The NTVA framework: Linking Cognition and Neuroscience
... Desimone, 1985). This effect is readily explained by NTVA's concept of filtering based on attentional weights. A second frequently observed effect of attention is a modest change in firing rates with a single stimulus in the receptive field. This finding can be explained by the pigeonholing mechanis ...
... Desimone, 1985). This effect is readily explained by NTVA's concept of filtering based on attentional weights. A second frequently observed effect of attention is a modest change in firing rates with a single stimulus in the receptive field. This finding can be explained by the pigeonholing mechanis ...
Lecture 6: Single neuron models
... somehow carry information through the brain: each spike would represent a binary 1 each lack of spike would represent a binary 0 They showed how spikes could be combined to do logical and arithmetical operations From modern perspective there is a design problem for these circuit elements: brevity of ...
... somehow carry information through the brain: each spike would represent a binary 1 each lack of spike would represent a binary 0 They showed how spikes could be combined to do logical and arithmetical operations From modern perspective there is a design problem for these circuit elements: brevity of ...
Functional and Dysfunctional Aspects of the Cerebral Cortex
... number of interneuronal connections or synapses. Morphologically speaking, a typical neuron presents three functional domains. These are the cell body or “soma” containing the nucleus and all major cytoplasmic organelles, a single axon, which extends away from the soma and has cable-like properties, ...
... number of interneuronal connections or synapses. Morphologically speaking, a typical neuron presents three functional domains. These are the cell body or “soma” containing the nucleus and all major cytoplasmic organelles, a single axon, which extends away from the soma and has cable-like properties, ...
Biomorphic Circuits and Systems: Control of Robotic and Prosthetic Limbs
... Nervous System (CNS), from supraspinal commands dictated by the brain to sensory information coming from the limbs. What the higher levels of the CNS and the sensory information can do, however, is modulate these rhythmic signals in order to ...
... Nervous System (CNS), from supraspinal commands dictated by the brain to sensory information coming from the limbs. What the higher levels of the CNS and the sensory information can do, however, is modulate these rhythmic signals in order to ...
The mirror system hypothesis
... actions. However, as we saw earlier, only humans have “complex imitation”, the ability to imitate sequences of behaviors and approximate novel actions as variants of known actions after one or just a few viewings of this novel behavior. As backdrop for our own work, we draw some important lessons fr ...
... actions. However, as we saw earlier, only humans have “complex imitation”, the ability to imitate sequences of behaviors and approximate novel actions as variants of known actions after one or just a few viewings of this novel behavior. As backdrop for our own work, we draw some important lessons fr ...
the mirror system hypothesis: from a macaque
... S2: A mirror system for grasping, shared with the common ancestor of human and monkey. S3: A system for simple imitation of grasping shared with the common ancestor of human and chimpanzee. The next 3 stages distinguish the hominid line from that of the great apes: S4: A complex imitation system for ...
... S2: A mirror system for grasping, shared with the common ancestor of human and monkey. S3: A system for simple imitation of grasping shared with the common ancestor of human and chimpanzee. The next 3 stages distinguish the hominid line from that of the great apes: S4: A complex imitation system for ...
THE MIRROR SYSTEM HYPOTHESIS: FROM A MACAQUE
... S2: A mirror system for grasping, shared with the common ancestor of human and monkey. S3: A system for simple imitation of grasping shared with the common ancestor of human and chimpanzee. The next 3 stages distinguish the hominid line from that of the great apes: S4: A complex imitation system for ...
... S2: A mirror system for grasping, shared with the common ancestor of human and monkey. S3: A system for simple imitation of grasping shared with the common ancestor of human and chimpanzee. The next 3 stages distinguish the hominid line from that of the great apes: S4: A complex imitation system for ...
Chapter 54: The Nervous System
... Are Pollutants Affecting the Sexual Development of Florida’s Alligators? Alligators are among the most interesting of animals for a biologist to study. Their ecology is closely tied to the environment, and their reptilian biology offers an interesting contrast to that of mammals like ourselves. Stud ...
... Are Pollutants Affecting the Sexual Development of Florida’s Alligators? Alligators are among the most interesting of animals for a biologist to study. Their ecology is closely tied to the environment, and their reptilian biology offers an interesting contrast to that of mammals like ourselves. Stud ...
