Modeling cortical maps with Topographica
... a review of this class of models, see [12].) However, the models to date have been limited in size and scope because existing simulation tools do not provide specific support for biologically realistic, densely interconnected topographic maps. Existing biological neural simulators, such as NEURON [7 ...
... a review of this class of models, see [12].) However, the models to date have been limited in size and scope because existing simulation tools do not provide specific support for biologically realistic, densely interconnected topographic maps. Existing biological neural simulators, such as NEURON [7 ...
48_Lectures_PPT
... • The vast majority of synapses are chemical synapses • In a chemical synapse, a presynaptic neuron releases chemical neurotransmitters stored in the synaptic terminal ...
... • The vast majority of synapses are chemical synapses • In a chemical synapse, a presynaptic neuron releases chemical neurotransmitters stored in the synaptic terminal ...
The Neural Basis of Addiction: A Pathology of Motivation and Choice
... of motivated behavior involves defining the neural substrates that 1) attach sufficient importance (salience) to an integrated stimulus that behavior is “activated” and 2) “direct” this state of activation toward a specific behavioral response. While we have made substantial progress toward identify ...
... of motivated behavior involves defining the neural substrates that 1) attach sufficient importance (salience) to an integrated stimulus that behavior is “activated” and 2) “direct” this state of activation toward a specific behavioral response. While we have made substantial progress toward identify ...
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
... o At each position along the axon, the process is identical, such that the shape and magnitude of the action potential remain constant. Immediately behind the traveling zone of depolarization due to Na+ inflow is a zone of repolarization due to K+ outflow. In the repolarized zone, the Na+ channels r ...
... o At each position along the axon, the process is identical, such that the shape and magnitude of the action potential remain constant. Immediately behind the traveling zone of depolarization due to Na+ inflow is a zone of repolarization due to K+ outflow. In the repolarized zone, the Na+ channels r ...
View PDF - CiteSeerX
... of motivated behavior involves defining the neural substrates that 1) attach sufficient importance (salience) to an integrated stimulus that behavior is “activated” and 2) “direct” this state of activation toward a specific behavioral response. While we have made substantial progress toward identify ...
... of motivated behavior involves defining the neural substrates that 1) attach sufficient importance (salience) to an integrated stimulus that behavior is “activated” and 2) “direct” this state of activation toward a specific behavioral response. While we have made substantial progress toward identify ...
chapter 3: biological psychology
... _____3. Chemicals that resemble opiate drugs in structure and that are involved in feelings of pain and pleasure. _____4. A neurotransmitter for which abnormal levels have been implicated in schizophrenia. _____5. The only neurotransmitter between motor neurons and voluntary muscles. ...
... _____3. Chemicals that resemble opiate drugs in structure and that are involved in feelings of pain and pleasure. _____4. A neurotransmitter for which abnormal levels have been implicated in schizophrenia. _____5. The only neurotransmitter between motor neurons and voluntary muscles. ...
Motor System & Behavior
... Here are the basal ganglia nuclei laid out for clarity. Let’s suppose Pallidus ...
... Here are the basal ganglia nuclei laid out for clarity. Let’s suppose Pallidus ...
m5zn_e06294c55d2e0eb
... The lumbar and sacral plexuses are found at the root of the lower limbs. ...
... The lumbar and sacral plexuses are found at the root of the lower limbs. ...
Tongue: Herpes Simplex Glossitis
... At this power it is easier to see the blood vessel with the perivascular hemorrhage and lymphocytic cuffing (1). In addition, the areas of edema and loss of neutrophil (2) can be better appreciated. Red shrunken neurons and glia with pyknotic nuclei (3) are also ...
... At this power it is easier to see the blood vessel with the perivascular hemorrhage and lymphocytic cuffing (1). In addition, the areas of edema and loss of neutrophil (2) can be better appreciated. Red shrunken neurons and glia with pyknotic nuclei (3) are also ...
Notes on Learning to Compute and Computing to Learn
... interact and intermingle to manifest as unities at a certain level of description: these unities include objects, events, concepts and emotions. The unities are dynamic in that they move, appear and disappear. The system that deals with each of these apparently independent modalities, the human nerv ...
... interact and intermingle to manifest as unities at a certain level of description: these unities include objects, events, concepts and emotions. The unities are dynamic in that they move, appear and disappear. The system that deals with each of these apparently independent modalities, the human nerv ...
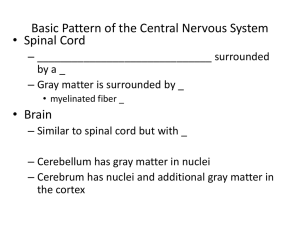
Basic Pattern of the Central Nervous System
... occipital lobes • Found in one hemisphere, _ • Integrates incoming signals _ • Involved in processing spatial relationships ...
... occipital lobes • Found in one hemisphere, _ • Integrates incoming signals _ • Involved in processing spatial relationships ...
大腦神經解剖與建置
... Incoming information from all the senses is sorted in the thalamus 視丘 and sent to the appropriate cerebral centers for further processing. Through the hypthalamus 下視丘 control of the pituitary gland 腦下垂 體, it regulates hunger and thirst, plays a role in sexual and mating behavior, and controls the fi ...
... Incoming information from all the senses is sorted in the thalamus 視丘 and sent to the appropriate cerebral centers for further processing. Through the hypthalamus 下視丘 control of the pituitary gland 腦下垂 體, it regulates hunger and thirst, plays a role in sexual and mating behavior, and controls the fi ...
