Unit 1 - Red Deer Lake School
... -Chemical formulas and balancing -Diatomic molecules and binary compounds, how to name and write -Ionic compounds, how to name and show bonding -Chemical reactions, balancing equations -Exothermic vs Endothermic -Reaction rate and factors that affect it (catalyst, inhibitor, concentration, surface a ...
... -Chemical formulas and balancing -Diatomic molecules and binary compounds, how to name and write -Ionic compounds, how to name and show bonding -Chemical reactions, balancing equations -Exothermic vs Endothermic -Reaction rate and factors that affect it (catalyst, inhibitor, concentration, surface a ...
8.1 Classifying inorganic compounds
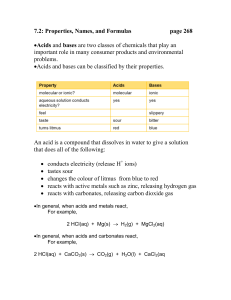
... Acidity is a measure of the relative amounts of H+ and OH- ions in solution (Table 4 p.205) – the higher the number of H+ ions in solution the more acidic it is (opposite is true for basic solutions). ...
... Acidity is a measure of the relative amounts of H+ and OH- ions in solution (Table 4 p.205) – the higher the number of H+ ions in solution the more acidic it is (opposite is true for basic solutions). ...
Title - Iowa State University
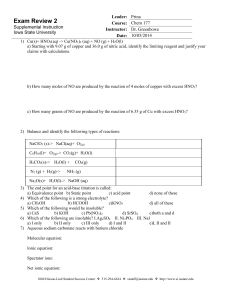
... b) HCOOH c)KNO3 d) all of these 5) Which of the following would be insoluble? a) CaS b) KOH c) Pb(NO3)2 d) SrSO4 e)both a and d 6) Which of the following are insoluble? I.Ag2SO4 II. Ni3PO4 III. NaI a) I only b) II only c) III only d) I and II ...
... b) HCOOH c)KNO3 d) all of these 5) Which of the following would be insoluble? a) CaS b) KOH c) Pb(NO3)2 d) SrSO4 e)both a and d 6) Which of the following are insoluble? I.Ag2SO4 II. Ni3PO4 III. NaI a) I only b) II only c) III only d) I and II ...
Acids and Bases
... It is useful to specify the amount of weak acid that has dissociated in achieving equilibrium in an aqueous solution. The percent dissociation is defined as follows: amount dissociated ( M ) % dissociation ...
... It is useful to specify the amount of weak acid that has dissociated in achieving equilibrium in an aqueous solution. The percent dissociation is defined as follows: amount dissociated ( M ) % dissociation ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... • Acids donate protons, i.e. provide H+(aq) or H3O+ (aq, hydronium) ions in water (Arrhenius). • Examples: acetic acid [CH3COOH] in vinegar, citrus acid [C5H8O5COOH] • in oranges, malic acid [C3H5O3COOH] is a sweetener, lactic acid [C2H5OCOOH] in milk, phosphoric acid in Coca-Cola, HCl in gastric ju ...
... • Acids donate protons, i.e. provide H+(aq) or H3O+ (aq, hydronium) ions in water (Arrhenius). • Examples: acetic acid [CH3COOH] in vinegar, citrus acid [C5H8O5COOH] • in oranges, malic acid [C3H5O3COOH] is a sweetener, lactic acid [C2H5OCOOH] in milk, phosphoric acid in Coca-Cola, HCl in gastric ju ...
Working with solutions
... hydrogen ion. (OH-) O A base is any substance that forms hydroxide ions in water. O A strong acid will produce more hydrogen ions than a weak one. O A strong base will produce more hydroxide ions than a weak one. ...
... hydrogen ion. (OH-) O A base is any substance that forms hydroxide ions in water. O A strong acid will produce more hydrogen ions than a weak one. O A strong base will produce more hydroxide ions than a weak one. ...
ACID AND BASES
... Neutralization The reaction between an acid and a base is called neutralization Acids are a source of H+ ions, hydrogen ions Bases are a source of OH- ions, hydroxide ions During neutralization these two ions combine to form water The products of neutralization are ALWAYS a salt and water ...
... Neutralization The reaction between an acid and a base is called neutralization Acids are a source of H+ ions, hydrogen ions Bases are a source of OH- ions, hydroxide ions During neutralization these two ions combine to form water The products of neutralization are ALWAYS a salt and water ...
