Sample Chapter
... potassium gates. These gates represent the only way that these ions can pass through the nerve cell membrane. In a resting nerve cell membrane, all the sodium gates are closed and some of the potassium gates are open. As a result, sodium cannot diffuse through the membrane and largely remains outsid ...
... potassium gates. These gates represent the only way that these ions can pass through the nerve cell membrane. In a resting nerve cell membrane, all the sodium gates are closed and some of the potassium gates are open. As a result, sodium cannot diffuse through the membrane and largely remains outsid ...
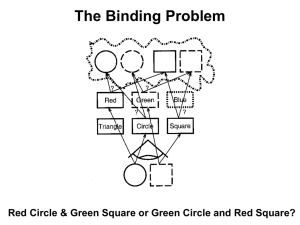
Optional extra slides on the Binding Problem
... Human electrophysiological evidence: Greater fronto-central gamma-range spectral power to attended than unattended auditory stimuli. Tiitinen, Sinkkonen, Reinikainen, Alho, Lavikainen, and Naatanen (1993) ...
... Human electrophysiological evidence: Greater fronto-central gamma-range spectral power to attended than unattended auditory stimuli. Tiitinen, Sinkkonen, Reinikainen, Alho, Lavikainen, and Naatanen (1993) ...
The Special Senses and Functional Aspects of the Nervous System
... Thought- What is a thought and how is it produced? A thought is a conscious understanding in the brain of image or language or words. It is the result of billions of exchanges of neurotransmitters across billions of synapses and the conductions of millions of impulses through millions of neurons. Th ...
... Thought- What is a thought and how is it produced? A thought is a conscious understanding in the brain of image or language or words. It is the result of billions of exchanges of neurotransmitters across billions of synapses and the conductions of millions of impulses through millions of neurons. Th ...
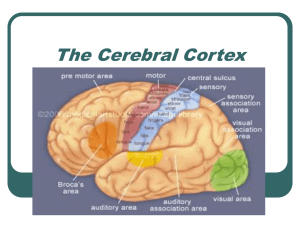
The Cerebral Cortex
... Sensory cortex (strip) lies within the parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s association areas work with the sensory cortex to process sensory signals for accurate perception. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it (lips, fingers…) ...
... Sensory cortex (strip) lies within the parietal lobe & therefore this lobe’s association areas work with the sensory cortex to process sensory signals for accurate perception. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex devoted to it (lips, fingers…) ...
No Slide Title - Computer Science Home
... neural net can identify input vectors that are sufficiently close to (but not necessary the same as the input ...
... neural net can identify input vectors that are sufficiently close to (but not necessary the same as the input ...
Parietal cortex neurons of the monkey related to the visual guidance
... recordings, we assumed that the difference in cell activity between the two conditions was likely to be due to some visual input received by these cells. Therefore, we called this type of cells "visual and motor" neurons. More than half of this group of cells tested (18/34) was activated by the fixa ...
... recordings, we assumed that the difference in cell activity between the two conditions was likely to be due to some visual input received by these cells. Therefore, we called this type of cells "visual and motor" neurons. More than half of this group of cells tested (18/34) was activated by the fixa ...
Transformation from temporal to rate coding in a somatosensory
... (below the natural whisking range), latencies at all stations barely changed between the ®rst stimulus cycles (left insets) and the steady-state periods (centre PSTHs). With stimulation frequencies of 5 and 8 Hz (both of which are within the whisking frequency range12), brainstem and lemniscal laten ...
... (below the natural whisking range), latencies at all stations barely changed between the ®rst stimulus cycles (left insets) and the steady-state periods (centre PSTHs). With stimulation frequencies of 5 and 8 Hz (both of which are within the whisking frequency range12), brainstem and lemniscal laten ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • Concerned with the innervation and control of visceral organs, smooth muscles and glands • Along with the endocrine system, its primary function is homeostasis of the internal environment • The majority of the activities of the autonomic system do not impinge on consciousness • The control exerted ...
