Neuroembryology I
... Neuroepithelial layer forms ca. 250K neurons/minute! More neurons are born than survive. Once all neurons & macroglia are formed it differentiates into ependymal cells that line the ventricular system. ...
... Neuroepithelial layer forms ca. 250K neurons/minute! More neurons are born than survive. Once all neurons & macroglia are formed it differentiates into ependymal cells that line the ventricular system. ...
construction of a model demonstrating neural pathways and reflex arcs
... that involves two neurons and the space between them. The synaptic space is very small, and it can be seen best with an electron microscope. A synapse is different from synaptic transmission. Synaptic transmission is an event that occurs at the synapse; the synapse itself is a structure. A schematic ...
... that involves two neurons and the space between them. The synaptic space is very small, and it can be seen best with an electron microscope. A synapse is different from synaptic transmission. Synaptic transmission is an event that occurs at the synapse; the synapse itself is a structure. A schematic ...
Ingestive Behaviour Chapter 12
... • Blood levels of NPY are elevated in patients with anorexia. – infusion of NPY into the cerebral ventricles further increased the time spent running in rats on a restricted feeding schedule. • Normally, NPY stimulates eating (as it does in rats with unlimited access to food), but under conditions o ...
... • Blood levels of NPY are elevated in patients with anorexia. – infusion of NPY into the cerebral ventricles further increased the time spent running in rats on a restricted feeding schedule. • Normally, NPY stimulates eating (as it does in rats with unlimited access to food), but under conditions o ...
construction of a model demonstrating neural pathways and reflex arcs
... that involves two neurons and the space between them. The synaptic space is very small, and it can be seen best with an electron microscope. A synapse is different from synaptic transmission. Synaptic transmission is an event that occurs at the synapse; the synapse itself is a structure. A schematic ...
... that involves two neurons and the space between them. The synaptic space is very small, and it can be seen best with an electron microscope. A synapse is different from synaptic transmission. Synaptic transmission is an event that occurs at the synapse; the synapse itself is a structure. A schematic ...
Chapter 06 Abstract Neuron Models
... The second paragraph just quoted is particularly pertinent when we examine larger scale behaviors of networks. At the level of neuron modeling, what is immediately of concern to us is Grossberg's comment, "Two seemingly different models can be equivalent from a functional viewpoint if they both gene ...
... The second paragraph just quoted is particularly pertinent when we examine larger scale behaviors of networks. At the level of neuron modeling, what is immediately of concern to us is Grossberg's comment, "Two seemingly different models can be equivalent from a functional viewpoint if they both gene ...
BRAINSTEM
... Located in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe, receives projections from VPL and VPM via the posterior limb of the internal capsule. Organized into columns which contain information from the same peripheral location on the body and same class of peripheral sensory receptor. Axons from VP nuc ...
... Located in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe, receives projections from VPL and VPM via the posterior limb of the internal capsule. Organized into columns which contain information from the same peripheral location on the body and same class of peripheral sensory receptor. Axons from VP nuc ...
Neural mechanisms for color perception in the primary visual cortex
... by large regions of color and therefore could be important for perception of color in extended regions. In studies of human color vision with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) [26,27,28•], color-preferring neurons probably contribute disproportionately to the signals thought to be evoked ...
... by large regions of color and therefore could be important for perception of color in extended regions. In studies of human color vision with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) [26,27,28•], color-preferring neurons probably contribute disproportionately to the signals thought to be evoked ...
Curriculum Vitae
... My laboratory was set up in March 2005. The long-term goal of the laboratory is to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the proper migration and distribution of different types of neurons in developing brain, one of the key steps for brain morphogenesis. Currently, we focus on the guidance ...
... My laboratory was set up in March 2005. The long-term goal of the laboratory is to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the proper migration and distribution of different types of neurons in developing brain, one of the key steps for brain morphogenesis. Currently, we focus on the guidance ...
Signals Conveyed in the Pulvinar Pathway from Superior Colliculus
... properties of these ascending-path PI neurons resembled those of SC visual neurons. Namely, they had brisk responses to spots of light, inhibitory surrounds, and relatively large receptive fields that increased with eccentricity, as well as minimal presaccadic activity. Beyond these basic properties ...