Acid and Bases Notes
... For strong acids and bases, it is easy to determine their strength, using pH For weak acids and bases, it is a bit more complex to determine their strength and pH (we’re not going to worry about those) Acid and Base Strength for Strong Acids and Bases Strong acids and bases dissociate 100% (equilibr ...
... For strong acids and bases, it is easy to determine their strength, using pH For weak acids and bases, it is a bit more complex to determine their strength and pH (we’re not going to worry about those) Acid and Base Strength for Strong Acids and Bases Strong acids and bases dissociate 100% (equilibr ...
Document
... Exercise 2: Aqueous Equilibria of Acids and Bases The basic principles of acid/base equilibria are identical to those of general chemical equilibria. Because the topic of acid/base equilibrium is so central to the science of chemistry, it has its own unique terminology. Since the reactions of weak ...
... Exercise 2: Aqueous Equilibria of Acids and Bases The basic principles of acid/base equilibria are identical to those of general chemical equilibria. Because the topic of acid/base equilibrium is so central to the science of chemistry, it has its own unique terminology. Since the reactions of weak ...
Conjugate Acids and Bases
... Many reactions never result in complete conversion of reactants to products. They proceed to a state of chemical equilibrium in which the ratio of concentrations of reactants and products is constant. Equilibrium-constant expressions are algebraic equations that describe the concentration relationsh ...
... Many reactions never result in complete conversion of reactants to products. They proceed to a state of chemical equilibrium in which the ratio of concentrations of reactants and products is constant. Equilibrium-constant expressions are algebraic equations that describe the concentration relationsh ...
Acids and Bases Intr.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... theory, the hydronium ion explains the chemical properties of an acid, and the hydroxide ion explains the chemical properties of a base. • acid-base neutralization the hydronium ion from the acid reacts with the hydroxide ion from the base to produce water. H3O+(aq) + OH-(aq) → 2H2O(l) ...
... theory, the hydronium ion explains the chemical properties of an acid, and the hydroxide ion explains the chemical properties of a base. • acid-base neutralization the hydronium ion from the acid reacts with the hydroxide ion from the base to produce water. H3O+(aq) + OH-(aq) → 2H2O(l) ...
Chapter 3
... Important Definitions • Electrophiles- reagents which in their reactions seek extra electrons that will give them a stable valence shell. Electron deficient • Nucleophiles- reagents that seek a proton or some other positive center. Electron rich ...
... Important Definitions • Electrophiles- reagents which in their reactions seek extra electrons that will give them a stable valence shell. Electron deficient • Nucleophiles- reagents that seek a proton or some other positive center. Electron rich ...
Chapter 3
... Important Definitions • Electrophiles- reagents which in their reactions seek extra electrons that will give them a stable valence shell. Electron deficient • Nucleophiles- reagents that seek a proton or some other positive center. Electron rich ...
... Important Definitions • Electrophiles- reagents which in their reactions seek extra electrons that will give them a stable valence shell. Electron deficient • Nucleophiles- reagents that seek a proton or some other positive center. Electron rich ...
Chapters 14
... 4. Show the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base in following reactions: a) H2SO4 + Mg(OH)2 → MgSO4 + 2H2O ...
... 4. Show the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base in following reactions: a) H2SO4 + Mg(OH)2 → MgSO4 + 2H2O ...
II. Acids and Bases
... V. pH and pOH Therefore, the value of Kw is 1.0 x 10-14. This is also the product of [H+] and [OH-] for other solutions. 8. Because concentrations of H+ ions are often small numbers expressed in scientific notation, chemists adopted an easier way to express H+ ion concentration using a pH scale bas ...
... V. pH and pOH Therefore, the value of Kw is 1.0 x 10-14. This is also the product of [H+] and [OH-] for other solutions. 8. Because concentrations of H+ ions are often small numbers expressed in scientific notation, chemists adopted an easier way to express H+ ion concentration using a pH scale bas ...
Analysing Acids and Bases
... The base – is a proton (H+) acceptor An acid-base reaction involves two conjugate acid-base pairs. ...
... The base – is a proton (H+) acceptor An acid-base reaction involves two conjugate acid-base pairs. ...
Solute
... Aqueous solutions- water is the solvent due to hydrogen bonding Water = universal solvent because it can dissolve most things ...
... Aqueous solutions- water is the solvent due to hydrogen bonding Water = universal solvent because it can dissolve most things ...