... • Concerned with the innervation and control of visceral organs, smooth muscles and glands • Along with the endocrine system, its primary function is homeostasis of the internal environment • The majority of the activities of the autonomic system do not impinge on consciousness • The control exerted ...
Layer-Specific Markers as Probes for Neuron Type Identity in
... cerebral cortex contains 2 main classes of neurons, pyramidal and nonpyramidal neurons, which both encompass multiple distinct types. Pyramidal neurons are the more abundant class, accounting for 75% to 85% of cortical neurons, whereas nonpyramidal neurons account for 15% to 25% (34, 35). Neurons of ...
... cerebral cortex contains 2 main classes of neurons, pyramidal and nonpyramidal neurons, which both encompass multiple distinct types. Pyramidal neurons are the more abundant class, accounting for 75% to 85% of cortical neurons, whereas nonpyramidal neurons account for 15% to 25% (34, 35). Neurons of ...
BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH
... that mediated by P2X4 receptors, in brain areas related to the rewarding and reinforcing properties of alcohol. My portion of the project involves the investigation of the interaction of ATP and ethanol in mice, either wild-type mice, or KO mice, with and without dysfunction of the P2X4 receptor by ...
... that mediated by P2X4 receptors, in brain areas related to the rewarding and reinforcing properties of alcohol. My portion of the project involves the investigation of the interaction of ATP and ethanol in mice, either wild-type mice, or KO mice, with and without dysfunction of the P2X4 receptor by ...
Slide ()
... Organization of the anterior and posterior pituitary gland. Hypothalamic neurons in the supraoptic (SON) and paraventricular (PVN) nuclei synthesize arginine vasopressin (AVP) or oxytocin (OXY). Most of their axons project directly to the posterior pituitary, from which AVP and OXY are secreted into ...
... Organization of the anterior and posterior pituitary gland. Hypothalamic neurons in the supraoptic (SON) and paraventricular (PVN) nuclei synthesize arginine vasopressin (AVP) or oxytocin (OXY). Most of their axons project directly to the posterior pituitary, from which AVP and OXY are secreted into ...
MS Word Version
... autonomic nervous system act indirectly. • Norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and serotonin, another central nervous system neurotransmitter, all produce state changes in the central nervous system. One important example is the change from the sleep state, to wakefulness, to attentive arousal. • Theorie ...
... autonomic nervous system act indirectly. • Norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and serotonin, another central nervous system neurotransmitter, all produce state changes in the central nervous system. One important example is the change from the sleep state, to wakefulness, to attentive arousal. • Theorie ...
Slide - Reza Shadmehr
... Split brain patients A small number of individuals have had their corpus callosum sectioned to relieve intractable epilepsy. ...
... Split brain patients A small number of individuals have had their corpus callosum sectioned to relieve intractable epilepsy. ...
Document
... Location: They serve as the sensory neurons within the retina, olfactory, auditory systems. ...
... Location: They serve as the sensory neurons within the retina, olfactory, auditory systems. ...
Brain Anatomy “Science erases what was previously true.”
... negative events, like a punishment out of the blue, or the absence of an expected reward. It is part of the “disappointment circuit.” It lacks an opposing set of neuronal inputs. Antidepressants are active here, and may correct the negative bias present in ...
... negative events, like a punishment out of the blue, or the absence of an expected reward. It is part of the “disappointment circuit.” It lacks an opposing set of neuronal inputs. Antidepressants are active here, and may correct the negative bias present in ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... autonomic nervous system act indirectly. • Norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and serotonin, another central nervous system neurotransmitter, all produce state changes in the central nervous system. One important example is the change from the sleep state, to wakefulness, to attentive arousal. • Theorie ...
... autonomic nervous system act indirectly. • Norepinephrine, acetylcholine, and serotonin, another central nervous system neurotransmitter, all produce state changes in the central nervous system. One important example is the change from the sleep state, to wakefulness, to attentive arousal. • Theorie ...
Abstract Browser - The Journal of Neuroscience
... therefore important to individuals’ normal social functioning. Previous neuroimaging studies have highlighted the involvement of the insular and ventromedial prefrontal (vmPFC) cortices in representing norms. However, the necessity and dissociability of their involvement remain unclear. Using model- ...
