Operant Conditioning - Little Miami Schools
... Learning in which a certain action is reinforced or punished, resulting in behavioral change ...
... Learning in which a certain action is reinforced or punished, resulting in behavioral change ...
File - NOTES SOLUTION
... Classical Conditioning It grew out in response to teach dog to salivate in response to ringing of a bell in early 1900s by Ivan Pavlov. In Pavlov experiment meat was unconditional stimulus and salivation was unconditional response. Learning a conditioned response involves building an associat ...
... Classical Conditioning It grew out in response to teach dog to salivate in response to ringing of a bell in early 1900s by Ivan Pavlov. In Pavlov experiment meat was unconditional stimulus and salivation was unconditional response. Learning a conditioned response involves building an associat ...
Lecture 3 - Learning to make your brain happy
... 2. The CS must predict the US: Contingency is important Extinction 3. All associations are not equivalent: (e.g. Taste Aversion) Preparedness (revisited) 4. Timing is critical The Operant Conditioning paradigm Remember the Law of Effect Superstitious behavior Positive reinforcement ...
... 2. The CS must predict the US: Contingency is important Extinction 3. All associations are not equivalent: (e.g. Taste Aversion) Preparedness (revisited) 4. Timing is critical The Operant Conditioning paradigm Remember the Law of Effect Superstitious behavior Positive reinforcement ...
Operant conditioning - New Paltz Central School District
... play fetch. While playing fetch one afternoon with a tennis ball, she accidently picked up the ball after it had, landed in a fire ant hill. Needless to say, Greta’s mouth got many painful bites. From that point on, Greta avoided any ball that was the same size as a tennis ball or smaller. ...
... play fetch. While playing fetch one afternoon with a tennis ball, she accidently picked up the ball after it had, landed in a fire ant hill. Needless to say, Greta’s mouth got many painful bites. From that point on, Greta avoided any ball that was the same size as a tennis ball or smaller. ...
Behavior Therapies
... • Aversive Conditioning – Uses classical conditioning to create a negative response to a stimulus • i.e. – nausea or shock with undesirable actions, thoughts, situations (drinking, smoking, etc.) ...
... • Aversive Conditioning – Uses classical conditioning to create a negative response to a stimulus • i.e. – nausea or shock with undesirable actions, thoughts, situations (drinking, smoking, etc.) ...
Behavior Therapies
... • Aversive Conditioning – Uses classical conditioning to create a negative response to a stimulus • i.e. – nausea or shock with undesirable actions, thoughts, situations (drinking, smoking, etc.) ...
... • Aversive Conditioning – Uses classical conditioning to create a negative response to a stimulus • i.e. – nausea or shock with undesirable actions, thoughts, situations (drinking, smoking, etc.) ...
Behavior Therapies
... • Aversive Conditioning – Uses classical conditioning to create a negative response to a stimulus • i.e. – nausea or shock with undesirable actions, thoughts, situations (drinking, smoking, etc.) ...
... • Aversive Conditioning – Uses classical conditioning to create a negative response to a stimulus • i.e. – nausea or shock with undesirable actions, thoughts, situations (drinking, smoking, etc.) ...
1. Introduction and Chapter 1 What is Applied Behavior
... o How to measure bipolar personality (or manipulate it) independent of verbal report? ...
... o How to measure bipolar personality (or manipulate it) independent of verbal report? ...
The Tales of Operant Conditioning
... Goal of reinforcement is to strengthen behavior and increase likelihood that it will occur again in future. Examples: Continuous Reinforcement- reinforced every time something occurs. (Ex: Every time a little boy/girl draws a picture, you say, “Oh, how pretty!” Partial Reinforcement- Response re ...
... Goal of reinforcement is to strengthen behavior and increase likelihood that it will occur again in future. Examples: Continuous Reinforcement- reinforced every time something occurs. (Ex: Every time a little boy/girl draws a picture, you say, “Oh, how pretty!” Partial Reinforcement- Response re ...
HISTORY AND METHODS
... Double-blind study- neither participants or researchers know who is in which group Hypothesis- a statement of the results that the experimenter expects Subjects- people or animals in the experiment Independent variable- factor that the experimenter manipulates in a study Dependent variable- the fact ...
... Double-blind study- neither participants or researchers know who is in which group Hypothesis- a statement of the results that the experimenter expects Subjects- people or animals in the experiment Independent variable- factor that the experimenter manipulates in a study Dependent variable- the fact ...
Behaviorism What is Learning? - University of California, Irvine
... • Operant Conditioning Is Intended to Explain All Behavior, Including Complex Behavior – All behavior is the product of reinforcement histories – What did you do today? ...
