REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION
... rate of acetylated histones and unmethylated DNA whereas inactive regions are associated with nonacetylated histones and methylated DNA. Histone modifications and DNA methylation constitute the base of a special mechanism of gene expression control called epigenetic inheritance. Epigenetic inheritan ...
... rate of acetylated histones and unmethylated DNA whereas inactive regions are associated with nonacetylated histones and methylated DNA. Histone modifications and DNA methylation constitute the base of a special mechanism of gene expression control called epigenetic inheritance. Epigenetic inheritan ...
Block 1: Genetics Dr. McKinney Test 1: Transcription (4) The order
... b. translation of the mRNA transcript can begin before it has been completely transcribed by RNA polymerase, and it occurs because both processes take place in the cytosol due to the lack of a nuclear membrane. c. translation by the RNA polymerase can begin while transcription is still occurring on ...
... b. translation of the mRNA transcript can begin before it has been completely transcribed by RNA polymerase, and it occurs because both processes take place in the cytosol due to the lack of a nuclear membrane. c. translation by the RNA polymerase can begin while transcription is still occurring on ...
Book Review Layout
... that it goes beyond the required descriptions of the structure and function of stable RNAs, with chapters on structural requirements of messenger RNAs, in regulating translation and transcription. This book conveys the message that RNA structure is relevant for anyone interested in fully understandi ...
... that it goes beyond the required descriptions of the structure and function of stable RNAs, with chapters on structural requirements of messenger RNAs, in regulating translation and transcription. This book conveys the message that RNA structure is relevant for anyone interested in fully understandi ...
TOPIC 16: REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION
... (e) Activators- special class of transcription factors which bind to the enhancers thereby initiating the activation of gene expression Figure 19.9 – Activation of transcription (a) binding of activators to enhancer sites ...
... (e) Activators- special class of transcription factors which bind to the enhancers thereby initiating the activation of gene expression Figure 19.9 – Activation of transcription (a) binding of activators to enhancer sites ...
Coding Potential
... The genetic code: -Is read by the ribosome, converting RNA into proteins -Is redundant, or degenerate (there are 64 codons, and only 20 amino acids) -Is the same in almost all organisms Translation in individual organisms may be biased towards particular tRNA ...
... The genetic code: -Is read by the ribosome, converting RNA into proteins -Is redundant, or degenerate (there are 64 codons, and only 20 amino acids) -Is the same in almost all organisms Translation in individual organisms may be biased towards particular tRNA ...
Document
... The genetic code is said to be degenerate, which means that: A. Each codon codes for more than one amino acid. B. An anticodon can interact with more than one codon in the mRNA in which the codon may differ in any or all of the three nucleotides. C. Most amino acids are coded for by more than one co ...
... The genetic code is said to be degenerate, which means that: A. Each codon codes for more than one amino acid. B. An anticodon can interact with more than one codon in the mRNA in which the codon may differ in any or all of the three nucleotides. C. Most amino acids are coded for by more than one co ...
Protein Synthesis and Processing
... found within the nucleus (or nucleoplasm). 11. What is the base found in pre-mRNA that is not present in DNA? Uracil 12. What is the base pair rule for making pre-mRNA from DNA?) A-U; U-A; C-G; G-C 13. Which strand of the DNA is “read” to produce pre-mRNA? The template strand or coding strand 14. Wh ...
... found within the nucleus (or nucleoplasm). 11. What is the base found in pre-mRNA that is not present in DNA? Uracil 12. What is the base pair rule for making pre-mRNA from DNA?) A-U; U-A; C-G; G-C 13. Which strand of the DNA is “read” to produce pre-mRNA? The template strand or coding strand 14. Wh ...
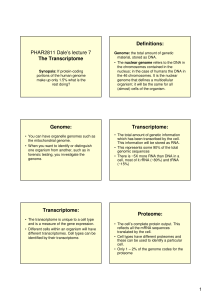
PHAR2811 Dale`s lecture 7 The Transcriptome Definitions: Genome
... • The rRNA is then modified by methylation at some sites. • There are many copies of the ribosomal RNA sequences in the genome (as well as the histone proteins). • Some sequences are required by all cells in such large quantities that they have multiple copies in the genome. ...
... • The rRNA is then modified by methylation at some sites. • There are many copies of the ribosomal RNA sequences in the genome (as well as the histone proteins). • Some sequences are required by all cells in such large quantities that they have multiple copies in the genome. ...
Slides PPT
... because it contains both RNA and protein and it is the RNA component that is capable of the RNase activity. • It was this enzyme that led scientists to the discovery of ribozymes; the RNA species capable of catalytic activity. ...
... because it contains both RNA and protein and it is the RNA component that is capable of the RNase activity. • It was this enzyme that led scientists to the discovery of ribozymes; the RNA species capable of catalytic activity. ...
doc - FSU Biology
... Escherichia coli (and other similar bacteria) contains in its genome about 120 RNA genes. These genes code for a variety of RNA products, most of which have known functions. Examples are the three ribosomal RNA genes which code for the 16S, 23S and 5S rRNAs found in all bacterial ribosomes, and the ...
... Escherichia coli (and other similar bacteria) contains in its genome about 120 RNA genes. These genes code for a variety of RNA products, most of which have known functions. Examples are the three ribosomal RNA genes which code for the 16S, 23S and 5S rRNAs found in all bacterial ribosomes, and the ...
mRNA
... How is RNA Assembled? • Transcription begins when an RNA polymerase and regulatory proteins attach to a DNA site called a promoter – RNA polymerase moves over a gene region and unwinds the double helix a bit so it can “read” the base sequence of the DNA strand – The polymerase joins free RNA nucleo ...