... therefore important to individuals’ normal social functioning. Previous neuroimaging studies have highlighted the involvement of the insular and ventromedial prefrontal (vmPFC) cortices in representing norms. However, the necessity and dissociability of their involvement remain unclear. Using model- ...
chapt07_lecture
... a) An active process needed to move organelles and proteins from the cell body to axon terminals b) Fast component moves membranous vesicles c) Slow components move microfilaments, microtubules, and proteins d) Anterograde transport – from cell body to dendrites and axon; uses kinesin molecular moto ...
... a) An active process needed to move organelles and proteins from the cell body to axon terminals b) Fast component moves membranous vesicles c) Slow components move microfilaments, microtubules, and proteins d) Anterograde transport – from cell body to dendrites and axon; uses kinesin molecular moto ...
Genetic analysis of dopaminergic system development in zebrafish
... telencephalon. It appears that local patterning of the dorsoventral and anterioposterior axis of the CNS may generate a ‘‘prepattern’’, which in combination with different local signals serves to specify neural cells to take on a dopaminergic fate. As such, the regulatory inputs which control DA dif ...
... telencephalon. It appears that local patterning of the dorsoventral and anterioposterior axis of the CNS may generate a ‘‘prepattern’’, which in combination with different local signals serves to specify neural cells to take on a dopaminergic fate. As such, the regulatory inputs which control DA dif ...
Prediction on Soccer Matches using Multi
... the change of strategies used in the game that does not work as planned, such as where the opposition team playing in a defensive manner resulting in a draw instead of a win for the home team. Finally, luck may come into play, where a highly favored team will be shocked by the opposition team. ...
... the change of strategies used in the game that does not work as planned, such as where the opposition team playing in a defensive manner resulting in a draw instead of a win for the home team. Finally, luck may come into play, where a highly favored team will be shocked by the opposition team. ...
Unsupervised Learning
... The winning node is commonly known as the Best Matching Unit (BMU). The radius of the neighbourhood of the BMU is now calculated. This is a value that starts large, typically set to the 'radius' of the lattice, but diminishes each time-step. Any nodes found within this radius are deemed to be inside ...
... The winning node is commonly known as the Best Matching Unit (BMU). The radius of the neighbourhood of the BMU is now calculated. This is a value that starts large, typically set to the 'radius' of the lattice, but diminishes each time-step. Any nodes found within this radius are deemed to be inside ...
Memory Intro - Walker Bioscience
... long-lasting change in the postsynaptic response by electrically stimulating neural pathways, rather than by having the animals actually learn something, they realized that they had identified a mechanism that might be able to translate neural activity generated by environmental stimuli into changes ...
... long-lasting change in the postsynaptic response by electrically stimulating neural pathways, rather than by having the animals actually learn something, they realized that they had identified a mechanism that might be able to translate neural activity generated by environmental stimuli into changes ...
firing pattern modulation by oscillatory input in
... wave injection current was superimposed upon a steady-state depolarizing o¡set. In six neurons the magnitude of this depolarization was systematically varied resulting in a response progression similar to those described above (see Fig. 4D^F). In Fig. 4D^F the amplitude and frequency of the sine wav ...
... wave injection current was superimposed upon a steady-state depolarizing o¡set. In six neurons the magnitude of this depolarization was systematically varied resulting in a response progression similar to those described above (see Fig. 4D^F). In Fig. 4D^F the amplitude and frequency of the sine wav ...
Modeling cortical maps with Topographica
... a review of this class of models, see [12].) However, the models to date have been limited in size and scope because existing simulation tools do not provide specific support for biologically realistic, densely interconnected topographic maps. Existing biological neural simulators, such as NEURON [7 ...
... a review of this class of models, see [12].) However, the models to date have been limited in size and scope because existing simulation tools do not provide specific support for biologically realistic, densely interconnected topographic maps. Existing biological neural simulators, such as NEURON [7 ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.