chapter 4 - reactions in solution
... Weak acids, such as acetic acid (CH3COOH), hydrofluoric acid (HF), nitrous acid (HNO2), etc., and weak bases such as NH3(aq) do not ionize completely and they form weak electrolytes. CH3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + CH3COO-(aq) Ionic compounds that are only slightly soluble in water, such as Ag ...
... Weak acids, such as acetic acid (CH3COOH), hydrofluoric acid (HF), nitrous acid (HNO2), etc., and weak bases such as NH3(aq) do not ionize completely and they form weak electrolytes. CH3COOH(aq) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + CH3COO-(aq) Ionic compounds that are only slightly soluble in water, such as Ag ...
Review on N acylation reaction
... In recent years with the introduction of new peptide coupling reagents in organic synthesis, the methods of amide synthesis have been significantly advanced. But the two step acylation, activation of carboxylic acid and reaction with amines have been often used in non-peptide chemistry. Acid chlorid ...
... In recent years with the introduction of new peptide coupling reagents in organic synthesis, the methods of amide synthesis have been significantly advanced. But the two step acylation, activation of carboxylic acid and reaction with amines have been often used in non-peptide chemistry. Acid chlorid ...
CHEM 122 - Nmt.edu
... What is the Molarity of this solution? C = / RT = (0.272 atm) / (0.08206 L atm/K mol) (298.15 K) = 0.011 M ...
... What is the Molarity of this solution? C = / RT = (0.272 atm) / (0.08206 L atm/K mol) (298.15 K) = 0.011 M ...
Hydration Number of Sodium Ions Determined by Sodium Magnetic
... the sodium magnetic resonance, or some other suitable probe. From the titration curve, we find a value of 3-4 for the hydration number of sodium and also obtain the equilibrium constant for the hydration. Previously reported hydration number^^-^ for the sodium ion vary from 3 to 21. By X-ray diffrac ...
... the sodium magnetic resonance, or some other suitable probe. From the titration curve, we find a value of 3-4 for the hydration number of sodium and also obtain the equilibrium constant for the hydration. Previously reported hydration number^^-^ for the sodium ion vary from 3 to 21. By X-ray diffrac ...
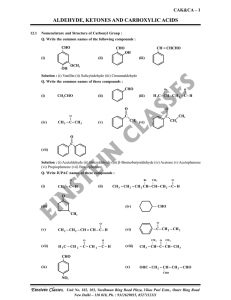
aldehyde, ketones and carboxylic acids
... Solution : Aromatic aldehydes (benzaldehyde and its derivatives) are prepared from aromatic hydrocarbons by the following methods : (i) By oxidation of methylbenzene : Strong oxidising agents oxidise toluene and its derivatives to benzoic acids. However, it is possible to stop the oxidation at the a ...
... Solution : Aromatic aldehydes (benzaldehyde and its derivatives) are prepared from aromatic hydrocarbons by the following methods : (i) By oxidation of methylbenzene : Strong oxidising agents oxidise toluene and its derivatives to benzoic acids. However, it is possible to stop the oxidation at the a ...
PREPARATORY PROBLEMS
... ii) Similarly, find the absolute values of the coefficients c1 – c3 for an sp2 hybrid orbital. ...
... ii) Similarly, find the absolute values of the coefficients c1 – c3 for an sp2 hybrid orbital. ...
PREPARATORY PROBLEMS (Theoretical)
... ii) Similarly, find the absolute values of the coefficients c1 – c3 for an sp2 hybrid orbital. ...
... ii) Similarly, find the absolute values of the coefficients c1 – c3 for an sp2 hybrid orbital. ...
SOLLIQSOL questions
... (b) Describe any changes that can be observed in a sample of solid argon when the temperature is increased from 40 K to 160 K at a constant pressure of 0.50 atmosphere. (c) Describe any changes that can be observed in a sample of liquid argon when the pressure is reduced from 10 atmospheres to 1 atm ...
... (b) Describe any changes that can be observed in a sample of solid argon when the temperature is increased from 40 K to 160 K at a constant pressure of 0.50 atmosphere. (c) Describe any changes that can be observed in a sample of liquid argon when the pressure is reduced from 10 atmospheres to 1 atm ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... Changing the volume of a reactant container changes the concentration of gaseous reactants and therefore their partial pressures Equilibrium position will therefore move The value of Kc or Kp does NOT change Changing pressure by adding more of an inert gas has no effect of the equilibrium position - ...
... Changing the volume of a reactant container changes the concentration of gaseous reactants and therefore their partial pressures Equilibrium position will therefore move The value of Kc or Kp does NOT change Changing pressure by adding more of an inert gas has no effect of the equilibrium position - ...
Classifying Chemical Reactions by What Atoms Do
... Acids and Bases in Solution Acids ionize in water to form H+ ions. (More precisely, the H+ from the acid molecule is donated to a water molecule to form hydronium ion, H3O+) Bases dissociate in water to form OH- ions. (Bases, such as NH3, that do not contain OH- ions, produce OH- by pulling H+ off ...
