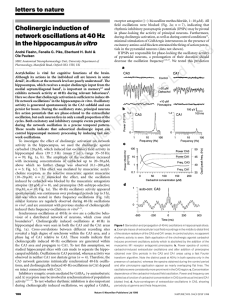
Cholinergic induction of network oscillations at 40 Hz in the
... oscillation, but each neuron fires in only a small proportion of the cycles. Both excitatory and inhibitory synaptic events participate during the network oscillation in a precise temporal pattern. These results indicate that subcortical cholinergic input can control hippocampal memory processing by ...
... oscillation, but each neuron fires in only a small proportion of the cycles. Both excitatory and inhibitory synaptic events participate during the network oscillation in a precise temporal pattern. These results indicate that subcortical cholinergic input can control hippocampal memory processing by ...
nervous system
... (response). The nervous system is thus a connection between sensory inputs and motor outputs. As evolution proceeded the nervous system becomes more complex. The radically symmetrical animals have simple nervous system consisting of nerve net work, conducts signals from sensory cells to muscle cells ...
... (response). The nervous system is thus a connection between sensory inputs and motor outputs. As evolution proceeded the nervous system becomes more complex. The radically symmetrical animals have simple nervous system consisting of nerve net work, conducts signals from sensory cells to muscle cells ...
1. Materials and Methods
... were found to fall within the 3 categories illustrated in Figure 2. These categories are not sharply delimited: some cells show intermediate behaviours. ...
... were found to fall within the 3 categories illustrated in Figure 2. These categories are not sharply delimited: some cells show intermediate behaviours. ...
A dedicated circuit links direction-selective retinal
... of the mCherry1 cells resided in the DSGC-RZ (Fig. 3e, f) (Extended Data Fig. 4) (Methods). We observed putative sites of contact between the axon terminals of DSGCs and the dendrites of mCherry1 dLGN neurons (Fig. 3g), some of which contained VGLUT2 (Fig. 3h–k) (Extended Data Fig. 5), a presynaptic ...
... of the mCherry1 cells resided in the DSGC-RZ (Fig. 3e, f) (Extended Data Fig. 4) (Methods). We observed putative sites of contact between the axon terminals of DSGCs and the dendrites of mCherry1 dLGN neurons (Fig. 3g), some of which contained VGLUT2 (Fig. 3h–k) (Extended Data Fig. 5), a presynaptic ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... soma. Microtubules provide the structural basis for transport, axoplasmic flow. This mechanism of transport is not diffusion but rather retrograde axonal transport associated with the microtubule network that exists throughout the nerve cell. The rate of flow varies depending upon the product being ...
... soma. Microtubules provide the structural basis for transport, axoplasmic flow. This mechanism of transport is not diffusion but rather retrograde axonal transport associated with the microtubule network that exists throughout the nerve cell. The rate of flow varies depending upon the product being ...
6th ANNUAL NEUROSCIENCE, BEHAVIOR AND HEALTH RESEARCH FORUM The University of Vermont
... and mechanisms of a Class B GPCR Chenyi Liao and Jianing Li Department of Chemistry, University of Vermont, Burlington, VT 05405 We have studied a class B G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR), pituitary adenylate cyclaseactivating polypeptide receptor (PAC1R), which is crucial for transducing signal in ...
... and mechanisms of a Class B GPCR Chenyi Liao and Jianing Li Department of Chemistry, University of Vermont, Burlington, VT 05405 We have studied a class B G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR), pituitary adenylate cyclaseactivating polypeptide receptor (PAC1R), which is crucial for transducing signal in ...
What Are the Units of Brain Function?
... can vary its speed or perhaps change directions by varying the speed of one wheel relative to the other. The robot’s many exposed wires show that it is not intended to go into water. And, because this robot has no lights or cameras, you can infer that it is not meant to see. The structure of the rob ...
... can vary its speed or perhaps change directions by varying the speed of one wheel relative to the other. The robot’s many exposed wires show that it is not intended to go into water. And, because this robot has no lights or cameras, you can infer that it is not meant to see. The structure of the rob ...