... properties of these ascending-path PI neurons resembled those of SC visual neurons. Namely, they had brisk responses to spots of light, inhibitory surrounds, and relatively large receptive fields that increased with eccentricity, as well as minimal presaccadic activity. Beyond these basic properties ...
Print - Stroke
... frequency.8 This value varies depending on the location of the cell in the retina and the intensity of the stimulus; it is partly representative of the threshold of stimulation and the refractory period of cells of the retina. The number of cells stimulated by a flash of light depends on its locatio ...
... frequency.8 This value varies depending on the location of the cell in the retina and the intensity of the stimulus; it is partly representative of the threshold of stimulation and the refractory period of cells of the retina. The number of cells stimulated by a flash of light depends on its locatio ...
PDF
... corridor for the tangential migration of interneurons and it contains Cajal-Retzius neurons. Preplate (PP). A transient cell-dense structure, which was formerly termed the early MZ or primordial plexiform layer, that contains some of the earliest-born cortical neurons. It is split by incoming CP neu ...
... corridor for the tangential migration of interneurons and it contains Cajal-Retzius neurons. Preplate (PP). A transient cell-dense structure, which was formerly termed the early MZ or primordial plexiform layer, that contains some of the earliest-born cortical neurons. It is split by incoming CP neu ...
Evolving Connectionist and Fuzzy-Connectionist Systems for
... (1) Input patterns are presented one by one, in a pattern mode, having not necessarily the same input feature sets. After each input example is presented, the ECOS either associates this example with an already existing rule (case) node, or creates a new one. A NN module, or a neuron is created when ...
... (1) Input patterns are presented one by one, in a pattern mode, having not necessarily the same input feature sets. After each input example is presented, the ECOS either associates this example with an already existing rule (case) node, or creates a new one. A NN module, or a neuron is created when ...
1 - optometrie.ch
... machinery (organelles) in the cell body, which produce axoplasm One of the important basic science concepts is understanding that axoplasmic flow is a dynamic process; and that when it stops, the axon dies. This is because the axon has little machinery (organelles) to make molecules that the axon re ...
... machinery (organelles) in the cell body, which produce axoplasm One of the important basic science concepts is understanding that axoplasmic flow is a dynamic process; and that when it stops, the axon dies. This is because the axon has little machinery (organelles) to make molecules that the axon re ...
Motor Cortical Networks for Skilled Movements Have Reaching
... There is emerging evidence to suggest that the prevalence of spiking associations in MI may also be influenced by the morphological properties of the cells involved. A recent study has shown that during reaching, fast spiking (FS) ...
... There is emerging evidence to suggest that the prevalence of spiking associations in MI may also be influenced by the morphological properties of the cells involved. A recent study has shown that during reaching, fast spiking (FS) ...
A Neural Model of Rule Generation in Inductive Reasoning
... VSAs have a number of other advantages: vectors are easier to represent in populations of neurons than complex visual information, they are easier to manipulate mathematically, and perhaps most importantly the logical operation of the inductive system is not dependent on the details of the visual sy ...
... VSAs have a number of other advantages: vectors are easier to represent in populations of neurons than complex visual information, they are easier to manipulate mathematically, and perhaps most importantly the logical operation of the inductive system is not dependent on the details of the visual sy ...
Luczak, 2015 - University of Lethbridge
... two different tactile stimuli applied to the palm or a digit of the contralateral forelimb are shown. Together with those of other studies35,48, these findings indicate that somatosensory neurons also show stereotypical sequential order at stimulus onset. d | In the olfactory bulb, neuronal populati ...
... two different tactile stimuli applied to the palm or a digit of the contralateral forelimb are shown. Together with those of other studies35,48, these findings indicate that somatosensory neurons also show stereotypical sequential order at stimulus onset. d | In the olfactory bulb, neuronal populati ...
Restraining influence of A2 neurons in chronic control of arterial
... AGT and JFRP are equal last authors. ...
... AGT and JFRP are equal last authors. ...
