Abstract Booklet
... Motor adaptation is a motor system’s response to a change in the environment, such as a perturbation of the visual feedback about one’s movements. Many experimental studies have focused on the factors determining how fast subjects adapt to a perturbation, and how fast they readapt upon reexposure to ...
... Motor adaptation is a motor system’s response to a change in the environment, such as a perturbation of the visual feedback about one’s movements. Many experimental studies have focused on the factors determining how fast subjects adapt to a perturbation, and how fast they readapt upon reexposure to ...
Functional features of the rat subicular microcircuits studied in vitro
... inputs are differentially modulated. The CA1-activated EPSPs are the main targets of a dopaminergic control that depresses glutamate release via presynaptic D1 receptors [7], in contrast to the weakly modulated perforant path. Subicular EPSPs activated by CA1 stimulation also exhibit diverse forms o ...
... inputs are differentially modulated. The CA1-activated EPSPs are the main targets of a dopaminergic control that depresses glutamate release via presynaptic D1 receptors [7], in contrast to the weakly modulated perforant path. Subicular EPSPs activated by CA1 stimulation also exhibit diverse forms o ...
15 2nd,3rd, 4th &6th..
... pretectal area and superior colliculus. These fibers are related to light reflexes ...
... pretectal area and superior colliculus. These fibers are related to light reflexes ...
Chapter Two - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... here do you live? You probably don’t think about it much, but the thinking, feeling, W and acting part of you has to have a body to live in. Psychological life depends on biological life for its very existence. This means that the way we behave is influenced to a great extent by the nature of the bo ...
... here do you live? You probably don’t think about it much, but the thinking, feeling, W and acting part of you has to have a body to live in. Psychological life depends on biological life for its very existence. This means that the way we behave is influenced to a great extent by the nature of the bo ...
Prosjektoppgave - Mirror neurons_ver4.2
... Placing neurons discharge when moving a stimulus towards a plane or support. They start to fire when an experimenter, for example, places a piece of food on an empty tray, and they stop firing when the hand starts moving away from the food. The grasping of the same food from the same tray by the ex ...
... Placing neurons discharge when moving a stimulus towards a plane or support. They start to fire when an experimenter, for example, places a piece of food on an empty tray, and they stop firing when the hand starts moving away from the food. The grasping of the same food from the same tray by the ex ...
EVOLUTIONARY AUTONOMOUS AGENTS: A NEUROSCIENCE
... on the basis of certain sensory stimuli16, and in particular, as in the EAA simulation, by food arousal17,18. This activity has been shown to control a variety of motor repertoires, mainly by inducing different activity patterns in the same network by modulating neuronal activity21,22 — again, in a ...
... on the basis of certain sensory stimuli16, and in particular, as in the EAA simulation, by food arousal17,18. This activity has been shown to control a variety of motor repertoires, mainly by inducing different activity patterns in the same network by modulating neuronal activity21,22 — again, in a ...
Gao JCN 2000 - Georgia State University
... The inhibitory neurotransmitter ␥-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is thought to play an important role in activity-dependent stages of brain development. Previous studies have shown that different functional subclasses of cortical GABA-containing neurons can be distinguished by antibodies to the calcium-bi ...
... The inhibitory neurotransmitter ␥-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is thought to play an important role in activity-dependent stages of brain development. Previous studies have shown that different functional subclasses of cortical GABA-containing neurons can be distinguished by antibodies to the calcium-bi ...
Alterations in Synaptic Strength Preceding Axon Withdrawal
... hemicholinium – 3 they turned to decreases in the density of AChRs in the areas of the postsynaptic membrane. Given that a low density of AChRs could account for small quantal responses, area with low density of receptor density were identified in NMJs and overlying nerve terminals were studied for ...
... hemicholinium – 3 they turned to decreases in the density of AChRs in the areas of the postsynaptic membrane. Given that a low density of AChRs could account for small quantal responses, area with low density of receptor density were identified in NMJs and overlying nerve terminals were studied for ...
Whole-brain functional imaging at cellular resolution using light
... brain, is typically still tiny. This limitation arises from constraints on the number of neurons that can be imaged at the same time and the total brain size of the animal under study. Thus, interactions between neurons in different brain areas are easily missed, and functionally related ensembles o ...
... brain, is typically still tiny. This limitation arises from constraints on the number of neurons that can be imaged at the same time and the total brain size of the animal under study. Thus, interactions between neurons in different brain areas are easily missed, and functionally related ensembles o ...
