Classical Conditioning Documentary
... Unconditioned stimulus–unconditioned response pairings are unlearned and untrained. During conditioning, a previously neutral stimulus is transformed into a conditioned stimulus. A conditioned stimulus leads to a conditioned response, and a conditioned stimulus– conditioned response pairing is ...
... Unconditioned stimulus–unconditioned response pairings are unlearned and untrained. During conditioning, a previously neutral stimulus is transformed into a conditioned stimulus. A conditioned stimulus leads to a conditioned response, and a conditioned stimulus– conditioned response pairing is ...
pleasure principle”.
... Social – other people are an important source of information Self-efficacy – the result of experience which results in a person’s belief about their own abilities/talents. This sense of self esteem will significantly affect interaction, resulting in the “self-fulfilling prophecy” and reflects CONT ...
... Social – other people are an important source of information Self-efficacy – the result of experience which results in a person’s belief about their own abilities/talents. This sense of self esteem will significantly affect interaction, resulting in the “self-fulfilling prophecy” and reflects CONT ...
Learning, Memory, Emotion and Language - Ping Pong
... However, the tone (neutral stimulus) does not ...
... However, the tone (neutral stimulus) does not ...
Katie Ross EDUF 7130 Dr. Jonathan Hilpert 5 September 2015
... Expanding on the behaviorist principles of Pavlov, Thorndike, and Watson, among others, B. F. Skinner developed the principle known as operant conditioning in the 1930s. He is often regarded as the “father of operant conditioning,” because he coined the term after a series of experiments performed o ...
... Expanding on the behaviorist principles of Pavlov, Thorndike, and Watson, among others, B. F. Skinner developed the principle known as operant conditioning in the 1930s. He is often regarded as the “father of operant conditioning,” because he coined the term after a series of experiments performed o ...
Learning
... Conditioning is learned through association. Classical Conditioning is a learning process in which associations are made between a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus. ...
... Conditioning is learned through association. Classical Conditioning is a learning process in which associations are made between a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus. ...
Behavior Analysis in Animal Training
... several people including Watson and Pavlov. Skinner actually expanded Watson’s work on behaviorism when he described the science of operant conditioning. Operant conditioning is the area of behaviorism that explains the relationship between environmental events and actions. Skinner discovered while ...
... several people including Watson and Pavlov. Skinner actually expanded Watson’s work on behaviorism when he described the science of operant conditioning. Operant conditioning is the area of behaviorism that explains the relationship between environmental events and actions. Skinner discovered while ...
Griggs Chapter 4: Learning
... In a fixed interval schedule, a reinforcer is delivered after the first response is given once a set interval of time has elapsed (e.g., periodic exams in a class, with most behaving/studying occurring right before the exam/reinforcer) In a variable interval schedule, a reinforcer is delivered after ...
... In a fixed interval schedule, a reinforcer is delivered after the first response is given once a set interval of time has elapsed (e.g., periodic exams in a class, with most behaving/studying occurring right before the exam/reinforcer) In a variable interval schedule, a reinforcer is delivered after ...
Griggs Chapter 4: Learning
... In a fixed interval schedule, a reinforcer is delivered after the first response is given once a set interval of time has elapsed (e.g., periodic exams in a class, with most behaving/studying occurring right before the exam/reinforcer) In a variable interval schedule, a reinforcer is delivered after ...
... In a fixed interval schedule, a reinforcer is delivered after the first response is given once a set interval of time has elapsed (e.g., periodic exams in a class, with most behaving/studying occurring right before the exam/reinforcer) In a variable interval schedule, a reinforcer is delivered after ...
PPT
... • reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses • faster you respond the more rewards you get • very high rate of responding • like piecework pay ...
... • reinforces a response only after a specified number of responses • faster you respond the more rewards you get • very high rate of responding • like piecework pay ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Mr. Padron`s Psychology
... – Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS): any stimulus that will always and naturally ELICIT a response – Unconditioned Response (UCR): any response that always and naturally occurs at the presentation of the UCS – Neutral Stimulus (NS): any stimulus that does not naturally elicit a response associated with t ...