Neurons - LPS.org
... on any single neuron), a very small, fluid-filled gap called a synapse exists that action potentials cannot jump. At this point, chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters continue the job and carry the information across the gap. When an action potential works its way to the end of a neuron, it ...
... on any single neuron), a very small, fluid-filled gap called a synapse exists that action potentials cannot jump. At this point, chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters continue the job and carry the information across the gap. When an action potential works its way to the end of a neuron, it ...
YG013807812
... possible non-invasive interface, mainly due to its acceptable temporal, comfort of usage, portability and low set-up cost. When technology's vulnerability to noise, additional considerable barrier to using EEG as a braincomputer interface is the wide exercise required before users can work the techn ...
... possible non-invasive interface, mainly due to its acceptable temporal, comfort of usage, portability and low set-up cost. When technology's vulnerability to noise, additional considerable barrier to using EEG as a braincomputer interface is the wide exercise required before users can work the techn ...
test - Scioly.org
... Nerve impulses create a change in voltage which is measured by and can a. Stethoscope b. Electrocardiogram c. OscilloscoPe d. AparoscoPe 18. Axoplasm is the a. Blood plasma that nourishes a nerve b. Fluid external to the axon but inside the myelin sheath c. Cytoplasm of the dendrite d. Cytoplasm oft ...
... Nerve impulses create a change in voltage which is measured by and can a. Stethoscope b. Electrocardiogram c. OscilloscoPe d. AparoscoPe 18. Axoplasm is the a. Blood plasma that nourishes a nerve b. Fluid external to the axon but inside the myelin sheath c. Cytoplasm of the dendrite d. Cytoplasm oft ...
Neuronal activity in dorsomedial frontal cortex and prefrontal cortex
... and PF was affected by stimulus location, even when that stimulus dimension was behaviorally irrelevant. Previous studies of both PF (Rainer et al. 1998; Rao et al. 1997; White and Wise 1999) and DMF (Olson et al. 2000; White and Wise 1999) have shown that stimulus location influences neuronal activ ...
... and PF was affected by stimulus location, even when that stimulus dimension was behaviorally irrelevant. Previous studies of both PF (Rainer et al. 1998; Rao et al. 1997; White and Wise 1999) and DMF (Olson et al. 2000; White and Wise 1999) have shown that stimulus location influences neuronal activ ...
Spinal Cord – Gross Anatomy
... All other spinal nerves exit just below their corresponding vertebrae ...
... All other spinal nerves exit just below their corresponding vertebrae ...
Nervous Systems
... the following questions. No talking!!!!!!! 1. The parts of the body that make up the Peripheral Nervous System are the _______ and __________. 2. A _____________ has 4 parts and carries message sent from the brain all over the body. 3. A __________ is the part of a neuron that sends the messages to ...
... the following questions. No talking!!!!!!! 1. The parts of the body that make up the Peripheral Nervous System are the _______ and __________. 2. A _____________ has 4 parts and carries message sent from the brain all over the body. 3. A __________ is the part of a neuron that sends the messages to ...
Chapter 9 Part 3 Central Nervous System
... Neuroendocrine and visceral responses – Coordinated in the hypothalamus and medulla – Hypothalamus contains centers for: • Temperature regulation • Eating • Control of body osmolarity, etc. • Response to stimulation of these centers can be in the form of neural or hormonal reflexes or a behavioral ...
... Neuroendocrine and visceral responses – Coordinated in the hypothalamus and medulla – Hypothalamus contains centers for: • Temperature regulation • Eating • Control of body osmolarity, etc. • Response to stimulation of these centers can be in the form of neural or hormonal reflexes or a behavioral ...
microcircuits in the striatum striatal cell types and their
... evidence for the existence of the recurrent feedback inhibition between spiny projection neurons has only been forthcoming during the last 2 years, and does not fit the relatively simple previously suggested role of a selection circuit. Similarly, striatal interneurons (e.g., the fast-spiking intern ...
... evidence for the existence of the recurrent feedback inhibition between spiny projection neurons has only been forthcoming during the last 2 years, and does not fit the relatively simple previously suggested role of a selection circuit. Similarly, striatal interneurons (e.g., the fast-spiking intern ...
Linear Combinations of Optic Flow Vectors for Estimating Self
... have shown, the achievable accuracy would probably be more than enough for head stabilization under closed loop conditions. Finally, we have to point out a basic limitation of the proposed theory: It assumes linear EMDs as input to the neurons (see Eq. (1)). The output of fly EMDs, however, is only ...
