BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
The role of the C-terminal tail of the ribosomal protein S13 in protein
... mRNA by transcription, and then passed onto proteins by translation. The ribosome synthesizes proteins based on the information on the mRNA sequence in the cell; like building a house using bricks according to a blueprint. Bacterial growth is determined by how fast the whole process is. The bacteria ...
... mRNA by transcription, and then passed onto proteins by translation. The ribosome synthesizes proteins based on the information on the mRNA sequence in the cell; like building a house using bricks according to a blueprint. Bacterial growth is determined by how fast the whole process is. The bacteria ...
Document
... ASOs are a bit like a cross between DNA and mRNA. They are chemically similar to DNA, but are made of a single strand like mRNA. Just like other gene silencing drugs, they are designed to stick to the HD mRNA and tell the cell to destroy it, so preventing the abnormal huntingtin protein from ever be ...
... ASOs are a bit like a cross between DNA and mRNA. They are chemically similar to DNA, but are made of a single strand like mRNA. Just like other gene silencing drugs, they are designed to stick to the HD mRNA and tell the cell to destroy it, so preventing the abnormal huntingtin protein from ever be ...
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Learning Objectives The
... 10. Explain how RNA polymerase recognizes where transcription should begin. Describe the role of the promoter, the terminator (in bacterial cells), and define the transcription unit. 11. Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and term ...
... 10. Explain how RNA polymerase recognizes where transcription should begin. Describe the role of the promoter, the terminator (in bacterial cells), and define the transcription unit. 11. Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and term ...
Gene Expression Overview
... Exon: a segment of a gene that is represented in the mature RNA product. Individual exons may contain coding DNAand/or noncoding DNA (untranslated sequences). Bioinformatics I is the application of computer science and information technology to the field of biology and medicine Introns (intervening ...
... Exon: a segment of a gene that is represented in the mature RNA product. Individual exons may contain coding DNAand/or noncoding DNA (untranslated sequences). Bioinformatics I is the application of computer science and information technology to the field of biology and medicine Introns (intervening ...
RNA_and_Protein_Synthesis
... mRNA carries the “message” from the DNA (found in the nucleus) to the Ribosomes (within the cytoplasm) for protein synthesis to occur Ribosomes are composed of several proteins along with a form of RNA called rRNA tRNA = transfers amino acids to ribosomes ...
... mRNA carries the “message” from the DNA (found in the nucleus) to the Ribosomes (within the cytoplasm) for protein synthesis to occur Ribosomes are composed of several proteins along with a form of RNA called rRNA tRNA = transfers amino acids to ribosomes ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... o Who discovered the structure of DNA? __________________________________________ o DNA is made of two nucleotide chains, containing: ___________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ o Be able to label a nucleotide!! o In DNA, the 4 nitrogenous ...
... o Who discovered the structure of DNA? __________________________________________ o DNA is made of two nucleotide chains, containing: ___________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ o Be able to label a nucleotide!! o In DNA, the 4 nitrogenous ...
Chapter 10 - Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... • Transcription factors• proteins that recognize specific sequences in DNA when making mRNA and help RNA polymerase bind • ATPase• converts ATP to ADP and releases energy to do work ( used to bond tRNA to mRNA and GTPase also used when adding a.a to tRNA) • tRNA synthetase (tRNA activating enzyme) • ...
... • Transcription factors• proteins that recognize specific sequences in DNA when making mRNA and help RNA polymerase bind • ATPase• converts ATP to ADP and releases energy to do work ( used to bond tRNA to mRNA and GTPase also used when adding a.a to tRNA) • tRNA synthetase (tRNA activating enzyme) • ...
DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis Study Guide
... Concepts to know structure of a nucleotide structure of DNA monomer of DNA bonding of DNA molecule base pairing, A-T, C-G steps involved in replication direction replication occurs antiparallel nature of DNA product at the end of replication when in cell’s life cycle replication occurs where in cell ...
... Concepts to know structure of a nucleotide structure of DNA monomer of DNA bonding of DNA molecule base pairing, A-T, C-G steps involved in replication direction replication occurs antiparallel nature of DNA product at the end of replication when in cell’s life cycle replication occurs where in cell ...
Protein Synthesis
... • Made in the Nucleus • Copies DNA & leaves through nuclear pores • Contains the Nitrogen Bases A, G, C, U ( no T ) ...
... • Made in the Nucleus • Copies DNA & leaves through nuclear pores • Contains the Nitrogen Bases A, G, C, U ( no T ) ...
HOW SAGE WORKS (Reference http://www
... HOW SAGE WORKS (Reference http://www.embl-heidelberg.de/info/sage) Each type of RNA has a unique chemical composition that is a direct transcription of information stored in a particular gene. The basic units that make up DNA and RNAs are called nucleotides. The alphabet of nucleotides is very small ...
... HOW SAGE WORKS (Reference http://www.embl-heidelberg.de/info/sage) Each type of RNA has a unique chemical composition that is a direct transcription of information stored in a particular gene. The basic units that make up DNA and RNAs are called nucleotides. The alphabet of nucleotides is very small ...
