Physiology Ch 57 p697-709 [4-25
... d. Area for Naming Objects – lateral area of ant occipital lobe and post temporal lobe is where naming objects takes place; learned through auditory input and physical natures are learned through visual input 2. Prefrontal Association Area – functions in association with motor cortex to plan comple ...
... d. Area for Naming Objects – lateral area of ant occipital lobe and post temporal lobe is where naming objects takes place; learned through auditory input and physical natures are learned through visual input 2. Prefrontal Association Area – functions in association with motor cortex to plan comple ...
lecture 2
... The device pictured here is more elaborate than the one Pavlov used in his early experiments. ...
... The device pictured here is more elaborate than the one Pavlov used in his early experiments. ...
emotion (book review) - UWE Research Repository
... In part this book questions the nature of our emotional experiences. For example, Morgan and Averill argue that when discussing the experience of true feelings we talk of discovering our real selves, but this is a paradox. True feelings are often talked about as being organic, free from the constra ...
... In part this book questions the nature of our emotional experiences. For example, Morgan and Averill argue that when discussing the experience of true feelings we talk of discovering our real selves, but this is a paradox. True feelings are often talked about as being organic, free from the constra ...
phys Learning Objectives Chapter 57 [10-31
... between neurons as a result of previous neural activity. The new or facilitated pathways are memory traces. Once they are established, they can be selectively activated by the thinking mind to reproduce memories. 31. What is positive/negative memory? Negative Memory - the brain has capability to lea ...
... between neurons as a result of previous neural activity. The new or facilitated pathways are memory traces. Once they are established, they can be selectively activated by the thinking mind to reproduce memories. 31. What is positive/negative memory? Negative Memory - the brain has capability to lea ...
The Influence of Odor and Emotion on Memory
... emotional event is encoded also appear to be active during retrieval of that emotional memory (Maratos et al., 2001). Another way that emotion and memory appear to be connected can be seen by the effect one’s emotional mood can have on the emotionality of the memory recalled. For example, if one beg ...
... emotional event is encoded also appear to be active during retrieval of that emotional memory (Maratos et al., 2001). Another way that emotion and memory appear to be connected can be seen by the effect one’s emotional mood can have on the emotionality of the memory recalled. For example, if one beg ...
memory - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... instance, you may know that dinner is the last meal of the day (semantic memory) but you may not recall what you ate for dinner last night (episodic memory)! Indeed, all our implicit memories are not readily accessible to our conscious brain: and these are what make up who we are and how we think. H ...
... instance, you may know that dinner is the last meal of the day (semantic memory) but you may not recall what you ate for dinner last night (episodic memory)! Indeed, all our implicit memories are not readily accessible to our conscious brain: and these are what make up who we are and how we think. H ...
Multiple Memory Systems in the Brain
... continuously updating system, registering new experiences and reorganizing the entire memory structure, unless selective parts of the brain are damaged. We used to regard the memory to be like an encyclopedia where every thing is registered in a huge volume and we keep on adding new entries. The bra ...
... continuously updating system, registering new experiences and reorganizing the entire memory structure, unless selective parts of the brain are damaged. We used to regard the memory to be like an encyclopedia where every thing is registered in a huge volume and we keep on adding new entries. The bra ...
Motivation and Emotion
... • Wait until physiological arousal is down, don’t sulk • Express grievance in ways that promote reconciliation ...
... • Wait until physiological arousal is down, don’t sulk • Express grievance in ways that promote reconciliation ...
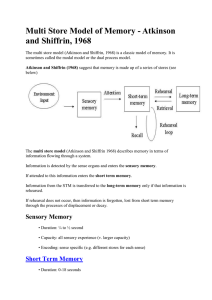
Models hand out File
... procedural (knowledge of how to do things) and semantic (general knowledge). The model suggests rehearsal helps to transfer information into LTM but this is not essential. Why are we able to recall information which we did not rehearse (e.g. swimming) yet unable to recall information which we have r ...
... procedural (knowledge of how to do things) and semantic (general knowledge). The model suggests rehearsal helps to transfer information into LTM but this is not essential. Why are we able to recall information which we did not rehearse (e.g. swimming) yet unable to recall information which we have r ...
M_5_Glossary Learning - user.meduni
... softness) considered apart from things having the property: universal 2: a property as it is experienced as distinct from any source it might have in a physical object. For instance Reductionsm holds that qualia can be fully explained in terms of neurophysiological events in the brain and its intera ...
... softness) considered apart from things having the property: universal 2: a property as it is experienced as distinct from any source it might have in a physical object. For instance Reductionsm holds that qualia can be fully explained in terms of neurophysiological events in the brain and its intera ...
Bauer 2006 - Ericastiftelsen
... proportion of 20-month-olds recall the order of events even after 1 year [14]. Sources of age-related change in recall A full explanation of changes in long-term recall will involve multiple levels of analysis, from proteins and synapses, to neural systems, to cultural influences on memory and its e ...
... proportion of 20-month-olds recall the order of events even after 1 year [14]. Sources of age-related change in recall A full explanation of changes in long-term recall will involve multiple levels of analysis, from proteins and synapses, to neural systems, to cultural influences on memory and its e ...
