Descending Systems Translate Transient Cortical Commands into a
... Activity in the motor cortex has been shown to be related to both low-level (Kalaska et al. 1989, 1997; Cabel et al. 2001; Kurtzer et al. 2005, 2006) and high-level (Georgopoulos et al. 1982, 1986; Schwartz et al. 2004) parameters but the coding of these attributes has often been found to be interde ...
... Activity in the motor cortex has been shown to be related to both low-level (Kalaska et al. 1989, 1997; Cabel et al. 2001; Kurtzer et al. 2005, 2006) and high-level (Georgopoulos et al. 1982, 1986; Schwartz et al. 2004) parameters but the coding of these attributes has often been found to be interde ...
PSY110 Week 2 Biology and Behavior
... between neurons • released into synapse by axon terminals of sending neuron • bind to receptor sites on dendrites of receiving neuron • taken back into axon terminal by the process of ...
... between neurons • released into synapse by axon terminals of sending neuron • bind to receptor sites on dendrites of receiving neuron • taken back into axon terminal by the process of ...
computational and in vitro studies of persistent activity
... stimulation rates: connectivity in the rightmost case (thin lines, pluses and diamonds) is approximately 70% of that of the leftmost case (thicker lines, crosses and squares), and external stimulation is 50% stronger in the rightmost than the leftmost graphs. Notice lower persistent activity rates i ...
... stimulation rates: connectivity in the rightmost case (thin lines, pluses and diamonds) is approximately 70% of that of the leftmost case (thicker lines, crosses and squares), and external stimulation is 50% stronger in the rightmost than the leftmost graphs. Notice lower persistent activity rates i ...
Plasticity in the developing brain: Implications for
... Several mechanisms that involve neuronal plasticity stand out as important contributors to the developing brain’s ability to acquire new information, change in response to environmental stimulation, and recover from injury [Johnston et al., 2009]. The processes that control neurogenesis and cell dea ...
... Several mechanisms that involve neuronal plasticity stand out as important contributors to the developing brain’s ability to acquire new information, change in response to environmental stimulation, and recover from injury [Johnston et al., 2009]. The processes that control neurogenesis and cell dea ...
Production and Survival of Projection Neurons in a Forebrain Vocal
... The number ofnew HVC neurons stayed fairly constant between 60 and 240 d after the injections of 3H-thymidine. This suggests that the great majority (all?) of new HVC neurons born in midSeptember and that had acquired an adult phenotype by 60 d survived at least 8 months. We cannot speak with equal ...
... The number ofnew HVC neurons stayed fairly constant between 60 and 240 d after the injections of 3H-thymidine. This suggests that the great majority (all?) of new HVC neurons born in midSeptember and that had acquired an adult phenotype by 60 d survived at least 8 months. We cannot speak with equal ...
PPT - 서울대 Biointelligence lab
... Central problem in neuroscience: How the brain or neocortex codes information and how the signals are used by neuronal processes for the control of behavior “self-referencing system” “ongoing self-maintaining system” – so treating brain as an input-output system can have only limited success. Many s ...
... Central problem in neuroscience: How the brain or neocortex codes information and how the signals are used by neuronal processes for the control of behavior “self-referencing system” “ongoing self-maintaining system” – so treating brain as an input-output system can have only limited success. Many s ...
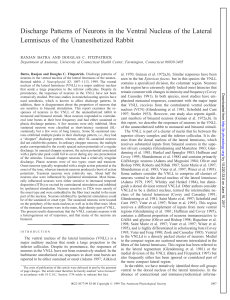
Discharge Patterns of Neurons in the Ventral Nucleus of the Lateral
... The multiunit cluster was included because it had a discharge pattern not reported in lower centers and because its location was marked. The responses of two neurons at marked recording sites in the rostral periolivary region also have been included for comparison. The responses of some of these neu ...
... The multiunit cluster was included because it had a discharge pattern not reported in lower centers and because its location was marked. The responses of two neurons at marked recording sites in the rostral periolivary region also have been included for comparison. The responses of some of these neu ...
Temporal delays among place cells determine the frequency of
... pose several questions. Given that the output of hippocampal pyramidal cells is in tune with their targets, how do phase precessing place cells generate a rhythmic activity at theta frequency? Furthermore, how does the neuronal coordination allow for large differences of place cell oscillation frequ ...
... pose several questions. Given that the output of hippocampal pyramidal cells is in tune with their targets, how do phase precessing place cells generate a rhythmic activity at theta frequency? Furthermore, how does the neuronal coordination allow for large differences of place cell oscillation frequ ...
Efficient gene delivery to the adult and fetal CNS using
... pseudotyped vector also showed neuron-specific transduction in the cortex (Figures 2g, h and j). However, although transduced neurons were observed in the cortex in both hemispheres, the efficiency of transduction was clearly much less than that seen using VSVG pseudotype. Similarly, low levels of n ...