A Simple Biophysically Plausible Model for Long Time
... Eq. (1) presents two major challenges for a biological circuit: 1. In order for the model to describe neural firing and behavioral effects up to long time scales, there should be neurons with time constants on the order of that time scale. The time constant of each unit in Eq. (1) is 1/s. 2. Rapid e ...
... Eq. (1) presents two major challenges for a biological circuit: 1. In order for the model to describe neural firing and behavioral effects up to long time scales, there should be neurons with time constants on the order of that time scale. The time constant of each unit in Eq. (1) is 1/s. 2. Rapid e ...
Institute of Psychology C.N.R.
... input is mapped into the neuron's activation state using a logistic function. Given a sequence of N successive activation states of the same neuron one can measure the variability of this distribution of states. A neuron will grow its branching axon only if this measure of activation variability is ...
... input is mapped into the neuron's activation state using a logistic function. Given a sequence of N successive activation states of the same neuron one can measure the variability of this distribution of states. A neuron will grow its branching axon only if this measure of activation variability is ...
Temporal and spatial alterations in GPi neuronal encoding might
... was modified by 10% from the mean in the same direction (i.e. activation or suppression). When a neuron was responsive to more than one stimulus, the slope of the first three bins deflecting from the mean by more than three SD was calculated for each stimulus. The steepest slope was considered to corre ...
... was modified by 10% from the mean in the same direction (i.e. activation or suppression). When a neuron was responsive to more than one stimulus, the slope of the first three bins deflecting from the mean by more than three SD was calculated for each stimulus. The steepest slope was considered to corre ...
Morphology and Physiology of the Cerebellar Vestibulolateral Lobe
... prevailing views derived from mammalian species have centered around either intrinsic changes within the cerebellum (Raymond and Lisberger 1998) through the mechanisms of long-term depression and potentiation (Boyden et al. 2004; Ito 1989) or, in more recent years, multiple plasticity mechanisms/ si ...
... prevailing views derived from mammalian species have centered around either intrinsic changes within the cerebellum (Raymond and Lisberger 1998) through the mechanisms of long-term depression and potentiation (Boyden et al. 2004; Ito 1989) or, in more recent years, multiple plasticity mechanisms/ si ...
Why light
... When activated by the RAS, visual information will be more likely to be passed to the visual projection Area I of the cortex. When inhibited by the RAS (during quiescence) visual information will be less likely to be passed to higher levels. Note the need for synapses for the inhibition that provide ...
... When activated by the RAS, visual information will be more likely to be passed to the visual projection Area I of the cortex. When inhibited by the RAS (during quiescence) visual information will be less likely to be passed to higher levels. Note the need for synapses for the inhibition that provide ...
Imitation, Empathy, and Mirror Neurons
... There is a convergence between cognitive models of imitation, constructs derived from social psychology studies on mimicry and empathy, and recent empirical findings from the neurosciences. The ideomotor framework of human actions assumes a common representational format for action and perception tha ...
... There is a convergence between cognitive models of imitation, constructs derived from social psychology studies on mimicry and empathy, and recent empirical findings from the neurosciences. The ideomotor framework of human actions assumes a common representational format for action and perception tha ...
Histamine neurons in the tuberomamillary nucleus: a whole center
... Spatial segregation due to probe localization does not explain the lack of response, as retrograde tracing with dye injections into the striatum or prefrontal cortex showed that most histaminergic somata are within the medial part of the ventral TMN (Köhler et al., 1985). This proximity suggests tha ...
... Spatial segregation due to probe localization does not explain the lack of response, as retrograde tracing with dye injections into the striatum or prefrontal cortex showed that most histaminergic somata are within the medial part of the ventral TMN (Köhler et al., 1985). This proximity suggests tha ...
“Congruent” and “Opposite” Neurons: Sisters for Multisensory
... However, multisensory integration is only half of the story of multisensory information processing, which works well when the sensory cues are originated from the same object. In cases where the sensory cues originate from different objects, the brain should segregate, rather than integrate, the cue ...
... However, multisensory integration is only half of the story of multisensory information processing, which works well when the sensory cues are originated from the same object. In cases where the sensory cues originate from different objects, the brain should segregate, rather than integrate, the cue ...
Neural Networks – State of Art, Brief History, Basic Models and
... This is perhaps the most popular network architecture in use today (Fig. 1). The units each perform a biased weighted sum of their inputs and pass this activation level through a transfer function to produce their output, and the units are arranged in a layered feedforward topology. ...
... This is perhaps the most popular network architecture in use today (Fig. 1). The units each perform a biased weighted sum of their inputs and pass this activation level through a transfer function to produce their output, and the units are arranged in a layered feedforward topology. ...
