chapter 17
... – observers who watch models being rewarded for certain behaviors tend to repeat them, whereas observers who watch models being punished for their actions tend not to repeat those actions. – observers are more likely to imitate aggressive models who receive no punishment for their behavior. • even w ...
... – observers who watch models being rewarded for certain behaviors tend to repeat them, whereas observers who watch models being punished for their actions tend not to repeat those actions. – observers are more likely to imitate aggressive models who receive no punishment for their behavior. • even w ...
Unit 3: Learning and Memory
... When a child cleans his room, his parents The child cleans his room more often, so read him a story as to hear more stories ...
... When a child cleans his room, his parents The child cleans his room more often, so read him a story as to hear more stories ...
Conditioning
... behavior. • only works when guaranteed • severe punishments may cause a person to simply leave the situation • Context must always be apparent • sometimes is accompanied by unseen benefits that make the behavior increase rather than decrease ...
... behavior. • only works when guaranteed • severe punishments may cause a person to simply leave the situation • Context must always be apparent • sometimes is accompanied by unseen benefits that make the behavior increase rather than decrease ...
Journal - Foothill Technology High School
... With a partner, come up with your own example for each of the following: – Positive Reinforcement – Negative Reinforcement – Positive Punishment – Negative Punishment ...
... With a partner, come up with your own example for each of the following: – Positive Reinforcement – Negative Reinforcement – Positive Punishment – Negative Punishment ...
BF Skinner: Operant Conditioning
... • Neutral operants: responses from the environment that neither increase nor decrease the probability of a behaviour being repeated. • Reinforcers: Responses from the environment that increase the probability of a behaviour being repeated. Reinforcers can be either positive or negative. • Punishers: ...
... • Neutral operants: responses from the environment that neither increase nor decrease the probability of a behaviour being repeated. • Reinforcers: Responses from the environment that increase the probability of a behaviour being repeated. Reinforcers can be either positive or negative. • Punishers: ...
Operant Conditioning
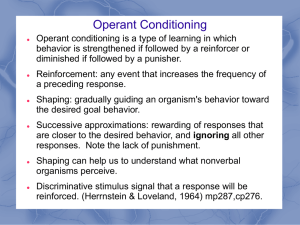
... strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. ...
... strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. ...
Behavior Therapy - Mypage Web Server
... The act of perceiving or watching something and learning from it. Retention processes: This basically refers to remembering that which has been observed. Motor reproduction processes: This refers to translating what one has seen into action using motor skills. ...
... The act of perceiving or watching something and learning from it. Retention processes: This basically refers to remembering that which has been observed. Motor reproduction processes: This refers to translating what one has seen into action using motor skills. ...
Strengths
... - Finkelstein and Ramey, 1977: two groups of babies; one was given control over a mobile, one wasn’t. After both were conditioned, the groups were switched…the babies that were not originally given control never learned to control the mobile. - Imprinting: any kind of phase-sensitive learning (learn ...
... - Finkelstein and Ramey, 1977: two groups of babies; one was given control over a mobile, one wasn’t. After both were conditioned, the groups were switched…the babies that were not originally given control never learned to control the mobile. - Imprinting: any kind of phase-sensitive learning (learn ...
Learning
... • Conditioned response – A learned response that occurs in response to a conditioned or learned stimulus. – This response is similar to but not as strong as the unconditioned response. For example, Pavlov’s dog produced less saliva in response to the bell than to the food. ...
... • Conditioned response – A learned response that occurs in response to a conditioned or learned stimulus. – This response is similar to but not as strong as the unconditioned response. For example, Pavlov’s dog produced less saliva in response to the bell than to the food. ...
Myers Module Twenty One
... Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Reinforcement: any event that increases the frequency of a preceding response. ...
... Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Reinforcement: any event that increases the frequency of a preceding response. ...
Operant Conditioning
... Other applications (cont.) At work Reward specific, achievable behaviors, not vaguely defined “merit” Reinforcement should be immediate ...
... Other applications (cont.) At work Reward specific, achievable behaviors, not vaguely defined “merit” Reinforcement should be immediate ...
Ch 9 Reviewx
... John B. Watson is associated with what type of behavior modification (classical, operant or social learning)? Classical conditioning ...