... pseudotyped vector also showed neuron-specific transduction in the cortex (Figures 2g, h and j). However, although transduced neurons were observed in the cortex in both hemispheres, the efficiency of transduction was clearly much less than that seen using VSVG pseudotype. Similarly, low levels of n ...
Neuropeptidergic Organization of the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus in
... the SCN, or microstimulation of the IGL, will both cause phase advances or delays depending on circadian phase. The phase response curve for the phase shifting effects of NPY are different from that caused by light [2,33,60,64]. In addition, the level of NPY in the SCN shows two peaks at the day/nig ...
... the SCN, or microstimulation of the IGL, will both cause phase advances or delays depending on circadian phase. The phase response curve for the phase shifting effects of NPY are different from that caused by light [2,33,60,64]. In addition, the level of NPY in the SCN shows two peaks at the day/nig ...
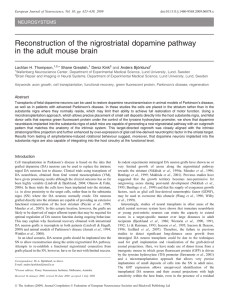
Reconstruction of the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway in the adult
... Structure and placement of intranigral grafts At killing (6 and 16 weeks after transplantation) the grafts appeared as well-demarcated round or oval cell clusters located within, or immediately adjacent to, the SN, identifiable by their content of GFP+ neurons (Figs 1a, 2g and 3a). In the animals not ...
... Structure and placement of intranigral grafts At killing (6 and 16 weeks after transplantation) the grafts appeared as well-demarcated round or oval cell clusters located within, or immediately adjacent to, the SN, identifiable by their content of GFP+ neurons (Figs 1a, 2g and 3a). In the animals not ...
chapter 4 the evolution of body, brain, behavior, and mind in
... are interconnected by way of a meshwork of vertically aligned bipolar cells and horizontally oriented amacrine cells, and there is a layer of ganglion cells whose axons form the optic nerve (Dowling, 1968; Fig. 4-5B). The processing of visual input begins at the retinal level where many ganglion cel ...
... are interconnected by way of a meshwork of vertically aligned bipolar cells and horizontally oriented amacrine cells, and there is a layer of ganglion cells whose axons form the optic nerve (Dowling, 1968; Fig. 4-5B). The processing of visual input begins at the retinal level where many ganglion cel ...
Spatial cognition and neuro-mimetic navigation: a model of
... medial septum via the fornix ®ber bundle) (Burgess et al. 1999). We focus on neocortical inputs and in particular on the information coming from the posterior parietal cortex. Lesion data on humans and monkeys suggest that parietal areas are involved in spatial cognition and spatial behavior (Burges ...
... medial septum via the fornix ®ber bundle) (Burgess et al. 1999). We focus on neocortical inputs and in particular on the information coming from the posterior parietal cortex. Lesion data on humans and monkeys suggest that parietal areas are involved in spatial cognition and spatial behavior (Burges ...
Effect of Tactile Inputs on Thalamic Responses to Noxious
... conditioning procedure by giving tactile stimulation either immediately before CRD or overlapping it. Twenty-five ventroposterior lateral (VPL) thalamic neurons were found among numerous tactile-only neurons to have convergent inputs from both tactile and visceral sources. Their responses to CRD wer ...
... conditioning procedure by giving tactile stimulation either immediately before CRD or overlapping it. Twenty-five ventroposterior lateral (VPL) thalamic neurons were found among numerous tactile-only neurons to have convergent inputs from both tactile and visceral sources. Their responses to CRD wer ...
Neurotransmitter Function
... The potential fluctuates depending on the flow and concentration of ions inside and outside the cell. • depolarized or hyperpolarized ...
... The potential fluctuates depending on the flow and concentration of ions inside and outside the cell. • depolarized or hyperpolarized ...
MIRROR NEURON FUNCTION: AN EXAMINATION OF
... referred to as emotional contagion, when you feel physically along with the other person as if their emotions are contagious. An example of this would be crying in response to a scene of a movie in which the character is sad or crying. Emotional empathy is a connection between individuals resulting ...
... referred to as emotional contagion, when you feel physically along with the other person as if their emotions are contagious. An example of this would be crying in response to a scene of a movie in which the character is sad or crying. Emotional empathy is a connection between individuals resulting ...
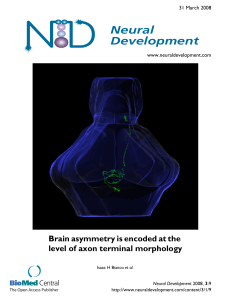
Brain asymmetry is encoded at the level of axon terminal morphology
... of neuron described to date. There are two quite distinct sub-types of axon arbor that differ both in branching morphology and in their localization within the target nucleus. Critically, both arbor morphologies are elaborated by both left and right-sided neurons, but at greatly differing frequencie ...