PDF
... instructive error signals. These error signals are thought to be conveyed by dopamine neurons. To test whether orbitofrontal cortex contributes to these error signals, we recorded from dopamine neurons in orbitofrontal-lesioned rats performing a reward learning task. Lesions caused marked changes in ...
... instructive error signals. These error signals are thought to be conveyed by dopamine neurons. To test whether orbitofrontal cortex contributes to these error signals, we recorded from dopamine neurons in orbitofrontal-lesioned rats performing a reward learning task. Lesions caused marked changes in ...
srep31126 - University of Aberdeen
... Schizophrenia is a debilitating familial neuropsychiatric disorder which affects 1% of people worldwide. Although the heritability for schizophrenia approaches 80% only a small proportion of the overall genetic risk has been accounted for, and to date only a limited number of genetic loci have been ...
... Schizophrenia is a debilitating familial neuropsychiatric disorder which affects 1% of people worldwide. Although the heritability for schizophrenia approaches 80% only a small proportion of the overall genetic risk has been accounted for, and to date only a limited number of genetic loci have been ...
Representing Spatial Information for Limb - Research
... Ml (Georgopoulos et al., 1984; Georgopoulos and Massey, 1985; Kettner et al., 1988), PMd (Caminiti et al., 1991), area 2 (Soechting et al., 1992), and area 5 (Georgopoulos et al., 1984; Georgopoulos and Massey, 1985). We have searched evidence for coherent representations of movement and posture in ...
... Ml (Georgopoulos et al., 1984; Georgopoulos and Massey, 1985; Kettner et al., 1988), PMd (Caminiti et al., 1991), area 2 (Soechting et al., 1992), and area 5 (Georgopoulos et al., 1984; Georgopoulos and Massey, 1985). We have searched evidence for coherent representations of movement and posture in ...
Impaired Cl Extrusion in Layer V Pyramidal Neurons of Chronically
... The lack of a significant difference in EGABA (ECl) between the undercut and control group was surprising because previous experiments have shown decreased KCC2 immunoreactivity in neurons of layer V of undercut cortex (Prince et al. 2000; D. A. Prince, unpublished data) and decreased KCC2 expressio ...
... The lack of a significant difference in EGABA (ECl) between the undercut and control group was surprising because previous experiments have shown decreased KCC2 immunoreactivity in neurons of layer V of undercut cortex (Prince et al. 2000; D. A. Prince, unpublished data) and decreased KCC2 expressio ...
DECISION MAKING AND THE BRAIN: NEUROLOGISTS` VIEW
... Distinct parts of the limbic cortico-subcortico-frontal loop represent different aspects of the rewarding behaviour: anterior cingulate gyrus and orbitofrontal cortex are active in the prediction of a mistake in the rewarding process, evaluation and choosing among current and long term benefit; cell ...
... Distinct parts of the limbic cortico-subcortico-frontal loop represent different aspects of the rewarding behaviour: anterior cingulate gyrus and orbitofrontal cortex are active in the prediction of a mistake in the rewarding process, evaluation and choosing among current and long term benefit; cell ...
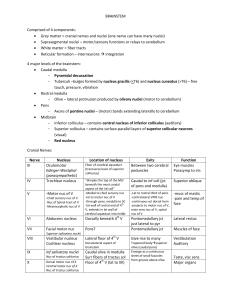
BRAINSTEM Comprised of 4 components: • Grey matter = cranial
... Originate in : Nucleus pontis oralis (rostral pons), nucleus pontis caudalis (caudal pons), gigantocellular reticular nucleus (medulla) - Raphespinal pathway Modulate pain transmission of nocioceptive inputs in the dorsal horn Originate in: Dorsal Raphe, Median Raphe (midbrain and pons) Ascend ...
... Originate in : Nucleus pontis oralis (rostral pons), nucleus pontis caudalis (caudal pons), gigantocellular reticular nucleus (medulla) - Raphespinal pathway Modulate pain transmission of nocioceptive inputs in the dorsal horn Originate in: Dorsal Raphe, Median Raphe (midbrain and pons) Ascend ...
Imitation, Empathy, and Mirror Neurons
... There is a convergence between cognitive models of imitation, constructs derived from social psychology studies on mimicry and empathy, and recent empirical findings from the neurosciences. The ideomotor framework of human actions assumes a common representational format for action and perception tha ...
... There is a convergence between cognitive models of imitation, constructs derived from social psychology studies on mimicry and empathy, and recent empirical findings from the neurosciences. The ideomotor framework of human actions assumes a common representational format for action and perception tha ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.