Theme 4: Rhythmical movements (6 p)
... c) You are walking along in the forest during a nice autumn day, looking for chanterelle mushrooms. After some time you suddenly spot a chanterelle in the periphery of your visual field, by the side of your walking path. Describe in a concise way the sequence of events in your CNS that allows you to ...
... c) You are walking along in the forest during a nice autumn day, looking for chanterelle mushrooms. After some time you suddenly spot a chanterelle in the periphery of your visual field, by the side of your walking path. Describe in a concise way the sequence of events in your CNS that allows you to ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... • Excitation of the Spinal Cord Motor Control Areas by the Primary Motor Cortex and the Red Nucleus a. Vertical columnar arrangement of the neurons in the motor cortex b. Each column functions as a unit, usually stimulating a group of synergistic muscles (sometimes a single muscle) c. Each column op ...
... • Excitation of the Spinal Cord Motor Control Areas by the Primary Motor Cortex and the Red Nucleus a. Vertical columnar arrangement of the neurons in the motor cortex b. Each column functions as a unit, usually stimulating a group of synergistic muscles (sometimes a single muscle) c. Each column op ...
Vision`s First Steps: Anatomy, Physiology, and Perception in the
... Gamma-aminobutyric acid Lateral geniculate nucleus ...
... Gamma-aminobutyric acid Lateral geniculate nucleus ...
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally
... frequently, were more likely to have place fields and were more strongly modulated by slow oscillations of sleep. Both deep and superficial pyramidal cells fired preferentially at the trough of theta oscillations during maze exploration, whereas deep pyramidal cells shifted their preferred phase of ...
... frequently, were more likely to have place fields and were more strongly modulated by slow oscillations of sleep. Both deep and superficial pyramidal cells fired preferentially at the trough of theta oscillations during maze exploration, whereas deep pyramidal cells shifted their preferred phase of ...
NeuralNets
... Presynaptic neuron releases neurotransmitters through synaptic vesicles at terminal button to the synaptic cleft – the gap between two neurons. Dendrite receives the signal via its receptors [Excitatory & Inhibitory Synapses – Later] ...
... Presynaptic neuron releases neurotransmitters through synaptic vesicles at terminal button to the synaptic cleft – the gap between two neurons. Dendrite receives the signal via its receptors [Excitatory & Inhibitory Synapses – Later] ...
Nerve activates contraction
... – Moves like a wave down the axon, with constant speed and amplitude © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... – Moves like a wave down the axon, with constant speed and amplitude © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Activity of Defined Mushroom Body Output Neurons
... performance of flies with M4/6 neural blockade to control flies carrying only the GAL4 or UAS-shits1 transgene. We first tested immediate memory performance following sucrose-reinforced appetitive conditioning (Tempel et al., 1983; Krashes and Waddell, 2008). All flies were trained and tested for 3 ...
... performance of flies with M4/6 neural blockade to control flies carrying only the GAL4 or UAS-shits1 transgene. We first tested immediate memory performance following sucrose-reinforced appetitive conditioning (Tempel et al., 1983; Krashes and Waddell, 2008). All flies were trained and tested for 3 ...
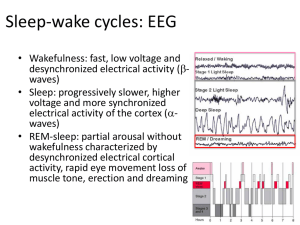
Sleep-wake cycles: EEG
... hybridization aimed at identifying mRNA’s species that are expressed only in discrete nuclei within the hypothalamus – New hypothalamic mRNA (hypocretin 1 and 2) found by in-situ hybridization to occur in the lateral hypothalamus • Sakurai et al. (1998) transfected cell lines that stably express eac ...
... hybridization aimed at identifying mRNA’s species that are expressed only in discrete nuclei within the hypothalamus – New hypothalamic mRNA (hypocretin 1 and 2) found by in-situ hybridization to occur in the lateral hypothalamus • Sakurai et al. (1998) transfected cell lines that stably express eac ...
Name: PID: SPRING 2013 COGS 1 Midterm 2 – Form B 1. Which of
... a. Prior probability b. Posterior probability c. Marginal probability d. Likelihood e. Evidence 42. Referring to an object's location as being ""due north"" is an example of a(n): a. Relative frame of reference b. Centric frame of reference c. Absolute frame of reference d. Intrinsic frame of refere ...
... a. Prior probability b. Posterior probability c. Marginal probability d. Likelihood e. Evidence 42. Referring to an object's location as being ""due north"" is an example of a(n): a. Relative frame of reference b. Centric frame of reference c. Absolute frame of reference d. Intrinsic frame of refere ...
The Problem of Consciousness by Francis Crick and
... Visual theorists would also agree that seeing is a constructive process, one in which the brain has to carry out complex activities (sometimes called computations) in order to decide which interpretation to adopt of the ambiguous visual input. “Computation” implies that the brain acts to form a symb ...