Biochem Option (D)
... Explain the double helical structure of DNA • Secondary structure • Why do Adenine and Thymine only pair with each other (and Cytosine and Guanine)? ...
... Explain the double helical structure of DNA • Secondary structure • Why do Adenine and Thymine only pair with each other (and Cytosine and Guanine)? ...
Slide 1
... • Others can make a protein malfunction and cause major diseases like sickle cell anemia which is a blood cell disorder. The Red Blood cells are not round, they are deformed in shape. ...
... • Others can make a protein malfunction and cause major diseases like sickle cell anemia which is a blood cell disorder. The Red Blood cells are not round, they are deformed in shape. ...
Molecular Genetics - Fall River Public Schools
... the polypeptides twist and fold • The function of a proteins depends on its ability to bind with another molecule, which is determined by it three-dimensional shape ...
... the polypeptides twist and fold • The function of a proteins depends on its ability to bind with another molecule, which is determined by it three-dimensional shape ...
DNA to RNA
... There are three main differences between DNA and RNA: 1) The sugar in RNA is ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2) RNA is singlestranded. 3) RNA contains uracil instead of thymine. ...
... There are three main differences between DNA and RNA: 1) The sugar in RNA is ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2) RNA is singlestranded. 3) RNA contains uracil instead of thymine. ...
Slide 1
... - presence of L1 retroelement can provide polyadenylation signal & bidirectional promoter leading to fission of pre-exising gene into two short genes ...
... - presence of L1 retroelement can provide polyadenylation signal & bidirectional promoter leading to fission of pre-exising gene into two short genes ...
Protein Production and the Genetic Code
... group of three nucleotides codes for one amino acid. Each set of three N bases that codes for an amino acid is called a codon. The order of nitrogen bases in the mRNA will determine the type and order of amino acids in a protein 64 combinations are possible when a sequence of 3 bases is used. Th ...
... group of three nucleotides codes for one amino acid. Each set of three N bases that codes for an amino acid is called a codon. The order of nitrogen bases in the mRNA will determine the type and order of amino acids in a protein 64 combinations are possible when a sequence of 3 bases is used. Th ...
protein synthesis worksheet
... Transcription. It occurs in the nucleus. During transcription, mRNA transcribes (copies) DNA. DNA is “unzipped” and the mRNA strand copies a strand of DNA. Once it does this, mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes into the cytoplasm. mRNA will then attach itself to a ribosome. The strand of mRNA is then r ...
... Transcription. It occurs in the nucleus. During transcription, mRNA transcribes (copies) DNA. DNA is “unzipped” and the mRNA strand copies a strand of DNA. Once it does this, mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes into the cytoplasm. mRNA will then attach itself to a ribosome. The strand of mRNA is then r ...
No Slide Title
... 1) CPSF binds AAUAAA in hnRNA 2) CStF binds; CFI, CFII bind in between 3) PAP (PolyA polymerase) binds & cleaves 10-35 b 3’ to ...
... 1) CPSF binds AAUAAA in hnRNA 2) CStF binds; CFI, CFII bind in between 3) PAP (PolyA polymerase) binds & cleaves 10-35 b 3’ to ...
Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
... all genes. • This is done by creating the complementary strands of the known gene sequences and assembling them on a chip. • The sequences are tagged with flourescent tags that glow a certain color when in contact with the complementary ...
... all genes. • This is done by creating the complementary strands of the known gene sequences and assembling them on a chip. • The sequences are tagged with flourescent tags that glow a certain color when in contact with the complementary ...
DNA
... Phosphoryl groups of nucleotides ensure that they bear a negative charge at physiologic pH nucleotides absorb light at a wavelength close to 260 nm The concentration of nucleotides and nucleic acids thus often is expressed in terms of “ABSORBANCE AT 260 nm.” ...
... Phosphoryl groups of nucleotides ensure that they bear a negative charge at physiologic pH nucleotides absorb light at a wavelength close to 260 nm The concentration of nucleotides and nucleic acids thus often is expressed in terms of “ABSORBANCE AT 260 nm.” ...
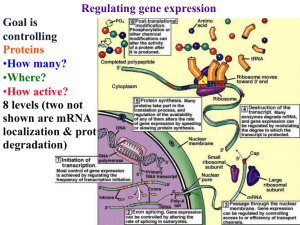
are mRNA
... codon. It terminates the protein synthesis by releasing: - Large & small ribosomal subunits - Polypeptide chain - tRNA molecule - Releasing factor - mRNA ...
... codon. It terminates the protein synthesis by releasing: - Large & small ribosomal subunits - Polypeptide chain - tRNA molecule - Releasing factor - mRNA ...
Key
... A polymer of nucleotides that can be covalently attached to a specific amino acid The nucleotide sequence that is responsible for determining where transcription begins in eukaryotes The sequence of mRNA that is discarded after splicing A DNA sequence that binds a specific activator to increase the ...
... A polymer of nucleotides that can be covalently attached to a specific amino acid The nucleotide sequence that is responsible for determining where transcription begins in eukaryotes The sequence of mRNA that is discarded after splicing A DNA sequence that binds a specific activator to increase the ...