LOGO - BCE Lab
... a puff of air to the eye. Eventually, the horn alone will produce an eye-blink. In operant conditioning, a response that is followed by a reinforcing consequence becomes more likely to occur on future occasions. In the example shown, a dog learns to sit up when it hears a whistle. ...
... a puff of air to the eye. Eventually, the horn alone will produce an eye-blink. In operant conditioning, a response that is followed by a reinforcing consequence becomes more likely to occur on future occasions. In the example shown, a dog learns to sit up when it hears a whistle. ...
Verbal Behavior Glossary Mark L. Sundberg 2/19/04 Audience
... etc. A speaker is also someone who uses sign language, gestures, signals, written words, codes, pictures, or any form of verbal behavior. Tact An elementary verbal operant involving a response that is evoked by a nonverbal discriminative stimulus and followed by generalized conditioned reinforcement ...
... etc. A speaker is also someone who uses sign language, gestures, signals, written words, codes, pictures, or any form of verbal behavior. Tact An elementary verbal operant involving a response that is evoked by a nonverbal discriminative stimulus and followed by generalized conditioned reinforcement ...
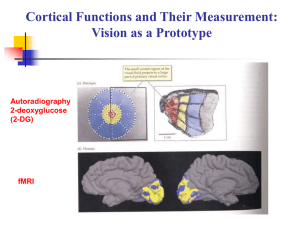
Visual Field and the Human Visual System
... Brain shows much greater activation as subjects look at visual words (2nd row) than when they view a static fixation point (top row). ...
... Brain shows much greater activation as subjects look at visual words (2nd row) than when they view a static fixation point (top row). ...
Unit 6 Study Guide - PSYCHOLOGY
... 16. For operant conditioning to be most effective, when should the reinforcers be presented in relation to the desired response? a. immediately before b. immediately after c. at the same time as d. at least a half hour before 17. The “piecework” or commission, method of payment is an example of whi ...
... 16. For operant conditioning to be most effective, when should the reinforcers be presented in relation to the desired response? a. immediately before b. immediately after c. at the same time as d. at least a half hour before 17. The “piecework” or commission, method of payment is an example of whi ...
Dec9
... given regarding evaluation of words. Always push or always pull, as soon as stimulus is recognized. Congruent responses (e.g., pull subjects responding to good words) significantly faster than incongruent response (e.g., pull subjects responding to bad words) ...
... given regarding evaluation of words. Always push or always pull, as soon as stimulus is recognized. Congruent responses (e.g., pull subjects responding to good words) significantly faster than incongruent response (e.g., pull subjects responding to bad words) ...
Learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning Chapter 7
... that has become associated with the unconditioned stimulus. Although the response to the CS is essentially the same as ...
... that has become associated with the unconditioned stimulus. Although the response to the CS is essentially the same as ...
Critical terms
... behavior that occurs with no particular goal or purpose other than for the pleasure it provides….and it improves future performance. ...
... behavior that occurs with no particular goal or purpose other than for the pleasure it provides….and it improves future performance. ...
Notes Homeostasis Stimulus Response Model
... Negative feedback is process in which a change in a variable/factor is detected which causes a response to occur in the body that reverses the direction of the change i.e. The response to the stimulus opposes or eliminates the stimulus. e.g. An increase in temperature is the change detected. The bod ...
... Negative feedback is process in which a change in a variable/factor is detected which causes a response to occur in the body that reverses the direction of the change i.e. The response to the stimulus opposes or eliminates the stimulus. e.g. An increase in temperature is the change detected. The bod ...
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes: Learning
... situations; punishment increases aggressiveness and attributes bad consequences to the punisher. Cognitive Map: mental images of one’s surroundings. (Mice develop cognitive maps that represent a maze they just ran through.) Latent Learning: demonstration of acquired knowledge only when it is nee ...
... situations; punishment increases aggressiveness and attributes bad consequences to the punisher. Cognitive Map: mental images of one’s surroundings. (Mice develop cognitive maps that represent a maze they just ran through.) Latent Learning: demonstration of acquired knowledge only when it is nee ...
Transfer of Latent Inhibition of Aversively Conditioned
... (Forsyth, 2000). Behavioral models have traditionally been criticised in terms of the absence of conditioning histories for many clients suffering from anxiety disorders (Lazarus, 1984; Rachman, 1977). It has been argued that human fears need not involve a traumatic history of aversive conditioning, ...
... (Forsyth, 2000). Behavioral models have traditionally been criticised in terms of the absence of conditioning histories for many clients suffering from anxiety disorders (Lazarus, 1984; Rachman, 1977). It has been argued that human fears need not involve a traumatic history of aversive conditioning, ...
Behavioral Theories - Educational Psychology Interactive
... Educational Psychology Define and contrast the three types of behavioral learning theories (contiguity, classical conditioning, and operant conditioning), giving examples of how each can be used in the classroom. ...
... Educational Psychology Define and contrast the three types of behavioral learning theories (contiguity, classical conditioning, and operant conditioning), giving examples of how each can be used in the classroom. ...