... • Operant Conditioning Is Intended to Explain All Behavior, Including Complex Behavior – All behavior is the product of reinforcement histories – What did you do today? ...
Behaviorism_298 (English) - UC Irvine, OpenCourseWare
... What’s Wrong With Behaviorism? Noam Chomsky’s Critique of Skinner’s Book, “Verbal Behavior” Language can’t be learned only through reinforcement The brain must be a built-in (innate) language ...
... What’s Wrong With Behaviorism? Noam Chomsky’s Critique of Skinner’s Book, “Verbal Behavior” Language can’t be learned only through reinforcement The brain must be a built-in (innate) language ...
Behavior - Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
... What’s Wrong With Behaviorism? Noam Chomsky’s Critique of Skinner’s Book, “Verbal Behavior” Language can’t be learned only through reinforcement The brain must be a builtin (innate) language ...
... What’s Wrong With Behaviorism? Noam Chomsky’s Critique of Skinner’s Book, “Verbal Behavior” Language can’t be learned only through reinforcement The brain must be a builtin (innate) language ...
Myers Module Twenty One
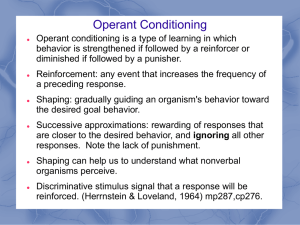
... Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Reinforcement: any event that increases the frequency of a preceding response. ...
... Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Reinforcement: any event that increases the frequency of a preceding response. ...
Behaviorism
... Behavior therapy is rooted in an outer paradigm that focuses on the environment instead of an inner paradigm that focuses on biological functions, mind, genes, etc. Behavior therapy originally included variables such as feelings and thoughts. Quoting Skinner, “Behavior is what the organism is doing ...
... Behavior therapy is rooted in an outer paradigm that focuses on the environment instead of an inner paradigm that focuses on biological functions, mind, genes, etc. Behavior therapy originally included variables such as feelings and thoughts. Quoting Skinner, “Behavior is what the organism is doing ...
Behavior - Catawba County Schools
... to any words that describe innate, or unlearned, behaviors. Write the letter “L” next to any words that describe learned behaviors. Student answers may include the following: Blinking eyes (I), Tapping pencil (L), Rubbing your eyes (I), Crying (I), Building a spider web (I), Migration (I and L), Hib ...
... to any words that describe innate, or unlearned, behaviors. Write the letter “L” next to any words that describe learned behaviors. Student answers may include the following: Blinking eyes (I), Tapping pencil (L), Rubbing your eyes (I), Crying (I), Building a spider web (I), Migration (I and L), Hib ...
classical conditioning
... • Ivan Pavlov exposed dogs to a bell ringing and at the same time sprayed their mouths with powdered meat, causing them to salivate. • Soon, the dogs would salivate after hearing the bell but not getting any powdered meat. ...
... • Ivan Pavlov exposed dogs to a bell ringing and at the same time sprayed their mouths with powdered meat, causing them to salivate. • Soon, the dogs would salivate after hearing the bell but not getting any powdered meat. ...
Chapter 5 - Behavior Therapy
... Complains of recurrent obsessive thoughts about stealing Not optimistic about therapy ...
... Complains of recurrent obsessive thoughts about stealing Not optimistic about therapy ...
Learning Theory Theorists (Alphabetical) Year Ideals Classroom
... will continue until the next time we need to make an adjustment to it. Skinner believed that the best way to understand behavior is to look at the causes of an action and its consequences. This approach is called Operant Conditioning. Based on the work of Thorndike (1905). Behavior that is reinforce ...
... will continue until the next time we need to make an adjustment to it. Skinner believed that the best way to understand behavior is to look at the causes of an action and its consequences. This approach is called Operant Conditioning. Based on the work of Thorndike (1905). Behavior that is reinforce ...
Overview of Ch. 6: Behavioral Views of Learning Respondent
... – Schedules of reinforcement. Which schedules of reinforcement are best for ...
... – Schedules of reinforcement. Which schedules of reinforcement are best for ...
Identifying goals and target behaviors. The first step is
... When they returned with the data, he carefully reviewed the records with them. In doing so, he noticed a pattern: Each of their arguments had occurred just after one or the other had left a household chore undone, such as leaving dirty dishes in the sink or drap ing dothes on the only chair in the ...
... When they returned with the data, he carefully reviewed the records with them. In doing so, he noticed a pattern: Each of their arguments had occurred just after one or the other had left a household chore undone, such as leaving dirty dishes in the sink or drap ing dothes on the only chair in the ...