... of neuron described to date. There are two quite distinct sub-types of axon arbor that differ both in branching morphology and in their localization within the target nucleus. Critically, both arbor morphologies are elaborated by both left and right-sided neurons, but at greatly differing frequencie ...
The role of nitric oxide in the hypothalamic control of LHRH and
... LHRH release. NO stimulates the release of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) in response to norepinephrine (NE), estrogen (E) and glutamic acid (GLU). NO released from vicinal NO-ergic neuron diffuses to NO-responsive LHRH neurosecretory neuron causing sGC-catalyzed conversion of GTP into ...
... LHRH release. NO stimulates the release of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) in response to norepinephrine (NE), estrogen (E) and glutamic acid (GLU). NO released from vicinal NO-ergic neuron diffuses to NO-responsive LHRH neurosecretory neuron causing sGC-catalyzed conversion of GTP into ...
Executive Control Over Cognition: Stronger and Earlier Rule
... Human cognition is characterized by flexibility, the ability to select not only which action but which cognitive process to engage to best achieve the current behavioral objective. The ability to tailor information processing in the brain to rules, goals, or context is typically referred to as execu ...
... Human cognition is characterized by flexibility, the ability to select not only which action but which cognitive process to engage to best achieve the current behavioral objective. The ability to tailor information processing in the brain to rules, goals, or context is typically referred to as execu ...
Unit 22.1: The Nervous System
... The sympathetic division deals with emergency situations. It prepares the body for “fight or flight.” Do you get clammy palms or a racing heart when you have to play a solo or give a speech? Nerves of the sympathetic division control these responses. • The parasympathetic division controls involunt ...
... The sympathetic division deals with emergency situations. It prepares the body for “fight or flight.” Do you get clammy palms or a racing heart when you have to play a solo or give a speech? Nerves of the sympathetic division control these responses. • The parasympathetic division controls involunt ...
Laminar Differences in Dendritic Structure of Pyramidal Neurons in
... less spinous, than those of the granular prefrontal cortex (Lund et al. 1993; Elston et al. 2001; Jacobs et al. 2001; Elston and Rockland 2002; Elston et al. 2011; Bianchi et al. 2013; Oga et al. 2013). Regional variations in pyramidal cell structure have also been reported in mice, although a lower ...
... less spinous, than those of the granular prefrontal cortex (Lund et al. 1993; Elston et al. 2001; Jacobs et al. 2001; Elston and Rockland 2002; Elston et al. 2011; Bianchi et al. 2013; Oga et al. 2013). Regional variations in pyramidal cell structure have also been reported in mice, although a lower ...
Massive Loss of Mid- and Hindbrain Neurons during Embryonic
... present in the nucleus at this age (Fig. 4). The large motor neurons of this nucleus appear indistinguishable in Lc/Lc animals when compared with their Lc/1 and wild-type (not shown) littermates. Furthermore, there was no large difference in neuronal cell number in either the hindbrain or midbrain a ...
... present in the nucleus at this age (Fig. 4). The large motor neurons of this nucleus appear indistinguishable in Lc/Lc animals when compared with their Lc/1 and wild-type (not shown) littermates. Furthermore, there was no large difference in neuronal cell number in either the hindbrain or midbrain a ...
the functional properties of the light
... system, for it is known to receive convergent inputs from both the geniculostriate and the collicular portions of the visual system. The striate and the prestriate areas are believed to project upon the inferior parietal lobule over a multiple-stage, transcortical system. Area 7 also receives and pr ...
... system, for it is known to receive convergent inputs from both the geniculostriate and the collicular portions of the visual system. The striate and the prestriate areas are believed to project upon the inferior parietal lobule over a multiple-stage, transcortical system. Area 7 also receives and pr ...
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION I Tim Murphy NRSC 500, 2011
... • Contrary to electrical transmission multiple steps are required to release transmitter chemicals and for them to act on postsynaptic receptors, resulting in a time delay (can be as short as 0.2 msec, from Ca2+ entry to secretion). • Directional, select localization of release machinery to presynap ...
... • Contrary to electrical transmission multiple steps are required to release transmitter chemicals and for them to act on postsynaptic receptors, resulting in a time delay (can be as short as 0.2 msec, from Ca2+ entry to secretion). • Directional, select localization of release machinery to presynap ...
dynamics of pathomorphological changes in rat ischemic spinal cord
... The damaging effect of ischemia results in irreversible neuronal changes – the formation of focal necrosis and infarct core (1). For several hours the area of the central “punctate” infarction is surrounded by ischemic, but viable tissue – the so-called ischemic penumbra (2). In the area of the penu ...
... The damaging effect of ischemia results in irreversible neuronal changes – the formation of focal necrosis and infarct core (1). For several hours the area of the central “punctate” infarction is surrounded by ischemic, but viable tissue – the so-called ischemic penumbra (2). In the area of the penu ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.