File
... to put them in his mouth. Then to bring them to you and so on…this is shaping behavior. ...
... to put them in his mouth. Then to bring them to you and so on…this is shaping behavior. ...
Lesson 1: Attributes of Learning and Classical Conditioning
... 1. Positive reinforcement occurs when an appetitive (desired) stimulus follows a behavior. This procedure makes the behavior more likely to recur. For example, if a child is given praise (appetitive stimulus) for picking up a toy (behavior), the child will be more likely to pick up the toy in the fu ...
... 1. Positive reinforcement occurs when an appetitive (desired) stimulus follows a behavior. This procedure makes the behavior more likely to recur. For example, if a child is given praise (appetitive stimulus) for picking up a toy (behavior), the child will be more likely to pick up the toy in the fu ...
answer - Easy Peasy All-in
... The correct order for the three stages of memory is short-term memory, long-term memory, retrieval. working memory, sensory memory, long-term memory. sensory memory, short-term memory, long-term memory. short-term memory, sensory memory, long-term memory. ...
... The correct order for the three stages of memory is short-term memory, long-term memory, retrieval. working memory, sensory memory, long-term memory. sensory memory, short-term memory, long-term memory. short-term memory, sensory memory, long-term memory. ...
Learning—It is all about Change Important terms in
... • Complex emotions (such as fear) are learned and not result of unconscious processes Give me a dozen healthy infants, well-formed, and my own specified world to bring them up in and I ll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to become any type of specialist I might select – doctor, law ...
... • Complex emotions (such as fear) are learned and not result of unconscious processes Give me a dozen healthy infants, well-formed, and my own specified world to bring them up in and I ll guarantee to take any one at random and train him to become any type of specialist I might select – doctor, law ...
Key - Cornell
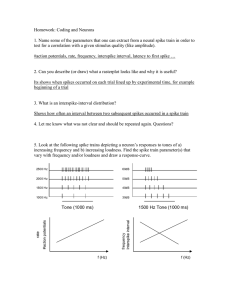
... How can noise be introduced in these simulations? You reset the voltage to 0 after a spike, which creates a refractory period. Or you can even reset it to a negative valule. Noise can be added by making the threshold variable, introducing a noise to the input 6. Look at the diagrams below. Label the ...
... How can noise be introduced in these simulations? You reset the voltage to 0 after a spike, which creates a refractory period. Or you can even reset it to a negative valule. Noise can be added by making the threshold variable, introducing a noise to the input 6. Look at the diagrams below. Label the ...
Reflexes Reaction time
... one motor neuron; monosynaptic refers to the presence of a single chemical synapse) – peripheral muscle reflexes or deep tendon reflexes (patellar reflex, achilles reflex): brief stimulation of the muscle spindle results in contraction of the muscle ...
... one motor neuron; monosynaptic refers to the presence of a single chemical synapse) – peripheral muscle reflexes or deep tendon reflexes (patellar reflex, achilles reflex): brief stimulation of the muscle spindle results in contraction of the muscle ...
Operant Conditioning
... • Do the first 10 on the sheet • Complete the rest for HW. • Turn in next class. ...
... • Do the first 10 on the sheet • Complete the rest for HW. • Turn in next class. ...
SENSORY AND MOTOR SYSTEMS: REFLEXES
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
LEARNING
... ASSOCIATIVE LEARNING – OPERANT CONDITIONING Partial/Intermittent Reinforcement – responses are sometimes reinforced based on rate or timing Fixed Ratio Schedule – behavior is reinforced after a set number of responses Variable-Ratio Schedule – behavior is reinforced after a random/unpredictab ...
... ASSOCIATIVE LEARNING – OPERANT CONDITIONING Partial/Intermittent Reinforcement – responses are sometimes reinforced based on rate or timing Fixed Ratio Schedule – behavior is reinforced after a set number of responses Variable-Ratio Schedule – behavior is reinforced after a random/unpredictab ...
Chapter 7 — Learning
... A. Repeated, spaced practice aids learning of semantic material, such as classroom information. B. ...
... A. Repeated, spaced practice aids learning of semantic material, such as classroom information. B. ...
Exemplary Elementary
... if you don’t follow them? Allowing a parent to drop off a student tardy without a tardy pass because you don’t want to ask them to walk to the office and back will hurt you in the long run. That parent will not understand when you call and explain that their child does not follow procedures because ...
... if you don’t follow them? Allowing a parent to drop off a student tardy without a tardy pass because you don’t want to ask them to walk to the office and back will hurt you in the long run. That parent will not understand when you call and explain that their child does not follow procedures because ...
10 - 11 : Fundamentals of Neurocomputing
... — elements are arranged in groups or layers. — a single layer of neurons that connects to itself is referred to as an autoassociative system. — multi-layer systems contain input and output neurons and neurons which are neither, called hidden units. • brain-like general rules for representations: 1. ...
... — elements are arranged in groups or layers. — a single layer of neurons that connects to itself is referred to as an autoassociative system. — multi-layer systems contain input and output neurons and neurons which are neither, called hidden units. • brain-like general rules for representations: 1. ...