... Acids and Bases in Solution Acids ionize in water to form H+ ions. (More precisely, the H+ from the acid molecule is donated to a water molecule to form hydronium ion, H3O+) Bases dissociate in water to form OH- ions. (Bases, such as NH3, that do not contain OH- ions, produce OH- by pulling H+ off ...
Chemistry-Maths-Student-Guide
... reaction gone. Two of these – calculations involving reacting quantities (or moles) and calculations involving reaction rates are ones that you’ll have come across at GCSE. The last one – the idea of reactions at equilibrium – is an idea you may have seen at GCSE, but you’ve yet to put numbers into ...
... reaction gone. Two of these – calculations involving reacting quantities (or moles) and calculations involving reaction rates are ones that you’ll have come across at GCSE. The last one – the idea of reactions at equilibrium – is an idea you may have seen at GCSE, but you’ve yet to put numbers into ...
File
... (ii) The C–C–C bond angle in compound K changes when the polymer is formed. State and explain how the C–C–C bond angle differs between a molecule of K and the polymer. angle changes from ............................................ to ................................................. ...
... (ii) The C–C–C bond angle in compound K changes when the polymer is formed. State and explain how the C–C–C bond angle differs between a molecule of K and the polymer. angle changes from ............................................ to ................................................. ...
Chapter 17 - Bakersfield College
... Each set of equilibrium concentration is called an equilibrium position and it depends on the initial concentrations (there are an infinite # of equilibrium positions but only one equilibrium constant). ...
... Each set of equilibrium concentration is called an equilibrium position and it depends on the initial concentrations (there are an infinite # of equilibrium positions but only one equilibrium constant). ...
9 free IB Chem labs (sent to OCC) - VicPark-IBRoundtable-2009
... 6. When you are ready with the stopwatch and the tubing, place the Mg inside the flask. Immediately start timing, cover the flask with the bung and hold the tubing inside the cylinder. 2 people should be operating the apparatus and 1 person should be recording data. 7. Take volume measurements every ...
... 6. When you are ready with the stopwatch and the tubing, place the Mg inside the flask. Immediately start timing, cover the flask with the bung and hold the tubing inside the cylinder. 2 people should be operating the apparatus and 1 person should be recording data. 7. Take volume measurements every ...
Chemistry Tests Questions
... 4. When silver nitrate solution is added to iron(II) nitrate solution a grey-black precipitate is formed and after a few minutes there is no further change. The mixture is now in dynamic equilibrium. Explain what this term means. ...
... 4. When silver nitrate solution is added to iron(II) nitrate solution a grey-black precipitate is formed and after a few minutes there is no further change. The mixture is now in dynamic equilibrium. Explain what this term means. ...
04 Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... • Solutions are defined as homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. • The solvent is present in greatest abundance. • All other substances are solutes. • When water is the solvent, the solution is called an aqueous solution. Aqueous Reactions © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Solutions are defined as homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. • The solvent is present in greatest abundance. • All other substances are solutes. • When water is the solvent, the solution is called an aqueous solution. Aqueous Reactions © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Basic Chemical Concepts I
... A 10.00 mL aliquot of vinegar (density = 1.02 g mLG1) is diluted to 100.0 mL with deionized water in a volumetric flask. A 25.00 mL sample of the diluted vinegar requires 9.10 mL of 0.2218 M NaOH(aq) to reach a pink phenolphthalein end point. Calculate the mass % of acetic acid, HC 2H3O2, in the und ...
... A 10.00 mL aliquot of vinegar (density = 1.02 g mLG1) is diluted to 100.0 mL with deionized water in a volumetric flask. A 25.00 mL sample of the diluted vinegar requires 9.10 mL of 0.2218 M NaOH(aq) to reach a pink phenolphthalein end point. Calculate the mass % of acetic acid, HC 2H3O2, in the und ...
Chemistry Revision Guide - Mr Cartlidge`s Science Blog
... example, ‘O2‘ means there is one oxygen molecule involved in a reaction but ‘2O2’ would mean there are two. Example:. CH4(g) + O2(g) CO2)g) + H2O(g)* This is unbalanced as there are 4 ‘H’ on the left but only 2 ‘H’ on the right. This must be corrected by placing a ‘2’ in front of the ‘H2O’ so ther ...
... example, ‘O2‘ means there is one oxygen molecule involved in a reaction but ‘2O2’ would mean there are two. Example:. CH4(g) + O2(g) CO2)g) + H2O(g)* This is unbalanced as there are 4 ‘H’ on the left but only 2 ‘H’ on the right. This must be corrected by placing a ‘2’ in front of the ‘H2O’ so ther ...
Exam 1
... • make sure chemical equations are balanced and that the formulas for individual substances include an indication of state; for example, H2 (g); NaCl (s). ...
... • make sure chemical equations are balanced and that the formulas for individual substances include an indication of state; for example, H2 (g); NaCl (s). ...