Systems of Memory - Faculty Web Sites at the University of Virginia
... areas as well as the striatum. Patients with striatal abnormalities (e.g., Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease) are impaired on many motor skills (Willingham et al., 1996). They are also impaired, though sometimes to a lesser extent, on other sorts of memory, including explicit and working mem ...
... areas as well as the striatum. Patients with striatal abnormalities (e.g., Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease) are impaired on many motor skills (Willingham et al., 1996). They are also impaired, though sometimes to a lesser extent, on other sorts of memory, including explicit and working mem ...
THE HUMAN MEMORY The human brain, one of the most complex
... Since time immemorial, humans have tried to understand what memory is, how it works and why it goes wrong. It is an important part of what makes us truly human, and yet it is one of the most elusive and misunderstood of human attributes. The popular image of memory is as a kind of tiny filing cabine ...
... Since time immemorial, humans have tried to understand what memory is, how it works and why it goes wrong. It is an important part of what makes us truly human, and yet it is one of the most elusive and misunderstood of human attributes. The popular image of memory is as a kind of tiny filing cabine ...
Following the discussion about mirror neurons and imagery we want
... Ego activity producing not only psychological activities (imagery emotions etc) but giving hierarchical organization to all biological levels of the organism. So the ego is a psycho-physic unit continuously generated and generating. We started with a research (Ruggieri, Fiorenza, Sabatini, 1986) whe ...
... Ego activity producing not only psychological activities (imagery emotions etc) but giving hierarchical organization to all biological levels of the organism. So the ego is a psycho-physic unit continuously generated and generating. We started with a research (Ruggieri, Fiorenza, Sabatini, 1986) whe ...
331CognitionWhatIsIt
... Kept in memory for about 30 seconds unless you focus on it, when it then is transferred into long term memory Can only manage about 7 (+- 2) things at a time in short term memory ...
... Kept in memory for about 30 seconds unless you focus on it, when it then is transferred into long term memory Can only manage about 7 (+- 2) things at a time in short term memory ...
Crash Course Study Guide for AP Psychology Exam
... 2. Midbrain: coordinates basic movements with sensory information 3. Forebrain: large in humans; includes the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures such as the thalamus, hypothalamus, and basal ganglia a. Basal ganglia: regulates muscle contractions/movements b. Thalamus: incorporates and relay ...
... 2. Midbrain: coordinates basic movements with sensory information 3. Forebrain: large in humans; includes the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures such as the thalamus, hypothalamus, and basal ganglia a. Basal ganglia: regulates muscle contractions/movements b. Thalamus: incorporates and relay ...
doc psych 100 review summary
... According to Hebb “set” occurs when two stimuli are presented one after the other and the response to the second is controlled or modified by the first. o The cell assembly theory explains set: The mechanism of thought is a recurrent neural loop that received sensory input from another loop but that ...
... According to Hebb “set” occurs when two stimuli are presented one after the other and the response to the second is controlled or modified by the first. o The cell assembly theory explains set: The mechanism of thought is a recurrent neural loop that received sensory input from another loop but that ...
Why is our capacity of working memory so large
... physiological parameters such as the strength of the NMDA effect and the width of the interaction structure. However, realistic physiological parameters lead typically to a small number of concurrent activity packets consistent with the capacity limit of working memory in the literature. A crucial p ...
... physiological parameters such as the strength of the NMDA effect and the width of the interaction structure. However, realistic physiological parameters lead typically to a small number of concurrent activity packets consistent with the capacity limit of working memory in the literature. A crucial p ...
Learning from a fly`s memory
... difficult (if not impossible) to distinguish between the formation and the retrieval of memories. Yet it will be important to make this distinction if we are to unravel fully the molecular and neural processes underlying the sequential stages of memory. On page 476 of this issue3, Dubnau and colleag ...
... difficult (if not impossible) to distinguish between the formation and the retrieval of memories. Yet it will be important to make this distinction if we are to unravel fully the molecular and neural processes underlying the sequential stages of memory. On page 476 of this issue3, Dubnau and colleag ...
Best Review Sheet Ever - Mr. Voigtschild
... Mood-congruent memory - It‟s easier to recall memories when you are in the same mood you were in when you first learned something. Somatoform Disorder (Somatic Symptom Disorder) – mental disorder – symptoms suggest physical illness/ injury but no cause can be found (mental or physical). ...
... Mood-congruent memory - It‟s easier to recall memories when you are in the same mood you were in when you first learned something. Somatoform Disorder (Somatic Symptom Disorder) – mental disorder – symptoms suggest physical illness/ injury but no cause can be found (mental or physical). ...
Definition of the limbic system
... the same way as the sympathetic nervous system. Being in the blood stream, it takes a bit longer to stop its effects. This is why, when you get upset, it sometimes takes a while before you can !calm yourself down again ...
... the same way as the sympathetic nervous system. Being in the blood stream, it takes a bit longer to stop its effects. This is why, when you get upset, it sometimes takes a while before you can !calm yourself down again ...
Paired-Associate Learning
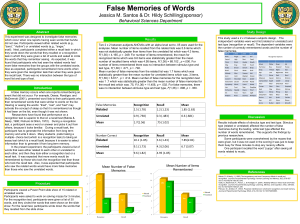
... A recent study by Pierce and Kensinger (2011) describe that “there may be special mechanisms at work when information is both high in arousal and also negative in valence” (p. 141). However, Pierce and Kensinger (2011) did not take into consideration the level of imagery of the word pairs. Their stu ...