Attack and Escape Behaviors
... Research indicates that paralyzed people report feeling emotion to the same degree as prior to their injury ...
... Research indicates that paralyzed people report feeling emotion to the same degree as prior to their injury ...
Cranial nerve of smell, plus olfactory pathway
... memory and emotion. (Remember the limbic gyrus / cingulate gyrus?) Cortical smell centers strongly linked to : – Hippocampus (associative learning/memory) – Amygdala (which processes emotion/mood) In your experience, smells (a certain perfume, chlorine, pumpkin bread…..) that are linked to: – memori ...
... memory and emotion. (Remember the limbic gyrus / cingulate gyrus?) Cortical smell centers strongly linked to : – Hippocampus (associative learning/memory) – Amygdala (which processes emotion/mood) In your experience, smells (a certain perfume, chlorine, pumpkin bread…..) that are linked to: – memori ...
Chapter 7: Long-term memory systems
... representations of categories of objects or items. Concepts are organised into hierarchical networks with three levels (Rosch et al., 1976): superordinate categories; basic-level categories; and subordinate categories. Rosch and Mervis (1975) found members in a category can vary in their typicality. ...
... representations of categories of objects or items. Concepts are organised into hierarchical networks with three levels (Rosch et al., 1976): superordinate categories; basic-level categories; and subordinate categories. Rosch and Mervis (1975) found members in a category can vary in their typicality. ...
What is Nervous System?
... Increment of stimulus intensity will enable a person to differentiate different type & degree of stimulus. Thus, an organism/individual must know whether the stimulus in his/her immediate environment is at a comfortable level or need to be change. 4. Stimulus Scaling All living beings are invo ...
... Increment of stimulus intensity will enable a person to differentiate different type & degree of stimulus. Thus, an organism/individual must know whether the stimulus in his/her immediate environment is at a comfortable level or need to be change. 4. Stimulus Scaling All living beings are invo ...
Chapter 1 - Learning and Memory
... declarative memory development. Facilitates attention, judgment, cognitive control. May inhibit hippocampal encoding during directed forgetting. Damage increases source amnesia (confusing reality and fantasy). ...
... declarative memory development. Facilitates attention, judgment, cognitive control. May inhibit hippocampal encoding during directed forgetting. Damage increases source amnesia (confusing reality and fantasy). ...
Optical controlling reveals time-dependent roles for adult
... The adult hippocampus continues to give rise to several thousand new dentate granule cells everyday. Studies using global perturbation or ablation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis has revealed deficits in some forms of hippocampal memory. ...
... The adult hippocampus continues to give rise to several thousand new dentate granule cells everyday. Studies using global perturbation or ablation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis has revealed deficits in some forms of hippocampal memory. ...
Introduction My research focuses on the link between perception
... formation of new mappings between auditory and motor representations of sound sequences. I have previously argued that the temporary binding of auditory and motor representations of speech - as is required during tasks of phonological short-term memory -- is mediated by area Spt and the auditory dor ...
... formation of new mappings between auditory and motor representations of sound sequences. I have previously argued that the temporary binding of auditory and motor representations of speech - as is required during tasks of phonological short-term memory -- is mediated by area Spt and the auditory dor ...
McGraw-Hill AccessScience: Information processing (psychology)
... dynamics for recognizing letters is faster than that for words, which is in turn faster than that for sentences. The more simply one codes material in terms of hierarchical depth, the faster it can be retrieved, provided the strength of the trace is the same in both cases. ...
... dynamics for recognizing letters is faster than that for words, which is in turn faster than that for sentences. The more simply one codes material in terms of hierarchical depth, the faster it can be retrieved, provided the strength of the trace is the same in both cases. ...
Neural Basis of Emotion - Caltech Division of Humanities and Social
... which an animal (including humans) will work, and punishers are stimuli that an animal will work to escape from or avoid. Rewards and punishers are reinforcers in that they alter the probability of behavior. Some stimuli are unlearned or primary reinforcers (e.g., the taste of food if the animal is ...
... which an animal (including humans) will work, and punishers are stimuli that an animal will work to escape from or avoid. Rewards and punishers are reinforcers in that they alter the probability of behavior. Some stimuli are unlearned or primary reinforcers (e.g., the taste of food if the animal is ...
Wagner for the Womb
... Similar studies in different animal models have been replicated to correlate prenatal music stimulation with enhancement of spatial learning. In another study, music or no stimulation was provided to fertilized chick eggs. Following hatching, the chicks were trained to perform a similar maze task to ...
... Similar studies in different animal models have been replicated to correlate prenatal music stimulation with enhancement of spatial learning. In another study, music or no stimulation was provided to fertilized chick eggs. Following hatching, the chicks were trained to perform a similar maze task to ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... from the rest of the brain (link) • used to relieve severe psychotic depression – lost ability to solve complex problems – unable to string together sequential tasks – unable to learn to do several parallel tasks at the same time – decreased level of aggressiveness ...
... from the rest of the brain (link) • used to relieve severe psychotic depression – lost ability to solve complex problems – unable to string together sequential tasks – unable to learn to do several parallel tasks at the same time – decreased level of aggressiveness ...