... – Unconditioned Stimulus (UCS): any stimulus that will always and naturally ELICIT a response – Unconditioned Response (UCR): any response that always and naturally occurs at the presentation of the UCS – Neutral Stimulus (NS): any stimulus that does not naturally elicit a response associated with t ...
AP Psychology Unit VI: Learning Biological, Latent, Cognitive
... YouTube: Do Lab Rats Dream of Running Mazes? ...
... YouTube: Do Lab Rats Dream of Running Mazes? ...
Current View - HCC Learning Web
... Exercises 1. (Voluntary, reflexive) responses are subject to operant conditioning. 3. Identify each change described below as an example of (E) extinction, (G) generalization, (D) discriminative stimulus, or (R) reinforcement _____ Ms. Jackson starting buying tickets more often after she won $100 pl ...
... Exercises 1. (Voluntary, reflexive) responses are subject to operant conditioning. 3. Identify each change described below as an example of (E) extinction, (G) generalization, (D) discriminative stimulus, or (R) reinforcement _____ Ms. Jackson starting buying tickets more often after she won $100 pl ...
Power Point - D. Fry Science
... Learning seems to be governed by what’s now known as PREPAREDNESS PRINCIPLE (Seligman,1970) By virtue of its evolutionary history, every species is predisposed to form certain kinds of associations. – Prepared (predisposed to acquire) – Unprepared (not predisposed to acquire) – Contraprepared (n ...
... Learning seems to be governed by what’s now known as PREPAREDNESS PRINCIPLE (Seligman,1970) By virtue of its evolutionary history, every species is predisposed to form certain kinds of associations. – Prepared (predisposed to acquire) – Unprepared (not predisposed to acquire) – Contraprepared (n ...
PSYC 120 Conditioning Homework Name
... The UCS (unconditioned stimulus) is the stimulus that automatically triggers a bodily response or emotional reaction. The UCR (unconditioned response) is the response the UCS automatically triggers. No learning is required for the UCS UCR. If some neutral stimulus is present before or during the U ...
... The UCS (unconditioned stimulus) is the stimulus that automatically triggers a bodily response or emotional reaction. The UCR (unconditioned response) is the response the UCS automatically triggers. No learning is required for the UCS UCR. If some neutral stimulus is present before or during the U ...
File
... 4. The key to classical conditioning is that it’s a natural thing, there is no decision involved. Usually it’s a biological process over which the person/animal has no control. 1. A person could be classically conditioned using the pucker response to a lemon, or cringe response to fingernails on a ...
... 4. The key to classical conditioning is that it’s a natural thing, there is no decision involved. Usually it’s a biological process over which the person/animal has no control. 1. A person could be classically conditioned using the pucker response to a lemon, or cringe response to fingernails on a ...
File
... 13. After pigs learned to pick up and deposit wooden coins in a piggy bank, the pigs subsequently dropped the coins repeatedly and pushed them with their snouts. This best illustrates the importance of ________ in operant conditioning. A) primary reinforcement B) spontaneous recovery C) latent lear ...
... 13. After pigs learned to pick up and deposit wooden coins in a piggy bank, the pigs subsequently dropped the coins repeatedly and pushed them with their snouts. This best illustrates the importance of ________ in operant conditioning. A) primary reinforcement B) spontaneous recovery C) latent lear ...
Learning
... number of responses- FR-5 VR (Variable ratio) = Reinforcement after varied number of responses (average number of responses set- VR-5) FI (Fixed Interval) =Fixed amount of time set before reward for behavior- FI 3 VI (variable interval) =varied amount of time ...
... number of responses- FR-5 VR (Variable ratio) = Reinforcement after varied number of responses (average number of responses set- VR-5) FI (Fixed Interval) =Fixed amount of time set before reward for behavior- FI 3 VI (variable interval) =varied amount of time ...