... have shown, the achievable accuracy would probably be more than enough for head stabilization under closed loop conditions. Finally, we have to point out a basic limitation of the proposed theory: It assumes linear EMDs as input to the neurons (see Eq. (1)). The output of fly EMDs, however, is only ...
Schwann cells - Dr. Par Mohammadian
... Nerve Cell Body (Perikaryon or Soma) • Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus • Is the major biosynthetic center • Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes ...
... Nerve Cell Body (Perikaryon or Soma) • Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus • Is the major biosynthetic center • Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes ...
Neuro_quiz3
... 85. Mechanoreceptive somatic senses are stimulated by ________ ________ of some tissue of the body. 86. Mechanoreceptive senses include: ________, ________, ________ & ________ (together known as the tactile senses) AND proprioception AKA ________ sense. 87. What is the difference between touch sens ...
... 85. Mechanoreceptive somatic senses are stimulated by ________ ________ of some tissue of the body. 86. Mechanoreceptive senses include: ________, ________, ________ & ________ (together known as the tactile senses) AND proprioception AKA ________ sense. 87. What is the difference between touch sens ...
Glutamatergic Modulation of the Pedunculopontine Nucleus and its
... BioMed-II Building, Rayford Auditorium Glutamatergic Modulation of the Pedunculopontine Nucleus and its Potential Effects on Waking and REM Sleep Abstract: The Pedunculopontine Nucleus (PPN) is the cholinergic arm of the Reticular Activating System and is involved in cortical arousal. More specifica ...
... BioMed-II Building, Rayford Auditorium Glutamatergic Modulation of the Pedunculopontine Nucleus and its Potential Effects on Waking and REM Sleep Abstract: The Pedunculopontine Nucleus (PPN) is the cholinergic arm of the Reticular Activating System and is involved in cortical arousal. More specifica ...
Forecasting & Demand Planner Module 4 – Basic Concepts
... • The cell that perform information processing in the brain • Fundamental functional unit of all nervous system tissue ...
... • The cell that perform information processing in the brain • Fundamental functional unit of all nervous system tissue ...
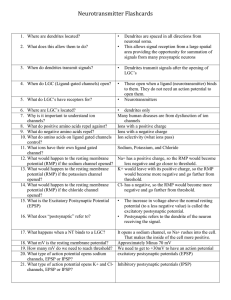
Neurotransmitter Flashcards
... 79. What are two categories of VGC’s? 80. The change in voltage causes what? 81. If it causes depolarization, what type of action potential is it called? 82. If it causes hyperpolarization (going farther from an action potential, what type of action potential is it called? 83. By what process are NT ...
... 79. What are two categories of VGC’s? 80. The change in voltage causes what? 81. If it causes depolarization, what type of action potential is it called? 82. If it causes hyperpolarization (going farther from an action potential, what type of action potential is it called? 83. By what process are NT ...
Biology
... As an impulse reaches a terminal, vesicles send neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and attach to membrane receptors on the next cell. ...
... As an impulse reaches a terminal, vesicles send neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These diffuse across the cleft and attach to membrane receptors on the next cell. ...
Brain Day Volunteer Instructor Manual
... Touch is categorized by the sensory receptors that detect the types of stimuli (see below). Receptors and neurons allow us to interpret sensation. Chemical, thermal or mechanical stimuli is changed to an electrical signal that the brain can understand. The size of sensory receiving areas, relative t ...
... Touch is categorized by the sensory receptors that detect the types of stimuli (see below). Receptors and neurons allow us to interpret sensation. Chemical, thermal or mechanical stimuli is changed to an electrical signal that the brain can understand. The size of sensory receiving areas, relative t ...
Anatomical Terminology
... a. Grey matter: Generic term for neurons in the CNS b. Nucleus: Clearly defined mass of neuron cell bodies c. Substantia: Less distinct borders than nuclei d. Locus: Small but well defined mass of neuron cell bodies 3. Ganglion is a term referring to collection of neurons in the PNS. 4. Terms referr ...
... a. Grey matter: Generic term for neurons in the CNS b. Nucleus: Clearly defined mass of neuron cell bodies c. Substantia: Less distinct borders than nuclei d. Locus: Small but well defined mass of neuron cell bodies 3. Ganglion is a term referring to collection of neurons in the PNS. 4. Terms referr ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.