File
... potassium voltage-activated channels opens and potassium ions rush out of the cell and the membrane voltage reaches -70 mV again. ...
... potassium voltage-activated channels opens and potassium ions rush out of the cell and the membrane voltage reaches -70 mV again. ...
12-1 Test Bank Huether and McCance: Understanding
... the CNS. Which of the following classifications would this neuron fall into? a. Bipolar b. Multipolar c. Pseudounipolar d. Interpolar ANS: C Pseudounipolar neurons have one process; the dendritic portion of each of these neurons extends away from the CNS, and the axon portion projects into the CNS. ...
... the CNS. Which of the following classifications would this neuron fall into? a. Bipolar b. Multipolar c. Pseudounipolar d. Interpolar ANS: C Pseudounipolar neurons have one process; the dendritic portion of each of these neurons extends away from the CNS, and the axon portion projects into the CNS. ...
ChennWalshCeCortexJu..
... including some bearing striking resemblance to neural precursors such as medulloblastoma (Huang et al., 2000). β-Catenin is expressed highly in mammalian neural precursors, and β-catenin protein is enriched at adherens junctions at the lumen of the ventricle (Chenn and Walsh, 2002). Embr yonic trans ...
... including some bearing striking resemblance to neural precursors such as medulloblastoma (Huang et al., 2000). β-Catenin is expressed highly in mammalian neural precursors, and β-catenin protein is enriched at adherens junctions at the lumen of the ventricle (Chenn and Walsh, 2002). Embr yonic trans ...
Regular Spiking and Intrinsic Bursting Pyramidal Cells
... for all post hoc t tests). In LVa, the S1 and S2 responses increased almost two fold at 3 days (197% and 205%, respectively) and maintained that level at 10 days (203% and 206% of control values), which was highly statistically significant (for S1, t(60) = 2.95, p < 0.005 and for S2 t(60) = 3.0, p < ...
... for all post hoc t tests). In LVa, the S1 and S2 responses increased almost two fold at 3 days (197% and 205%, respectively) and maintained that level at 10 days (203% and 206% of control values), which was highly statistically significant (for S1, t(60) = 2.95, p < 0.005 and for S2 t(60) = 3.0, p < ...
Visual Motion-Detection Circuits in Flies: Small
... in flies, beetles, moths, and locusts. With few exceptions (Torre and Poggio, 1978; Franceschini et al., 1989; Strausfeld and Lee, 1991), inputs to motion-sensitive tangential neurons are represented schematically by ensembles of Hassenstein and Reichardt elementary motion detectors (EMDs; Hausen an ...
... in flies, beetles, moths, and locusts. With few exceptions (Torre and Poggio, 1978; Franceschini et al., 1989; Strausfeld and Lee, 1991), inputs to motion-sensitive tangential neurons are represented schematically by ensembles of Hassenstein and Reichardt elementary motion detectors (EMDs; Hausen an ...
resting membrane potential
... communicate with other neurons. Efferent neurons originate in the central nervous system, where the cell body and dendrites receive synaptic communication from other neurons. Efferent axons, however, are part of the peripheral nervous system and terminate at a synapse with an effector organ. Interne ...
... communicate with other neurons. Efferent neurons originate in the central nervous system, where the cell body and dendrites receive synaptic communication from other neurons. Efferent axons, however, are part of the peripheral nervous system and terminate at a synapse with an effector organ. Interne ...
Richard G. Schuster, DO
... preparation and movement execution. A smaller influence originates from network in medial prefrontal cortex that is involved in regulation of cognition and emotion. Thus, cortical areas involved in the control of movement cognition, and affect are potential sources of central commands to influence s ...
... preparation and movement execution. A smaller influence originates from network in medial prefrontal cortex that is involved in regulation of cognition and emotion. Thus, cortical areas involved in the control of movement cognition, and affect are potential sources of central commands to influence s ...