... A recent study by Pierce and Kensinger (2011) describe that “there may be special mechanisms at work when information is both high in arousal and also negative in valence” (p. 141). However, Pierce and Kensinger (2011) did not take into consideration the level of imagery of the word pairs. Their stu ...
MEMORY, SLEEP AND OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA Although
... Recently in China, researchers investigated the effects of corticosterone on the hippocampus. They concluded that corticosterone is necessary for the “dentate gyrus,” an important part of the hippocampus that is thought to play a role in the formation of new memories. The researchers also determined ...
... Recently in China, researchers investigated the effects of corticosterone on the hippocampus. They concluded that corticosterone is necessary for the “dentate gyrus,” an important part of the hippocampus that is thought to play a role in the formation of new memories. The researchers also determined ...
File - AP Psychology
... Single-blind procedure – the subjects do not know to what group they belong Double-blind procedure – neither the experimenter nor the subject knows to what group the subjects are in Hawthorne effect – if you know you’re being studied, you will act differently than you normally/typically would Placeb ...
... Single-blind procedure – the subjects do not know to what group they belong Double-blind procedure – neither the experimenter nor the subject knows to what group the subjects are in Hawthorne effect – if you know you’re being studied, you will act differently than you normally/typically would Placeb ...
associative memory ENG - Weizmann Institute of Science
... • If the external inputs are constant the network may reach a stable state, but this is not guaranteed (the attractors may be limit cycles and the network may even be chaotic). • When the recurrent connections are symmetric and there is no self coupling we can write an energy function, such that at ...
... • If the external inputs are constant the network may reach a stable state, but this is not guaranteed (the attractors may be limit cycles and the network may even be chaotic). • When the recurrent connections are symmetric and there is no self coupling we can write an energy function, such that at ...
Psychology 1 - Lake Oswego High School
... ___ psychologists study how people influence one another, including the following areas: first impressions, interpersonal attraction, attitude formation, prejudice, and behavior in a group. ...
... ___ psychologists study how people influence one another, including the following areas: first impressions, interpersonal attraction, attitude formation, prejudice, and behavior in a group. ...
Multi-store Model (PPH 2012)
... When you go to the next page, you will be presented with a line of letters across the screen. Memorise as many of the letters as you can but do not write anything until the word NOW appears. When you see the word NOW appear on the screen, write down on your paper as many of the letters as you ...
... When you go to the next page, you will be presented with a line of letters across the screen. Memorise as many of the letters as you can but do not write anything until the word NOW appears. When you see the word NOW appear on the screen, write down on your paper as many of the letters as you ...
Introduction to Neurotransmitters
... • Neurotransmitters are stored in the neuron’s terminal buttons • When they cross the synapse they fit into receptor sites in the next neuron – like a lock-in a key, only certain neurotransmitters will fit in certain receptors ...
... • Neurotransmitters are stored in the neuron’s terminal buttons • When they cross the synapse they fit into receptor sites in the next neuron – like a lock-in a key, only certain neurotransmitters will fit in certain receptors ...
The Biology of Trauma - BC Association of Social Workers
... Information in SAM from extensive lower level sensory processing of traumatic scene ...
... Information in SAM from extensive lower level sensory processing of traumatic scene ...
Mean - Fitchburg State University
... recognition test is superior to that on a recall test (Balota & Neely ,1980; Petrusic & Dillon, 1972). During a recognition test, a participant sees a word or answer and picks it out from others, because it looks familiar. During a recall task, the participant has to generate the information from lo ...
... recognition test is superior to that on a recall test (Balota & Neely ,1980; Petrusic & Dillon, 1972). During a recognition test, a participant sees a word or answer and picks it out from others, because it looks familiar. During a recall task, the participant has to generate the information from lo ...
21st_Biology_B6_Revision_Powerpoint
... If neural pathways are not used then they are destroyed. If a new skill, such as language, has not been learned by a particular stage in development, an animal or child may not be able to learn it in the same way. Feral children are children who have been isolated in some way so don’t go through nor ...
... If neural pathways are not used then they are destroyed. If a new skill, such as language, has not been learned by a particular stage in development, an animal or child may not be able to learn it in the same way. Feral children are children who have been isolated in some way so don’t go through nor ...
OB-09 Emotions & Values
... toward an object, person, or event that create a state of readiness. • Most emotions occur without our awareness ...
... toward an object, person, or event that create a state of readiness. • Most emotions occur without our awareness ...
Biology of Learning and Memory
... • Mechanism of LTP: Repeated excitation of one type of glutamate receptors results in the delivery of additional receptors to the synapse. Also, axons and dendrites form new branches. • If axons are active at a very slow rate, their synapses may decrease in responsiveness—a process known as long-ter ...
... • Mechanism of LTP: Repeated excitation of one type of glutamate receptors results in the delivery of additional receptors to the synapse. Also, axons and dendrites form new branches. • If axons are active at a very slow rate, their synapses may decrease in responsiveness—a process known as long-ter ...
Ch. 10 ppt
... procedural memory: permanent storage of learned skills that does not require conscious recollection ...
... procedural memory: permanent storage of learned skills that does not require conscious recollection ...
learning memory anx disorders rv game (1)
... 3. Why did the mice in Tolman's experiment who had been exposed to the maze but not rewarded for completing it (at first) begin to complete the maze at much quicker rates when they began to be rewarded? 4. What is abstract learning? 5. What is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivatio ...
... 3. Why did the mice in Tolman's experiment who had been exposed to the maze but not rewarded for completing it (at first) begin to complete the maze at much quicker rates when they began to be rewarded? 4. What is abstract learning? 5. What is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivatio ...