Imitation, Empathy, and Mirror Neurons
... There is a convergence between cognitive models of imitation, constructs derived from social psychology studies on mimicry and empathy, and recent empirical findings from the neurosciences. The ideomotor framework of human actions assumes a common representational format for action and perception tha ...
... There is a convergence between cognitive models of imitation, constructs derived from social psychology studies on mimicry and empathy, and recent empirical findings from the neurosciences. The ideomotor framework of human actions assumes a common representational format for action and perception tha ...
BRAINSTEM Comprised of 4 components: • Grey matter = cranial
... Originate in : Nucleus pontis oralis (rostral pons), nucleus pontis caudalis (caudal pons), gigantocellular reticular nucleus (medulla) - Raphespinal pathway Modulate pain transmission of nocioceptive inputs in the dorsal horn Originate in: Dorsal Raphe, Median Raphe (midbrain and pons) Ascend ...
... Originate in : Nucleus pontis oralis (rostral pons), nucleus pontis caudalis (caudal pons), gigantocellular reticular nucleus (medulla) - Raphespinal pathway Modulate pain transmission of nocioceptive inputs in the dorsal horn Originate in: Dorsal Raphe, Median Raphe (midbrain and pons) Ascend ...
Olfaction
... – MAYBE information conveyed by timing. – In insects (now also in fish) brain neurons sychronize responses. (Gilles Laurent) ...
... – MAYBE information conveyed by timing. – In insects (now also in fish) brain neurons sychronize responses. (Gilles Laurent) ...
Axons, but not cell bodies, are activated by electrical stimulation in
... Extracellular recordings of single units were obtained with tungsten-in-glass microelectrodes (Merrill and Ainsworth 1972) with 15to 25- m exposed tips and plated with platinum black (impedance less than 0.5 MW at 1000 Hz). The Neurolog recording system was used for amplification and filtering. Filt ...
... Extracellular recordings of single units were obtained with tungsten-in-glass microelectrodes (Merrill and Ainsworth 1972) with 15to 25- m exposed tips and plated with platinum black (impedance less than 0.5 MW at 1000 Hz). The Neurolog recording system was used for amplification and filtering. Filt ...
PDF
... of the growth cones directly to its target area and the elimination of the others (Kuwada, 1982; Kuwada & Kramer, 1983). Consistent with this hypothesis are the two main findings of this investigation. 1) The primary growth cone of the PD neuron is the first growth cone to traverse the DP pathway an ...
... of the growth cones directly to its target area and the elimination of the others (Kuwada, 1982; Kuwada & Kramer, 1983). Consistent with this hypothesis are the two main findings of this investigation. 1) The primary growth cone of the PD neuron is the first growth cone to traverse the DP pathway an ...
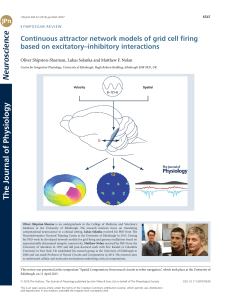
Continuous attractor network models of grid cell firing based on
... firing patterns are the result of computation of location from velocity inputs, with additional spatial input required to oppose drift in the attractor state. We focus on properties of continuous attractor networks that are revealed by explicitly considering excitatory and inhibitory neurons, their ...
... firing patterns are the result of computation of location from velocity inputs, with additional spatial input required to oppose drift in the attractor state. We focus on properties of continuous attractor networks that are revealed by explicitly considering excitatory and inhibitory neurons, their ...
Translational Dysregulation in Autism
... structures connecting an axon from one neuron to the dendritic spine, or shaft, of a receiving neuron. Formation and maturation of synapses constitute one of the most fundamental processes in brain development. In mature neurons, synapses are constantly regulated in their structure and function, and ...
... structures connecting an axon from one neuron to the dendritic spine, or shaft, of a receiving neuron. Formation and maturation of synapses constitute one of the most fundamental processes in brain development. In mature neurons, synapses are constantly regulated in their structure and function, and ...
Arterial Blood Supply to the Auditory Cortex of the Chinchilla
... often referred to as a blood oxygen level- dependent (BOLD) effect. In our experimental work, using optical imaging of intrinsic signals in the auditory cortex, we have used a chinchilla (Chinchilla laniger) animal model (6, 7). However, to date there has been no systematic study of the arterial blo ...
