Invariant selectivity of auditory neurons due to predictive coding
... Spectro-temporal receptive field (STRF) is the interpretation of auditory neurons as linear filters 1. We propose that auditory neurons are predictors rather than filters of their input and we hypothesize that they have a "true selectivity" independent of stimulus context 2. ...
... Spectro-temporal receptive field (STRF) is the interpretation of auditory neurons as linear filters 1. We propose that auditory neurons are predictors rather than filters of their input and we hypothesize that they have a "true selectivity" independent of stimulus context 2. ...
chapter 2- neuroscience genetics and behavior
... 1. EEG-ELECTROENCEPHLOGRAM-Amplified tracing of brain waves. 2. CT COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY-X-RAY PHOTOGRAPHYS THAT REVEAL BRAIN DAMAGE ...
... 1. EEG-ELECTROENCEPHLOGRAM-Amplified tracing of brain waves. 2. CT COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY-X-RAY PHOTOGRAPHYS THAT REVEAL BRAIN DAMAGE ...
Chapter 6 Chapter Review Questions Q2. This would be a
... c) Parasympathetic for eating food and Somatic for watching a movie d) Somatic ...
... c) Parasympathetic for eating food and Somatic for watching a movie d) Somatic ...
here - TurkoTek
... Nicotinic= nicotine; found in the autonomic ganglia- the receptors on the post-ganglionic. ---Autonomic postganglionic usually terminate on more than one cell. ---Usually autonomic responses are not located to a small area. ---Autonomic typically responds to Target Cells that are joined. ---Most tis ...
... Nicotinic= nicotine; found in the autonomic ganglia- the receptors on the post-ganglionic. ---Autonomic postganglionic usually terminate on more than one cell. ---Usually autonomic responses are not located to a small area. ---Autonomic typically responds to Target Cells that are joined. ---Most tis ...
Graduate School Systems Neuroscience, MEDS 5371 2011 BASAL
... Subthalamic Nucleus: is a lens-shaped nucleus, between diencephalon and mesencephalon. When lesioned the patient experience uncontrolled whole body movement- hemiballismus. Subthalamic nucleus sends excitatory impulses to Substantia Nigra and Internal Globus Pallidus, both of which are inhibitory t ...
... Subthalamic Nucleus: is a lens-shaped nucleus, between diencephalon and mesencephalon. When lesioned the patient experience uncontrolled whole body movement- hemiballismus. Subthalamic nucleus sends excitatory impulses to Substantia Nigra and Internal Globus Pallidus, both of which are inhibitory t ...
File - Lucinda Supernavage
... Ions in the cell and outside the cell create a positive and negative side, which produces an electric current. ...
... Ions in the cell and outside the cell create a positive and negative side, which produces an electric current. ...
Auditory information processing at the cortical level
... The most clear-cut parameter along which this organisation has been observed is the characteristic frequency of the nerve cells. Those neurons are sharply selective to one frequency of stimulation tend to the same characteristic frequency if they lie within the same column The nerve cells of the aud ...
... The most clear-cut parameter along which this organisation has been observed is the characteristic frequency of the nerve cells. Those neurons are sharply selective to one frequency of stimulation tend to the same characteristic frequency if they lie within the same column The nerve cells of the aud ...
BOX 42.2 WHY BRAIN SIZE IS IMPORTANT Larger brains are
... dendrites would be longer, unless the thickness of the axons and dendrites were increased with the added length (Bekkers & Stevens, 1970). Thus, larger brains would have larger neurons with longer, thicker axons and dendrites. This suggests that brains would reach a maximum size, perhaps not much la ...
... dendrites would be longer, unless the thickness of the axons and dendrites were increased with the added length (Bekkers & Stevens, 1970). Thus, larger brains would have larger neurons with longer, thicker axons and dendrites. This suggests that brains would reach a maximum size, perhaps not much la ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint Outline
... Voltage in cell goes from negative (-70 mV) to slightly positive (+30 – 40 mV) when neuron fires (1 – 2 milliseconds) Cell firing followed by refractory (‘recovery’) period (1 – 2 milliseconds) before returning to resting potential Entire action potential process takes an approximate average o ...
... Voltage in cell goes from negative (-70 mV) to slightly positive (+30 – 40 mV) when neuron fires (1 – 2 milliseconds) Cell firing followed by refractory (‘recovery’) period (1 – 2 milliseconds) before returning to resting potential Entire action potential process takes an approximate average o ...
Sample Prelab Assignment - Neurobiology Laboratory
... BIO365L – Neurobiology Laboratory [ from http://www.BIO365L.net] Sample Prelab for Module 3 There are two types of synapses in the brain, electrical and chemical synapses. In this lab, we will study chemical synapses by examining excitatory post synaptic potentials which are caused by the openi ...
... BIO365L – Neurobiology Laboratory [ from http://www.BIO365L.net] Sample Prelab for Module 3 There are two types of synapses in the brain, electrical and chemical synapses. In this lab, we will study chemical synapses by examining excitatory post synaptic potentials which are caused by the openi ...
Differential Permeability of the Membrane
... travels along an axon at a constant strength, no matter how far it must travel. It is slower then a straight electrical impulse, but has the advantage of maintaining it’s strength no matter how far it must travel. ...