BHG025.CHP:Corel VENTURA
... corticogenesis, populations of cells undergo long-range somal translocation from the VZ to their positions beneath the pial surface. These cells typically showed distinct morphological features with long radially oriented leading process terminating at the pial surface and a transient short trailing ...
... corticogenesis, populations of cells undergo long-range somal translocation from the VZ to their positions beneath the pial surface. These cells typically showed distinct morphological features with long radially oriented leading process terminating at the pial surface and a transient short trailing ...
Dopamine Neurons Mediate a Fast Excitatory Signal
... events. Local superfusion of the ventral tegmental area with the D2 agonist quinpirole, which should increase the threshold for dopamine neuron activation, inhibited the early response. So dopamine neurons make glutamatergic synaptic connections to accumbens neurons. We propose that dopamine neuron ...
... events. Local superfusion of the ventral tegmental area with the D2 agonist quinpirole, which should increase the threshold for dopamine neuron activation, inhibited the early response. So dopamine neurons make glutamatergic synaptic connections to accumbens neurons. We propose that dopamine neuron ...
Slide 1
... locus cerulus - axons projecting to limbic areas and spinal cord Lateral tegmental area – projections to forebrain regions •Cortical projections – arousal and alert state •Limbic projections - drive , motivation , mood and response ...
... locus cerulus - axons projecting to limbic areas and spinal cord Lateral tegmental area – projections to forebrain regions •Cortical projections – arousal and alert state •Limbic projections - drive , motivation , mood and response ...
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord PNS consists of nerves CNS
... Five lobes Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Insula ...
... Five lobes Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Insula ...
Lecture Outline
... Voltage-gated channels shape the action potential in a series of stages: 1. At the resting potential, most voltage-gated Na+ channels are closed. Some K+ channels are open, but most voltage-gated K+ channels are closed. 2. When a stimulus depolarizes the membrane, some gated Na+ channels open, allow ...
... Voltage-gated channels shape the action potential in a series of stages: 1. At the resting potential, most voltage-gated Na+ channels are closed. Some K+ channels are open, but most voltage-gated K+ channels are closed. 2. When a stimulus depolarizes the membrane, some gated Na+ channels open, allow ...
A visual processing task: Retina and V1
... from the fovea. Except for the ganglion cells, which have as one of their tasks to send the signal to the thalamus, the neurons in the retina do not spike. Instead, the neurons use their graded membrane potential and neurotransmitter is released all the time with a rate that is a function of the mem ...
... from the fovea. Except for the ganglion cells, which have as one of their tasks to send the signal to the thalamus, the neurons in the retina do not spike. Instead, the neurons use their graded membrane potential and neurotransmitter is released all the time with a rate that is a function of the mem ...
A1981ME66900001
... smaller than those of the 'fast' axon in accessible muscle fibers, a group of less accessible fibers showed the reverse pattern: much larger electrical events during stimulation of the 'slow' axon. These muscle fibers had distinctive membrane electrical properties 2 and were physiologically speciali ...
... smaller than those of the 'fast' axon in accessible muscle fibers, a group of less accessible fibers showed the reverse pattern: much larger electrical events during stimulation of the 'slow' axon. These muscle fibers had distinctive membrane electrical properties 2 and were physiologically speciali ...
Slide 1
... intestine with many features similar to humans • More than 10,000 worms can grow on a single petri dish reproducing rapidly (from egg to mature animal in 3.5 days) • Nobel Prize 2002 to S. Brenner, H. R. Horvitz and J. Sulston on their work of organ development and apoptosis in C. elegans • Nobel Pr ...
... intestine with many features similar to humans • More than 10,000 worms can grow on a single petri dish reproducing rapidly (from egg to mature animal in 3.5 days) • Nobel Prize 2002 to S. Brenner, H. R. Horvitz and J. Sulston on their work of organ development and apoptosis in C. elegans • Nobel Pr ...
Module Four: The Brain
... - Protects brain cells from harmful substances and pathogens o Regulates what substances can move from the bloodstream into the interstitial fluid of the brain - Selectively permeable barrier formed by tight junctions that seal together the endothelial cells of brain capillaries o Permeable to liq ...
... - Protects brain cells from harmful substances and pathogens o Regulates what substances can move from the bloodstream into the interstitial fluid of the brain - Selectively permeable barrier formed by tight junctions that seal together the endothelial cells of brain capillaries o Permeable to liq ...
Unlocking the Brain`s Deepest Secrets
... are reinforced, proteins within the neurons are activated to boost the signal at that particular synapse, and what we’ve learned becomes committed to memory. “We still don’t understand how we maintain memories for a lifetime.” But existing theories have a few loose ends. For one, the proteins respon ...
... are reinforced, proteins within the neurons are activated to boost the signal at that particular synapse, and what we’ve learned becomes committed to memory. “We still don’t understand how we maintain memories for a lifetime.” But existing theories have a few loose ends. For one, the proteins respon ...
Nick Gentile
... – “Each connection has associated with it a numerical weight. Each neuron's output is a single numerical activity which is computed as a monotonic function of the sum of the products of the activity of the input neurons with their corresponding connection weights.“ ...
... – “Each connection has associated with it a numerical weight. Each neuron's output is a single numerical activity which is computed as a monotonic function of the sum of the products of the activity of the input neurons with their corresponding connection weights.“ ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.