... often referred to as a blood oxygen level- dependent (BOLD) effect. In our experimental work, using optical imaging of intrinsic signals in the auditory cortex, we have used a chinchilla (Chinchilla laniger) animal model (6, 7). However, to date there has been no systematic study of the arterial blo ...
Article Conserved Higher-Order Chromatin Regulates NMDA Receptor Gene Expression and Cognition Neuron
... Gene expression is governed by distal regulatory elements, including enhancers and locus control regions which have been intensely studied in extraneural tissues such as blood for more than 30 years (Banerji et al., 1981; Li et al., 1999). These mechanisms, however, essentially remain unexplored in ...
... Gene expression is governed by distal regulatory elements, including enhancers and locus control regions which have been intensely studied in extraneural tissues such as blood for more than 30 years (Banerji et al., 1981; Li et al., 1999). These mechanisms, however, essentially remain unexplored in ...
Artificial neural network
... Take a collection of training patterns for a node, some of which cause it to fire (the 1-taught set of patterns) and others which prevent it from doing so (the 0taught set). Then the patterns not in the collection cause the node to fire if, on comparison, they have more input elements in common with ...
... Take a collection of training patterns for a node, some of which cause it to fire (the 1-taught set of patterns) and others which prevent it from doing so (the 0taught set). Then the patterns not in the collection cause the node to fire if, on comparison, they have more input elements in common with ...
Viewpoint Synaptic Connectivity and Neuronal Morphology: Two
... for a network of neurons within the cortical column. Initially, I compare theoretical predictions with data from mouse neocortex because of their relatively high quality, leaving interspecies comparison to the section on Comparison with Experiment. One cubic millimeter of mouse neocortex contains N ...
... for a network of neurons within the cortical column. Initially, I compare theoretical predictions with data from mouse neocortex because of their relatively high quality, leaving interspecies comparison to the section on Comparison with Experiment. One cubic millimeter of mouse neocortex contains N ...
neuro 13 descending tracts student
... Lower Motor Neurons Begin in CNS. From anterior horns of spinal cord. From brainstem cranial nerve nuclei. Made up of alpha motor neurons (A-α). Make up spinal and cranial nerves. ...
... Lower Motor Neurons Begin in CNS. From anterior horns of spinal cord. From brainstem cranial nerve nuclei. Made up of alpha motor neurons (A-α). Make up spinal and cranial nerves. ...
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... Burn patients experience the destruction of cells and the release of cellular contents into the ECF. Burn patients are more likely to suffer from which of the following conditions? A) action potentials with exaggerated amplitudes B) tachycardia (a rapid heart rate) C) hyperpolarization of nerves and ...
... Burn patients experience the destruction of cells and the release of cellular contents into the ECF. Burn patients are more likely to suffer from which of the following conditions? A) action potentials with exaggerated amplitudes B) tachycardia (a rapid heart rate) C) hyperpolarization of nerves and ...
File: Chap011, Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... Burn patients experience the destruction of cells and the release of cellular contents into the ECF. Burn patients are more likely to suffer from which of the following conditions? A) action potentials with exaggerated amplitudes B) tachycardia (a rapid heart rate) C) hyperpolarization of nerves and ...
... Burn patients experience the destruction of cells and the release of cellular contents into the ECF. Burn patients are more likely to suffer from which of the following conditions? A) action potentials with exaggerated amplitudes B) tachycardia (a rapid heart rate) C) hyperpolarization of nerves and ...
2013 Action Potential Modeling in PYTHON
... +50mV, the sodium gate becomes inactivated and Na+ channels close. This marks the end of the depolarization phase. Each gating variable modifies ion conductance to produce the action potential shown in Figure 4. This action potential will be compared to the measured membrane action potential trace ...
... +50mV, the sodium gate becomes inactivated and Na+ channels close. This marks the end of the depolarization phase. Each gating variable modifies ion conductance to produce the action potential shown in Figure 4. This action potential will be compared to the measured membrane action potential trace ...
Functional Integration of Embryonic Stem Cell
... EGFP (1:4.000; Abcam, Cambridge, UK), followed by a peroxidaselabeled secondary antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch) and staining with diaminobenzidine precipitate (DAKO). Stained sections were postfixed overnight in 2.5% glutaraldehyde, photodocumented, dehydrated in graded ethanol series, and embedde ...