... travels along an axon at a constant strength, no matter how far it must travel. It is slower then a straight electrical impulse, but has the advantage of maintaining it’s strength no matter how far it must travel. ...
Motor control
... generators - seem to provide the ability for simple sets of coordinated actions. • It is possible, then, that more complex actions are simply combinations or modifications of central pattern generators. ...
... generators - seem to provide the ability for simple sets of coordinated actions. • It is possible, then, that more complex actions are simply combinations or modifications of central pattern generators. ...
Here we can focus directly on the input neurons, the Schaffer
... pyramidal cells. We now see on the right hand side this is the whole synaptic cell, notice we are now focusing on the post-synaptic cell. The early change for explicit memory storage is going to have a pull synaptic target rather than a p synaptic target. The Schaffer collaterals come in, they re ...
... pyramidal cells. We now see on the right hand side this is the whole synaptic cell, notice we are now focusing on the post-synaptic cell. The early change for explicit memory storage is going to have a pull synaptic target rather than a p synaptic target. The Schaffer collaterals come in, they re ...
Presynaptic Questions
... glutamine (glutamine synthetase) The glutamine is then transferred back to the pre-synaptic nerve ending where it is used to produce new GABA What enzymes are involved in the degradative metabolism of catecholamines? Monoamine oxidase and catechol-o-methyltransferase Catecholamines can be further de ...
... glutamine (glutamine synthetase) The glutamine is then transferred back to the pre-synaptic nerve ending where it is used to produce new GABA What enzymes are involved in the degradative metabolism of catecholamines? Monoamine oxidase and catechol-o-methyltransferase Catecholamines can be further de ...
The human brain is a 3 pound mass of fatty tissue that controls all
... Huntington’s disease, GABA producing neurons in the basal ganglia die, causing uncontrollable movements. The activity of GABA is increased by drugs like Valium, which results in increased inhibition of neurons in the brain. Dopamine: Patients with Parkinson’s disease exhibit a deficiency of this neu ...
... Huntington’s disease, GABA producing neurons in the basal ganglia die, causing uncontrollable movements. The activity of GABA is increased by drugs like Valium, which results in increased inhibition of neurons in the brain. Dopamine: Patients with Parkinson’s disease exhibit a deficiency of this neu ...
17- The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
... one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron. This space between neurons is called the synapse. The synapse is a junction or connection between the neurons. A neuron transmits its impulses or message to another neuron across thesynapse by releasing chemicals called neurotransmitters. These neurotr ...
... one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron. This space between neurons is called the synapse. The synapse is a junction or connection between the neurons. A neuron transmits its impulses or message to another neuron across thesynapse by releasing chemicals called neurotransmitters. These neurotr ...
Readings to Accompany “Nerves” Worksheet (adapted from France
... To understand how impulses are carried along nerves or throughout a muscle to cause contraction, we need to learn a little more about membrane excitability. Nerves transmit impulses by movement of electrically charged particles. Neurons have a membrane that separates the cytoplasm inside from the ex ...
... To understand how impulses are carried along nerves or throughout a muscle to cause contraction, we need to learn a little more about membrane excitability. Nerves transmit impulses by movement of electrically charged particles. Neurons have a membrane that separates the cytoplasm inside from the ex ...
Nervous System Test Review After you accidentally touch a hot pan
... 1. After you accidentally touch a hot pan, you immediately jerk your hand away without thinking about your action, and before you even feel the pain of the burn. What type of response is the known as? a. Reflex 2. In order for a nerve impulse to pass from an axon tip to the next structure, it must c ...
... 1. After you accidentally touch a hot pan, you immediately jerk your hand away without thinking about your action, and before you even feel the pain of the burn. What type of response is the known as? a. Reflex 2. In order for a nerve impulse to pass from an axon tip to the next structure, it must c ...
Chapter 5: The First Two Years
... synapses • During the first months and years, major spurts of growth and refinement in axons, dendrites, and synapses occur (connections are being made) • Transient Exuberance is the great increase in the number of dendrites that occurs in an infant’s brain over 1st 2 years of life • Enables neurons ...
... synapses • During the first months and years, major spurts of growth and refinement in axons, dendrites, and synapses occur (connections are being made) • Transient Exuberance is the great increase in the number of dendrites that occurs in an infant’s brain over 1st 2 years of life • Enables neurons ...
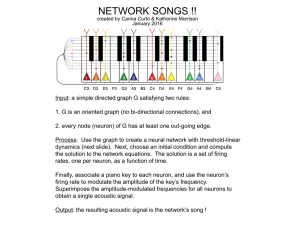
network songs - Personal.psu.edu
... 1. G is an oriented graph (no bi-directional connections), and 2. every node (neuron) of G has at least one out-going edge. Process: Use the graph to create a neural network with threshold-linear dynamics (next slide). Next, choose an initial condition and compute the solution to the network equatio ...
... 1. G is an oriented graph (no bi-directional connections), and 2. every node (neuron) of G has at least one out-going edge. Process: Use the graph to create a neural network with threshold-linear dynamics (next slide). Next, choose an initial condition and compute the solution to the network equatio ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.