3 slides
... problem: no evidence of conditioned goal-related responses during instrumental conditioning ...
... problem: no evidence of conditioned goal-related responses during instrumental conditioning ...
Instrumental Conditioning: Theoretical Issues
... different context effects of extinction trials limit ...
... different context effects of extinction trials limit ...
Learning - Amazon S3
... stimuli. When studying an animal, if a stimulus is played over and over and over again and the animal gets very bored with it, looking time will decrease. When faced with a new, or novel, stimulus (and the animal can tell that it's new), looking time will increase. But if it can't tell the differ ...
... stimuli. When studying an animal, if a stimulus is played over and over and over again and the animal gets very bored with it, looking time will decrease. When faced with a new, or novel, stimulus (and the animal can tell that it's new), looking time will increase. But if it can't tell the differ ...
Introduction
... Click may be particularly good for training as opposed to maintenance phase. I find clicker useful in teaching good timing. Cognitive View According to this view, the CR (or CP) provides the organism with info. o CR says “keep doing what your doing” or “you did great”. o CP says “stop that & ...
... Click may be particularly good for training as opposed to maintenance phase. I find clicker useful in teaching good timing. Cognitive View According to this view, the CR (or CP) provides the organism with info. o CR says “keep doing what your doing” or “you did great”. o CP says “stop that & ...
COMPLETE REVISION SUMMARY
... • Pavlov set up a series of trials to test this • Each time the dog was fed, a bell was rung for a few seconds • The amount of saliva produced by the dog was measured • The bell was then rung and no food was given • The same amount of saliva was produced, even without food • http://www.youtube.com/w ...
... • Pavlov set up a series of trials to test this • Each time the dog was fed, a bell was rung for a few seconds • The amount of saliva produced by the dog was measured • The bell was then rung and no food was given • The same amount of saliva was produced, even without food • http://www.youtube.com/w ...
PSYCHOLOGY
... stimulus that is paired with an unconditioned stimulus that provokes a response Bell + food salivates Bell salivates ...
... stimulus that is paired with an unconditioned stimulus that provokes a response Bell + food salivates Bell salivates ...
Ciccarelli Chapter 5
... having “free will” is an illusion or myth and that human and animal behavior is completely determined by environmental and genetic influences. For Skinner, the mind was a “black box” whose contents cannot be illuminated by science. For Skinner, behavior is shaped by its consequences. Reinforcer – ...
... having “free will” is an illusion or myth and that human and animal behavior is completely determined by environmental and genetic influences. For Skinner, the mind was a “black box” whose contents cannot be illuminated by science. For Skinner, behavior is shaped by its consequences. Reinforcer – ...
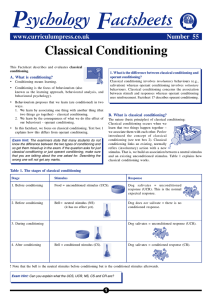
Classical Conditioning
... (b) Smelling a particular odour can bring back memories of a person/place. (c) Taste aversion is where the taste of a substance is associated with an unpleasant experience, such as nausea (e.g., if you have been sick from a particular food/drink, then you may feel sick again just seeing or smelling ...
... (b) Smelling a particular odour can bring back memories of a person/place. (c) Taste aversion is where the taste of a substance is associated with an unpleasant experience, such as nausea (e.g., if you have been sick from a particular food/drink, then you may feel sick again just seeing or smelling ...
Classical conditioning

Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a learning process in which an innate response to a potent stimulus comes to be elicited in response to a previously neutral stimulus; this is achieved by repeated pairings of the neutral stimulus with the potent stimulus. The basic facts about classical conditioning were discovered by Ivan Pavlov through his famous experiments with dogs. Together with operant conditioning, classical conditioning became the foundation of Behaviorism, a school of psychology that dominated psychology in the mid-20th century and is still an important influence on the practice of psychological therapy and the study of animal behaviour (ethology). Classical conditioning is now the best understood of the basic learning processes, and its neural substrates are beginning to be understood.