... EGFP (1:4.000; Abcam, Cambridge, UK), followed by a peroxidaselabeled secondary antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch) and staining with diaminobenzidine precipitate (DAKO). Stained sections were postfixed overnight in 2.5% glutaraldehyde, photodocumented, dehydrated in graded ethanol series, and embedde ...
Relationship of Prefrontal Connections to Inhibitory Systems in Superior Temporal
... prevalent than PV neurons, with the highest densities found in posterior high-order auditory association cortices. Axons from anterior lateral, medial prefrontal and orbitofrontal areas terminated in the anterior half of the superior temporal gyrus, targeting mostly the superficial layers (I to uppe ...
... prevalent than PV neurons, with the highest densities found in posterior high-order auditory association cortices. Axons from anterior lateral, medial prefrontal and orbitofrontal areas terminated in the anterior half of the superior temporal gyrus, targeting mostly the superficial layers (I to uppe ...
May 21, 04.doc
... Measures of relative optical density were obtained from all the tangential α1-GABAAimmunostained sections, from cortical layer I (whenever possible) to layer IV. Samples were taken within a computer-generated circle over each barrel column, allowing for comparisons between deprived and intact rows. ...
... Measures of relative optical density were obtained from all the tangential α1-GABAAimmunostained sections, from cortical layer I (whenever possible) to layer IV. Samples were taken within a computer-generated circle over each barrel column, allowing for comparisons between deprived and intact rows. ...
Organization of acetylcholine-containing structures in the cranial
... motor nuclei contained ChAT-positive cell bodies and fibres, but the intensity of staining differed between the nuclei. Furthermore, characteristic ChAT-immunoreactive bouton-like structures, which are known to be synaptic terminals of the cholinergic system, were observed in the borders of all stud ...
... motor nuclei contained ChAT-positive cell bodies and fibres, but the intensity of staining differed between the nuclei. Furthermore, characteristic ChAT-immunoreactive bouton-like structures, which are known to be synaptic terminals of the cholinergic system, were observed in the borders of all stud ...
- Princeton University
... of a custom-designed Hidden-Markov-Modelbased motion correction algorithm useful for postprocessing. Behaviorally correlated calcium transients from large neuronal and astrocytic populations were routinely measured, with an estimated motion-induced false positive error rate of <5%. INTRODUCTION Exis ...
... of a custom-designed Hidden-Markov-Modelbased motion correction algorithm useful for postprocessing. Behaviorally correlated calcium transients from large neuronal and astrocytic populations were routinely measured, with an estimated motion-induced false positive error rate of <5%. INTRODUCTION Exis ...
Cellular scaling rules for the brain of afrotherians
... cortex in all animals was manually dissected from the striatum and other subcortical structures. The hippocampus was then dissected from each cortical hemisphere, under a stereoscope. The cerebral cortex of the hyrax specimens was then cut into 2 mm coronal sections in order to allow the dissection ...
... cortex in all animals was manually dissected from the striatum and other subcortical structures. The hippocampus was then dissected from each cortical hemisphere, under a stereoscope. The cerebral cortex of the hyrax specimens was then cut into 2 mm coronal sections in order to allow the dissection ...
Data Supplement
... the first session mice were sent across the ladder 3 times, then twice for the second training session, and only once for third and fourth training sessions. Baseline was obtained from the last training run. Post stroke testing was performed with one run per mouse. Ladder test performance was scored ...
... the first session mice were sent across the ladder 3 times, then twice for the second training session, and only once for third and fourth training sessions. Baseline was obtained from the last training run. Post stroke testing was performed with one run per mouse. Ladder test performance was scored ...
Reinforcement learning in cortical networks
... and adapts the synaptic connection strengths w along the reward gradient, i.e. such that the expected weight change satisfies h∆wi = η dhRi dw with some small but positive learning rate η (Williams, 1992). Hedonistic synapse In the current form, a synapse is assumed to estimate how the change in w a ...
... and adapts the synaptic connection strengths w along the reward gradient, i.e. such that the expected weight change satisfies h∆wi = η dhRi dw with some small but positive learning rate η (Williams, 1992). Hedonistic synapse In the current form, a synapse is assumed to estimate how the change in w a ...
String Art: Axon Tracts in the Spinal Cord Spinal reflex arcs
... motor neurons on both sides of the spinal cord. ...
... motor neurons on both sides of the spinal cord. ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.