Document
... III. Chromophores C. Substituent Effects General – Substituents may have any of four effects on a chromophore i. Bathochromic shift (red shift) – a shift to longer l; lower energy ...
... III. Chromophores C. Substituent Effects General – Substituents may have any of four effects on a chromophore i. Bathochromic shift (red shift) – a shift to longer l; lower energy ...
Chemistry 1110 – Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature
... containing one degree of unsaturation does not necessarily have to be unsaturated (you will learn more about this topic from your instructor in the classroom). A saturated compound is one that contains only single bonds while an unsaturated compound is one that contains at least one multiple bond; i ...
... containing one degree of unsaturation does not necessarily have to be unsaturated (you will learn more about this topic from your instructor in the classroom). A saturated compound is one that contains only single bonds while an unsaturated compound is one that contains at least one multiple bond; i ...
Workshop #1 Part 1. Organic Chemistry Nomenclature
... Alkyl halide = a hydrocarbon having at least one halide connected to a carbon atom. Alkene = a hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between carbon atoms. Alkyne = a hydrocarbon having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Alcohol = a hydrocarbon containing an “O-H” functional group c ...
... Alkyl halide = a hydrocarbon having at least one halide connected to a carbon atom. Alkene = a hydrocarbon having at least one double bond between carbon atoms. Alkyne = a hydrocarbon having at least one triple bond between carbon atoms. Alcohol = a hydrocarbon containing an “O-H” functional group c ...
Synthesis of hetero cyclic compounds pyrazole and pyridiazine from
... intermediates for synthesis of hetero cyclic compound and they have been reported to exhibit biological activity[1].The hydrazide is still used in many fields of chemical and biological as anti-TB or Tuberculosis materials[2],As well as the possibility of its transformation into a five non homogeneo ...
... intermediates for synthesis of hetero cyclic compound and they have been reported to exhibit biological activity[1].The hydrazide is still used in many fields of chemical and biological as anti-TB or Tuberculosis materials[2],As well as the possibility of its transformation into a five non homogeneo ...
Full Text - Iraqi National Journal of Chemistry
... intermediates for synthesis of hetero cyclic compound and they have been reported to exhibit biological activity[1].The hydrazide is still used in many fields of chemical and biological as anti-TB or Tuberculosis materials[2],As well as the possibility of its transformation into a five non homogeneo ...
... intermediates for synthesis of hetero cyclic compound and they have been reported to exhibit biological activity[1].The hydrazide is still used in many fields of chemical and biological as anti-TB or Tuberculosis materials[2],As well as the possibility of its transformation into a five non homogeneo ...
Document
... When noble gases are cooled sufficiently they will condense. This shows that there must be some forces acting between the atoms. These forces are called van der Waals' forces. The random motion of electrons around a nucleus produces a fluctuating dipole, which changes from one instant to the next. E ...
... When noble gases are cooled sufficiently they will condense. This shows that there must be some forces acting between the atoms. These forces are called van der Waals' forces. The random motion of electrons around a nucleus produces a fluctuating dipole, which changes from one instant to the next. E ...
Organometallic Organometallic Chemistry
... g to do with real life chemical transformations. Most of the 'fragments' mentioned above do not exist as such; they cannot be kept in a bottle. these formalisms are only used to predict stabilities or properties of compounds! ii. The 18-electron rule is just that - a rule, not a law. Many MT complex ...
... g to do with real life chemical transformations. Most of the 'fragments' mentioned above do not exist as such; they cannot be kept in a bottle. these formalisms are only used to predict stabilities or properties of compounds! ii. The 18-electron rule is just that - a rule, not a law. Many MT complex ...
Document
... (reagent) is Br2(g) or Br2(l) or Br2 in an organic solvent. (NB Salters includes catalysts in this ...
... (reagent) is Br2(g) or Br2(l) or Br2 in an organic solvent. (NB Salters includes catalysts in this ...
91391 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic
... Investigate and measure the chemical and physical properties of a range of groups of substances. Relate properties of matter to structure and bonding. Develop an understanding of and use the fundamental concepts of chemistry (for example, equilibrium and thermochemical principles) to interpret obser ...
... Investigate and measure the chemical and physical properties of a range of groups of substances. Relate properties of matter to structure and bonding. Develop an understanding of and use the fundamental concepts of chemistry (for example, equilibrium and thermochemical principles) to interpret obser ...
Monosaccharide
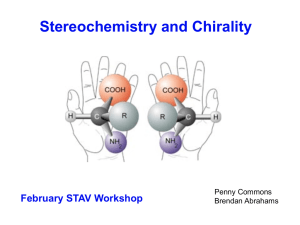
... • The D and L designations do not represent dextrorotatory and levorotatory. • The property of rotating the plane of polarized light is called optical activity, and the molecules with this property are said to be optically active. • Measurements of optical activity are useful for differentiating bet ...