... Visual theorists would also agree that seeing is a constructive process, one in which the brain has to carry out complex activities (sometimes called computations) in order to decide which interpretation to adopt of the ambiguous visual input. “Computation” implies that the brain acts to form a symb ...
The role of synaptic ion channels in synaptic
... (AMPA), N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA), and kainate. All three bind glutamate with high affinity and have varying preferences for other glutamate agonists, including AMPA, NMDA and kainate (Erreger et al, 2004). AMPA receptors are tetrameric ion channels that principally conduct sodium and potassiu ...
... (AMPA), N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA), and kainate. All three bind glutamate with high affinity and have varying preferences for other glutamate agonists, including AMPA, NMDA and kainate (Erreger et al, 2004). AMPA receptors are tetrameric ion channels that principally conduct sodium and potassiu ...
CHARLES UNIVERSITY
... system in epileptiform activity (Schuchmann, 2002). NMDA receptor is a specific type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. These receptors when tonically activated can trigger an excessive increase in intracellular calcium; nerve cells start to induce abnormal excessive activity and intracellular calciu ...
... system in epileptiform activity (Schuchmann, 2002). NMDA receptor is a specific type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. These receptors when tonically activated can trigger an excessive increase in intracellular calcium; nerve cells start to induce abnormal excessive activity and intracellular calciu ...
Dual single unit recording in Globus Pallidus (GP) and Subthalamic
... stained with Cresyl Violet in order to determine the location of the recording sites. The data were assessed using one-way ANOVA/two way ANOVA or paired Student Ttest, when appropriate. All data are expressed as mean SEM or as percentage of the baseline firing rate. A P value of less than 0.05 was d ...
... stained with Cresyl Violet in order to determine the location of the recording sites. The data were assessed using one-way ANOVA/two way ANOVA or paired Student Ttest, when appropriate. All data are expressed as mean SEM or as percentage of the baseline firing rate. A P value of less than 0.05 was d ...
Neurophysiology – Action Potential, Nerve Impulse, and Synapses
... The distribution of ions inside and outside cell membranes is determined in part by channels in the membranes. Some channels are always open, others can be opened or closed. Channels can be selective i.e., a channel may allow one kind of ion to pass through and exclude other kinds. Potassium ions te ...
... The distribution of ions inside and outside cell membranes is determined in part by channels in the membranes. Some channels are always open, others can be opened or closed. Channels can be selective i.e., a channel may allow one kind of ion to pass through and exclude other kinds. Potassium ions te ...
multispectral labeling technique to map many neighboring axonal
... In contrast, when we injected a mixture of the colors to one site, the centers of gravity for the two colors in each vesicle were nearly identical. Thus, when axons extended into areas that had different colored dyes, the individual vesicles showed no mixing. These results imply that when a vesicle ...
... In contrast, when we injected a mixture of the colors to one site, the centers of gravity for the two colors in each vesicle were nearly identical. Thus, when axons extended into areas that had different colored dyes, the individual vesicles showed no mixing. These results imply that when a vesicle ...
CURRICULUM OF PHYSIOLOGY
... mechanism, characteristic. Examples. - Feedforward control and its strategy used to control systems in the body. Communication. – Means of communication. - Direct communication via gap junction. - Autocrine and paracrine signaling via chemical messengers. - Nervous signaling. - Neuroendocrine signal ...
... mechanism, characteristic. Examples. - Feedforward control and its strategy used to control systems in the body. Communication. – Means of communication. - Direct communication via gap junction. - Autocrine and paracrine signaling via chemical messengers. - Nervous signaling. - Neuroendocrine signal ...
P312 Ch05_PerceivingObjectsII
... a) picture of Harrison Ford, b) a picture of someone else, or c) a random texture. Each presentation was about 50 ms, followed by a masking stimulus. Observers responded by indicating “Harrison Ford”, “Other Face” , or “Nothing”. They recorded brain activity occurring before the response of “Harriso ...
... a) picture of Harrison Ford, b) a picture of someone else, or c) a random texture. Each presentation was about 50 ms, followed by a masking stimulus. Observers responded by indicating “Harrison Ford”, “Other Face” , or “Nothing”. They recorded brain activity occurring before the response of “Harriso ...
Neuronal subtype specification in the cerebral cortex
... Box 1 | Distant progenitor zones contribute to the neuronal diversity of the neocortex A wealth of evidence has accumulated indicating that neocortical GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid)-containing interneurons are derived from germinal zones outside the neocortex and migrate long distances to their final l ...
... Box 1 | Distant progenitor zones contribute to the neuronal diversity of the neocortex A wealth of evidence has accumulated indicating that neocortical GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid)-containing interneurons are derived from germinal zones outside the neocortex and migrate long distances to their final l ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.