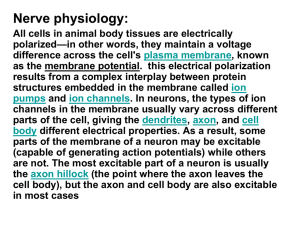
are involved in a few types of action potentials
... precipitating a domino-like propagation. In contrast to passive spread of electric potentials (electrotonic potential), action potentials are generated anew along excitable stretches of membrane and propagate without decay. Myelinated sections of axons are not excitable and do not produce action pot ...
... precipitating a domino-like propagation. In contrast to passive spread of electric potentials (electrotonic potential), action potentials are generated anew along excitable stretches of membrane and propagate without decay. Myelinated sections of axons are not excitable and do not produce action pot ...
Summary - SCIENCE HELP @ ne3me.com
... heart rate. Stimulants also increase the release of neurotransmitters in the brain. Depressants decrease actions, such as heart rate, that are controlled by the brain. Cocaine causes the sudden release in the brain of a neurotransmitter called dopamine. Opiates act like natural brain chemicals calle ...
... heart rate. Stimulants also increase the release of neurotransmitters in the brain. Depressants decrease actions, such as heart rate, that are controlled by the brain. Cocaine causes the sudden release in the brain of a neurotransmitter called dopamine. Opiates act like natural brain chemicals calle ...
HTM Neuron paper 12-1
... then propose a neuron model where some of the patterns recognized by a neuron lead to action potentials and define the classic receptive field of the neuron, whereas the majority of the patterns recognized by a neuron act as predictions by slightly depolarizing the neuron without immediately generat ...
... then propose a neuron model where some of the patterns recognized by a neuron lead to action potentials and define the classic receptive field of the neuron, whereas the majority of the patterns recognized by a neuron act as predictions by slightly depolarizing the neuron without immediately generat ...
nips2.frame - /marty/papers/drotdil
... movement, object, and scene recognition under noisy conditions--feats we would like to copy with artificial networks. We are just beginning to understand how biological networks are wired up during development and during learning in the adult. Even at this stage, however, it is clear that explicit e ...
... movement, object, and scene recognition under noisy conditions--feats we would like to copy with artificial networks. We are just beginning to understand how biological networks are wired up during development and during learning in the adult. Even at this stage, however, it is clear that explicit e ...
Test yourself on lesions in section pictures
... spinal trigeminal tract and nucleus. This pathway has not yet crossed, since these are the primary afferents and cell bodies of the second order neurons. Loss of pain and temperature in the contralateral body occurs due to elimination of the lateral spinothalamic tract. This tract crossed back in th ...
... spinal trigeminal tract and nucleus. This pathway has not yet crossed, since these are the primary afferents and cell bodies of the second order neurons. Loss of pain and temperature in the contralateral body occurs due to elimination of the lateral spinothalamic tract. This tract crossed back in th ...
Hypocretinergic Neurons are Primarily involved in Activation
... Therefore, the hypocretinergic system is well positioned to initiate, maintain and facilitate motor activity by operating directly on motoneurons and/or by modifying the activity of supraspinal systems that are involved in motor functions. A recent study in rats suggested that the activity of the hy ...
... Therefore, the hypocretinergic system is well positioned to initiate, maintain and facilitate motor activity by operating directly on motoneurons and/or by modifying the activity of supraspinal systems that are involved in motor functions. A recent study in rats suggested that the activity of the hy ...
Nervous System - Discovery Education
... nerve cells. You are born with all the neurons you will ever have, for these special cells can not duplicate themselves like other body cells. Don’t worry, there are more than enough neurons to last a lifetime. In fact, these cells die at the rate of thousands every day and yet this isn’t a problem. ...
... nerve cells. You are born with all the neurons you will ever have, for these special cells can not duplicate themselves like other body cells. Don’t worry, there are more than enough neurons to last a lifetime. In fact, these cells die at the rate of thousands every day and yet this isn’t a problem. ...
Pathophysiology of Pain
... involves the normal activation of the nociceptive system by noxious stimuli. Nociception consists of four processes: ...
... involves the normal activation of the nociceptive system by noxious stimuli. Nociception consists of four processes: ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.