Membrane potential moves toward the K equilibrium
... Some higher functions only exist in one hemisphere - unilateral (eg language in left hemisphere only). PNS – cutting of an axon leads to sprouting from the cut end in order to re-establish a connection – i.e. it can regenerate, although this is not always successful as the connections can get mixed ...
... Some higher functions only exist in one hemisphere - unilateral (eg language in left hemisphere only). PNS – cutting of an axon leads to sprouting from the cut end in order to re-establish a connection – i.e. it can regenerate, although this is not always successful as the connections can get mixed ...
Spinal Cord
... 1. Important role in protection of the body. 2. Responsible for maintenance of: a. muscle tone. b. body posture. 3. Center can be anywhere except cerebral cortex. 4. Center can be in spinal cord or in brain stem. ...
... 1. Important role in protection of the body. 2. Responsible for maintenance of: a. muscle tone. b. body posture. 3. Center can be anywhere except cerebral cortex. 4. Center can be in spinal cord or in brain stem. ...
The Nervous System
... Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Advanced biomaterial strategies to transplant preformed micro
... et al 2010), but these methods do not replace the loss of neurons that is prevalent in neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s disease. Thus, although many neurological conditions present both neuronal and axonal loss (Coleman and Perry, 2002, Bjartmar et al 2003, Dauer and Przedb ...
... et al 2010), but these methods do not replace the loss of neurons that is prevalent in neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s disease. Thus, although many neurological conditions present both neuronal and axonal loss (Coleman and Perry, 2002, Bjartmar et al 2003, Dauer and Przedb ...
Nothing can be coincidence: synaptic inhibition and plasticity in the
... likely to be the tonic inhibition from Purkinje cells that keeps them firing. Minimizing inhibitory synaptic depression in spontaneously firing neurons During cerebellar behaviors, increased activity in Purkinje neurons can and does suppress firing by nuclear neurons [21,22]. Studies in cerebellar s ...
... likely to be the tonic inhibition from Purkinje cells that keeps them firing. Minimizing inhibitory synaptic depression in spontaneously firing neurons During cerebellar behaviors, increased activity in Purkinje neurons can and does suppress firing by nuclear neurons [21,22]. Studies in cerebellar s ...
the neural impulse
... The soma (or cell body) is the neuron’s control centre. It contains the nucleus and other organelles which are necessary for the neuron’s survival. Dendrites are branched structures specialized to receive information from other neurons or cells. Therefore, the dendrites are the neuron's information ...
... The soma (or cell body) is the neuron’s control centre. It contains the nucleus and other organelles which are necessary for the neuron’s survival. Dendrites are branched structures specialized to receive information from other neurons or cells. Therefore, the dendrites are the neuron's information ...
Modeling the spinal cord neural circuitry controlling cat hindlimb
... high-threshold calcium, calcium-dependent potassium, leakage and synaptic ionic channels. The schematic of re4ex circuits was modi;ed from the previous models [1,4] and applied to each antagonistic group of muscles. The synaptic connections within and between the NMs and the structure of inputs of I ...
... high-threshold calcium, calcium-dependent potassium, leakage and synaptic ionic channels. The schematic of re4ex circuits was modi;ed from the previous models [1,4] and applied to each antagonistic group of muscles. The synaptic connections within and between the NMs and the structure of inputs of I ...
Analogues of simple and complex cells in rhesus monkey auditory
... A small number of neurons (n = 11) were tested at more than one sound level. Ten neurons were tested at two, and one neuron at three levels. Although response amplitude varied with sound level (sometimes in a nonmonotonic fashion), as one would expect, ON and OFF responses changed in similar proport ...
... A small number of neurons (n = 11) were tested at more than one sound level. Ten neurons were tested at two, and one neuron at three levels. Although response amplitude varied with sound level (sometimes in a nonmonotonic fashion), as one would expect, ON and OFF responses changed in similar proport ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.