... • The D and L designations do not represent dextrorotatory and levorotatory. • The property of rotating the plane of polarized light is called optical activity, and the molecules with this property are said to be optically active. • Measurements of optical activity are useful for differentiating bet ...
Document
... Like that of carbonyls As electron-withdrawing sigma-donating capacity decreases At the same time, the energy of the p-acceptor (sigma-*) on phosphorous is lowered in energy, providing an increase in backbonding ability. Therefore, range of each capabilities –tuning rough ordering -CO stretching fre ...
... Like that of carbonyls As electron-withdrawing sigma-donating capacity decreases At the same time, the energy of the p-acceptor (sigma-*) on phosphorous is lowered in energy, providing an increase in backbonding ability. Therefore, range of each capabilities –tuning rough ordering -CO stretching fre ...
Organometallic Chemistry
... Like that of carbonyls As electron-withdrawing sigma-donating capacity decreases At the same time, the energy of the p-acceptor (sigma-*) on phosphorous is lowered in energy, providing an increase in backbonding ability. Therefore, range of each capabilities –tuning rough ordering -CO stretching fre ...
... Like that of carbonyls As electron-withdrawing sigma-donating capacity decreases At the same time, the energy of the p-acceptor (sigma-*) on phosphorous is lowered in energy, providing an increase in backbonding ability. Therefore, range of each capabilities –tuning rough ordering -CO stretching fre ...
Chem1101 – Semester 1
... No two electrons in an atom may be in the same quantum state {i.e no 2 electrons can have the same 4 quantum numbers -‐ n, l, ml, ms} ...
... No two electrons in an atom may be in the same quantum state {i.e no 2 electrons can have the same 4 quantum numbers -‐ n, l, ml, ms} ...
Carbon Bond - Rutgers Chemistry
... industrial and synthetic organic chemical processes. Our initial finding of C-H oxidative addition reactions in low-valent iridium (I) complexes was followed by a more recent discovery and exploration of C-H activation processes at Ir (III) centers. This paper reviews recent studies of the Ir (III) ...
... industrial and synthetic organic chemical processes. Our initial finding of C-H oxidative addition reactions in low-valent iridium (I) complexes was followed by a more recent discovery and exploration of C-H activation processes at Ir (III) centers. This paper reviews recent studies of the Ir (III) ...
Cyclopropane CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 Cyclobutane CH 2 CH 2
... Chemical Ideas 12 Organic chemistry frameworks 12.1 Alkanes ...
... Chemical Ideas 12 Organic chemistry frameworks 12.1 Alkanes ...
Organic chemistry involves the study of the structures, properties
... a study of this subject helps one in solving problems systematically by digging into their causes and reasons to be able to find best solutions. Learning and organizing abilities will be developed to be able to relate and interpret ...
... a study of this subject helps one in solving problems systematically by digging into their causes and reasons to be able to find best solutions. Learning and organizing abilities will be developed to be able to relate and interpret ...
Aromaticity

In organic chemistry, the term aromaticity is formally used to describe an unusually stable nature of some flat rings of atoms. These structures contain a number of double bonds that interact with each other according to certain rules. As a result of their being so stable, such rings tend to form easily, and once formed, tend to be difficult to break in chemical reactions. Since one of the most commonly encountered aromatic system of compounds in organic chemistry is based on derivatives of the prototypical aromatic compound benzene (common in petroleum), the word “aromatic” is occasionally used to refer informally to benzene derivatives, and this is how it was first defined. Nevertheless, many non-benzene aromatic compounds exist. In living organisms, for example, the most common aromatic rings are the double-ringed bases in RNA and DNA.The earliest use of the term “aromatic” was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. Hofmann used the term for a class of benzene compounds, many of which do have odors (unlike pure saturated hydrocarbons). Today, there is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds, although in 1855, before the structure of benzene or organic compounds was understood, chemists like Hofmann were beginning to understand that odiferous molecules from plants, such as terpenes, had chemical properties we recognize today are similar to unsaturated petroleum hydrocarbons like benzene.In terms of the electronic nature of the molecule, aromaticity describes the way a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs of electrons, or empty molecular orbitals exhibit a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. Aromaticity can be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double-bonded to one another. These bonds may be seen as a hybrid of a single bond and a double bond, each bond in the ring identical to every other. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by August Kekulé (see History section below). The model for benzene consists of two resonance forms, which corresponds to the double and single bonds superimposing to produce six one-and-a-half bonds. Benzene is a more stable molecule than would be expected without accounting for charge delocalization.