... John B. Watson is associated with what type of behavior modification (classical, operant or social learning)? Classical conditioning ...
Habituation - WordPress.com
... Spontaneous Recovery: Returning to a behavior for which you are no longer reinforced. Generalization: Assuming that similar behaviors will also generate the same consequence. Discrimination: Knowing which behaviors will generate a consequence and which won’t. Discriminatory Stimulus: A stimulus, in ...
... Spontaneous Recovery: Returning to a behavior for which you are no longer reinforced. Generalization: Assuming that similar behaviors will also generate the same consequence. Discrimination: Knowing which behaviors will generate a consequence and which won’t. Discriminatory Stimulus: A stimulus, in ...
Psy 113 Assignment 3: Learning Activities 10 points DUE Monday 2
... For each of the following examples, identify the type of operant condition that is taking place: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, punishment or extinction. (Identify whether the consequences for person performing the behavior was good, bad, or none. Consider whether the behavior is li ...
... For each of the following examples, identify the type of operant condition that is taking place: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, punishment or extinction. (Identify whether the consequences for person performing the behavior was good, bad, or none. Consider whether the behavior is li ...
Behavior Analysis in Animal Training
... effects that different consequences have on new behaviors. His “Law of Effect” said that responses that produce rewards will tend to increase in frequency. Thorndike’s work laid the groundwork for the development of operant conditioning. Another key person in the development of behaviorism as we kno ...
... effects that different consequences have on new behaviors. His “Law of Effect” said that responses that produce rewards will tend to increase in frequency. Thorndike’s work laid the groundwork for the development of operant conditioning. Another key person in the development of behaviorism as we kno ...
2. Operant Conditioning
... a) Distinction with CC b) Skinner -Shaping c) Reinforcement d) Punishment e) Application: Gaining Self-Control** ...
... a) Distinction with CC b) Skinner -Shaping c) Reinforcement d) Punishment e) Application: Gaining Self-Control** ...
Chapter15
... For example, “ate because hungry” “ate because good price, 6 hours since last meal, etc.” Free Will vs. Determinism: -Free Will: We are free and spontaneous. We are responsible for what we did. -Determinism: Our behaviors are determined by Environmental control. For example, you bought a computer ...
... For example, “ate because hungry” “ate because good price, 6 hours since last meal, etc.” Free Will vs. Determinism: -Free Will: We are free and spontaneous. We are responsible for what we did. -Determinism: Our behaviors are determined by Environmental control. For example, you bought a computer ...
Structuralism and Functionalism
... Man processes early childhood experiences as a reference for behaviors ...
... Man processes early childhood experiences as a reference for behaviors ...
File - Lindsay Social Studies
... An unconditioned response is the unlearned response that occurs naturally in response to the unconditioned stimulus. How you feel about something is your unconditioned response Can be different each time we see it ...
... An unconditioned response is the unlearned response that occurs naturally in response to the unconditioned stimulus. How you feel about something is your unconditioned response Can be different each time we see it ...
A4 Innate and Learned Behavior
... Innate behavior is inherited from parents and so develops independently of the environment Autonomic and involuntary responses are referred to as reflexes Reflex arcs comprise the neurons that mediate reflexes Reflex conditioning involves forming new associations Learned behavior develops as a resul ...
... Innate behavior is inherited from parents and so develops independently of the environment Autonomic and involuntary responses are referred to as reflexes Reflex arcs comprise the neurons that mediate reflexes Reflex conditioning involves forming new associations Learned behavior develops as a resul ...
Verbal Behavior

Verbal Behavior is a 1957 book by psychologist B. F. Skinner that inspects human behavior, describing what is traditionally called linguistics. The book Verbal Behavior is almost entirely theoretical, involving little experimental research in the work itself. It was an outgrowth of a series of lectures first presented at the University of Minnesota in the early 1940s and developed further in his summer lectures at Columbia and William James lectures at Harvard in the decade before the book's publication. A growing body of research and applications based on Verbal Behavior has occurred since its original publication, particularly in the past decade.In addition, a growing body of research has developed on structural topics in verbal behavior such as grammar.