs MAY BE ENZYMATICALLY BROKEN DOWN (e.g. ACETYLCHOLINE BY THE ACTION OF ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE) OR TAKEN BACK UP AGAIN BY THE PRESYNAPSE (e.g. NOREPINEPHRINE IS TAKEN BACK UP BY A TRANSPORT PROTEIN). ...
... THEIR RECEPTORS. AFTER BINDING TO THEIR RECEPTORS, NTs MAY BE ENZYMATICALLY BROKEN DOWN (e.g. ACETYLCHOLINE BY THE ACTION OF ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE) OR TAKEN BACK UP AGAIN BY THE PRESYNAPSE (e.g. NOREPINEPHRINE IS TAKEN BACK UP BY A TRANSPORT PROTEIN). ...
Biomorphic Circuits and Systems: Control of Robotic and Prosthetic Limbs
... What the higher levels of the CNS and the sensory information can do, however, is modulate these rhythmic signals in order to ...
... What the higher levels of the CNS and the sensory information can do, however, is modulate these rhythmic signals in order to ...
Nervous System Intro Part 1
... after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Neural Coding: A Least Squares Approach
... is loosely a sequence of delta functions at the spike times. Observe that (3) may be interpreted as a filtering operation . The model can be shown to be equivalent to an all pole filter, see Fig 4 (upper). Note that this is now partially an impulse response estimation problem (Hawkes, ...
... is loosely a sequence of delta functions at the spike times. Observe that (3) may be interpreted as a filtering operation . The model can be shown to be equivalent to an all pole filter, see Fig 4 (upper). Note that this is now partially an impulse response estimation problem (Hawkes, ...
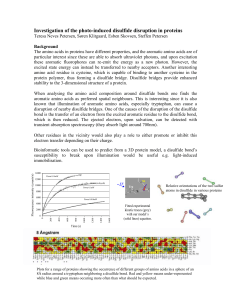
Investigation of the photo-induced disulfide disruption in
... stability to the 3-dimensional structure of a protein. When analysing the amino acid composition around disulfide bonds one finds the aromatic amino acids as preferred spatial neighbours. This is interesting since it is also known that illumination of aromatic amino acids, especially tryptophan, can ...
... stability to the 3-dimensional structure of a protein. When analysing the amino acid composition around disulfide bonds one finds the aromatic amino acids as preferred spatial neighbours. This is interesting since it is also known that illumination of aromatic amino acids, especially tryptophan, can ...
Parallel Transformation of Tactile Signals in Central Circuits of
... all experiments except for those in Figure 7, all six legs were glued to the holder with UV-cured glue. A small hole was manually dissected in the cuticle of the ventral thorax to expose the prothoracic neuromeres, and the perineural sheath was gently removed with fine forceps to expose neuronal cel ...
... all experiments except for those in Figure 7, all six legs were glued to the holder with UV-cured glue. A small hole was manually dissected in the cuticle of the ventral thorax to expose the prothoracic neuromeres, and the perineural sheath was gently removed with fine forceps to expose neuronal cel ...
Spinal cord 1
... Uniform and simple organization of other parts of CNS Very important in day-to-day activities that we don’t even think about ...
... Uniform and simple organization of other parts of CNS Very important in day-to-day activities that we don’t even think about ...
Neuronal Diversity and Temporal Dynamics: The Unity of
... a compartmentalized structure of pyramidal cells allows spatially segregated activities at the same time. Interestingly, different types of parvalbumin (PV)–expressing, GABAergic interneuron also innervate distinct subcellular domains: Axo-axonic cells (Fig. 1, type 1) innervate exclusively the axon ...
... a compartmentalized structure of pyramidal cells allows spatially segregated activities at the same time. Interestingly, different types of parvalbumin (PV)–expressing, GABAergic interneuron also innervate distinct subcellular domains: Axo-axonic cells (Fig. 1, type 1) innervate exclusively the axon ...
Spontaneous firing patterns of identified spiny neurons in the rat
... between these cells. For example, neurons with relatively high tonic spontaneous firing rates have been found to be most likely to show inhibitory responses to iontophoretic application to dopamine5 or to stimulation of substantia nigra or cerebral cortex11,21, to respond with EPSPIPSP sequences to ...
... between these cells. For example, neurons with relatively high tonic spontaneous firing rates have been found to be most likely to show inhibitory responses to iontophoretic application to dopamine5 or to stimulation of substantia nigra or cerebral cortex11,21, to respond with EPSPIPSP sequences to ...
Making New Memories
... cell during new learning to the response of the same cell to the reference scenes with the same rewarded target location (i.e., the same motor response for both new and reference scenes). In no case did the changing cells respond similarly to the reference scenes suggesting that the changing signal ...
... cell during new learning to the response of the same cell to the reference scenes with the same rewarded target location (i.e., the same motor response for both new and reference scenes). In no case did the changing cells respond similarly to the reference scenes suggesting that the changing signal ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.