... How is RNA Assembled? • Transcription begins when an RNA polymerase and regulatory proteins attach to a DNA site called a promoter – RNA polymerase moves over a gene region and unwinds the double helix a bit so it can “read” the base sequence of the DNA strand – The polymerase joins free RNA nucleo ...
RNA-Seq Sample Recommendations (Craig Praul, PSU and Caitlyn
... experience in helping customers isolate RNA from every conceivable species/tissue/cell. We do however have a few general recommendations regarding RNA isolation techniques based upon our experience. We do not recommend the use of Trizol alone for total RNA isolation as the use of Trizol often result ...
... experience in helping customers isolate RNA from every conceivable species/tissue/cell. We do however have a few general recommendations regarding RNA isolation techniques based upon our experience. We do not recommend the use of Trizol alone for total RNA isolation as the use of Trizol often result ...
Ch. 10 ppt
... the actions of a wide variety of proteins. • DNA specifies the synthesis of proteins in two stages: – Transcription, the transfer of genetic information from DNA into an RNA molecule – Translation, the transfer of information from RNA into a protein ...
... the actions of a wide variety of proteins. • DNA specifies the synthesis of proteins in two stages: – Transcription, the transfer of genetic information from DNA into an RNA molecule – Translation, the transfer of information from RNA into a protein ...
Origin of Life
... as a template for specific proteins. • Since RNA may assume different shapes, some RNA molecules may behave like proteins and catalyze chemical reactions. • A ribosome can act as an enzyme and may have the ability to replicate itself. • Since RNA plays a vital role in the replication of DNA, self-re ...
... as a template for specific proteins. • Since RNA may assume different shapes, some RNA molecules may behave like proteins and catalyze chemical reactions. • A ribosome can act as an enzyme and may have the ability to replicate itself. • Since RNA plays a vital role in the replication of DNA, self-re ...
RrYy - Lemon Bay High School
... What happens during the process of translation? • Messenger RNA is made from DNA. • The cell uses information from messenger RNA to produce proteins. • Transfer RNA is made from messenger RNA. • Copies of DNA molecules are made. ...
... What happens during the process of translation? • Messenger RNA is made from DNA. • The cell uses information from messenger RNA to produce proteins. • Transfer RNA is made from messenger RNA. • Copies of DNA molecules are made. ...
CS "Autism and epilepsy"
... data that uses a four letter alphabet to “create words”. These “words” are amino acids, which combine with each other to form proteins, the functional bricks of the cells. RNA is a molecule that acts as a bridge, a link, that transforms the information contained in DNA into proteins. While the prote ...
... data that uses a four letter alphabet to “create words”. These “words” are amino acids, which combine with each other to form proteins, the functional bricks of the cells. RNA is a molecule that acts as a bridge, a link, that transforms the information contained in DNA into proteins. While the prote ...
video slide - Your School
... 1 When a ribosome reaches a stop 2 The release factor hydrolyzes 3 The two ribosomal subunits codon on mRNA, the A site of the the bond between the tRNA in and the other components of ribosome accepts a protein called the P site and the last amino the assembly dissociate. a release factor instead of ...
... 1 When a ribosome reaches a stop 2 The release factor hydrolyzes 3 The two ribosomal subunits codon on mRNA, the A site of the the bond between the tRNA in and the other components of ribosome accepts a protein called the P site and the last amino the assembly dissociate. a release factor instead of ...
22(L)/S/O - India Environment Portal
... Recent discoveries have substantially changed, if not overturned, this belief. Now it has been found that besides doing this, RNA molecules regulate many important processes, including shutting off the blue-print carrying genes themselves. DNA carries the genetic code in the form of precise sequence ...
... Recent discoveries have substantially changed, if not overturned, this belief. Now it has been found that besides doing this, RNA molecules regulate many important processes, including shutting off the blue-print carrying genes themselves. DNA carries the genetic code in the form of precise sequence ...
Section 6 - DNA history. (most of this will serve only as conversation
... no side-effects or positive side effects. there are two types of mutations: 1. chromosomal mutations, which affect many genes or even the entire organism (ex. trisomy ...
... no side-effects or positive side effects. there are two types of mutations: 1. chromosomal mutations, which affect many genes or even the entire organism (ex. trisomy ...
Gene regulation - Department of Plant Sciences
... Controlling gene expression post-transcriptionally. microRNA is an abundant class of newly identified small ...
... Controlling gene expression post-transcriptionally. microRNA is an abundant class of newly identified small ...
Biological information flow
... * preventing RNA polymerase from binding promoter * inhibition of initiation reactions (e.g. transition bubble formation, primer synthesis, promoter clearance) Repressors are allosterically regulated** **inducer: ligands that bind to, and inactivate, repressors ...
... * preventing RNA polymerase from binding promoter * inhibition of initiation reactions (e.g. transition bubble formation, primer synthesis, promoter clearance) Repressors are allosterically regulated** **inducer: ligands that bind to, and inactivate, repressors ...
2015/5/13 9:24 AM
... 32. Viruses have a simple cellular structure. 33. In general, viral replication involves production of viral proteins and assembly of viral particles within a host cell. 34. A promoter is a binding site for DNA polymerase. 35. Prokaryotes genes turn on or off in response to genetic factors. 36. Spec ...
... 32. Viruses have a simple cellular structure. 33. In general, viral replication involves production of viral proteins and assembly of viral particles within a host cell. 34. A promoter is a binding site for DNA polymerase. 35. Prokaryotes genes turn on or off in response to genetic factors. 36. Spec ...