Whittier Union High School District
... 43. What are the three main stages of cellular respiration (in order)? 1) Glycolysis- takes place in the cytoplasm and produces a total of 4 ATP molecules, but requires 2 ATP to work 2) Kreb’s cycle (AKA citric acid cycle)- takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria and produces 2 ATP molecules 3 ...
... 43. What are the three main stages of cellular respiration (in order)? 1) Glycolysis- takes place in the cytoplasm and produces a total of 4 ATP molecules, but requires 2 ATP to work 2) Kreb’s cycle (AKA citric acid cycle)- takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria and produces 2 ATP molecules 3 ...
STAAR Review 4
... b. The deoxyribose sugar became separated from the DNA. c. The genetic code change caused the wrong protein to form. d. The RNA necessary to produce proteins was not present. ...
... b. The deoxyribose sugar became separated from the DNA. c. The genetic code change caused the wrong protein to form. d. The RNA necessary to produce proteins was not present. ...
Power point
... Mechanisms of Post-Transcriptional Regulation • RNA processing- alternative RNA splicing, regulatory proteins determine what is removed • mRNA degradation- can get translated repeatedly • Regulation of the initiation of translation – Most common method for regulation of gene expression – translatio ...
... Mechanisms of Post-Transcriptional Regulation • RNA processing- alternative RNA splicing, regulatory proteins determine what is removed • mRNA degradation- can get translated repeatedly • Regulation of the initiation of translation – Most common method for regulation of gene expression – translatio ...
Gene Section SEPT5 (septin 5) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... leukemia (ANLL) --> MLL - hCDCRel-1 Disease M4, M2, and M1 ANLL. Hybrid/Mutated gene 5' MLL - 3' hCDCRel, with fusion of MLL exon 7 to hCDCRel exon 3. Abnormal protein NH2 - AT hook and DNA methyltransferase from MLL fused to hCDCREL-1 - COOH. ...
... leukemia (ANLL) --> MLL - hCDCRel-1 Disease M4, M2, and M1 ANLL. Hybrid/Mutated gene 5' MLL - 3' hCDCRel, with fusion of MLL exon 7 to hCDCRel exon 3. Abnormal protein NH2 - AT hook and DNA methyltransferase from MLL fused to hCDCREL-1 - COOH. ...
Biology 11: Year-End Biology 11 Review - biology-rocks
... Natural Selection is the process by which the most fit organisms reproduce. Variations that make an organisms more fit could be passed on to offspring in a process that does not require human intervention. Darwin observed that all organisms are in a constant struggle to survive against both the envi ...
... Natural Selection is the process by which the most fit organisms reproduce. Variations that make an organisms more fit could be passed on to offspring in a process that does not require human intervention. Darwin observed that all organisms are in a constant struggle to survive against both the envi ...
Untitled
... excise 400 nucleotides from its RNA in the absence of any protein. Other examples of catalytic RNAs have now been discovered in different types of cells. Catalytic RNA (ribozymes) can cut out parts of their own sequences, connect some RNA molecules together, replicate others, and even catalyze the f ...
... excise 400 nucleotides from its RNA in the absence of any protein. Other examples of catalytic RNAs have now been discovered in different types of cells. Catalytic RNA (ribozymes) can cut out parts of their own sequences, connect some RNA molecules together, replicate others, and even catalyze the f ...
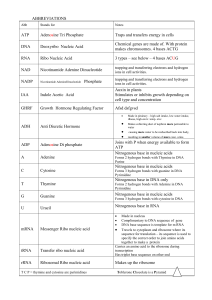
abbreviations - Spanish Point Biology
... Complimentary to DNA sequence of gene DNA base sequence is template for m RNA Travels to cytoplasm and ribosome where its sequence for translation – its sequence is used to specify the correct order to join amino acids together to make a protein Carries an amino acid to the ribosome during transcr ...
... Complimentary to DNA sequence of gene DNA base sequence is template for m RNA Travels to cytoplasm and ribosome where its sequence for translation – its sequence is used to specify the correct order to join amino acids together to make a protein Carries an amino acid to the ribosome during transcr ...
UC Irvine FOCUS! 5 E Lesson Plan Title: Genetics Scavenger Hunt
... eye — and each cell in your body contains about 6 feet of DNA thread, for a total of about 3 billion miles (if all your DNA threads were stretched out straight) of DNA inside you! The DNA patterns are the codes for manufacturing proteins, chemicals that enable the body to work and grow. Genes hold t ...
... eye — and each cell in your body contains about 6 feet of DNA thread, for a total of about 3 billion miles (if all your DNA threads were stretched out straight) of DNA inside you! The DNA patterns are the codes for manufacturing proteins, chemicals that enable the body to work and grow. Genes hold t ...
Scientific Method Scientific Method- 1.) Make an observation 2.) Ask
... enters and exits cell Cell Wall-provides support and structure to the outside of plant cells Golgi Apparatus-cellular “post office”, packages and ships proteins throughout cell Mitochondria-“powerhouse” of cell, site of cellular respiration Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth and Rough)-cellular transport ...
... enters and exits cell Cell Wall-provides support and structure to the outside of plant cells Golgi Apparatus-cellular “post office”, packages and ships proteins throughout cell Mitochondria-“powerhouse” of cell, site of cellular respiration Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth and Rough)-cellular transport ...
Genes & Development
... Non-homologous recombination inserts thymidine kinase. The presence of gene allows cells containing it to be killed by the thymidine analog gancyclovir or FIAU. Only HSV (viral) tk will phosphorylate the nucleotide analog so only the cells with HSV-tk will be killed. The phosphorylated analog stops ...
... Non-homologous recombination inserts thymidine kinase. The presence of gene allows cells containing it to be killed by the thymidine analog gancyclovir or FIAU. Only HSV (viral) tk will phosphorylate the nucleotide analog so only the cells with HSV-tk will be killed. The phosphorylated analog stops ...
Codon Bingo - Flinn Scientific
... start codon. The ribosome reads three mRNA nucleotides at a time—these base triplets are called codons. A single mRNA nucleotide sequence—adenine-uracil-guanine (AUG)—acts as the starting point for the translation of any mRNA into a chain of amino acids. There are three different codons that are rea ...
... start codon. The ribosome reads three mRNA nucleotides at a time—these base triplets are called codons. A single mRNA nucleotide sequence—adenine-uracil-guanine (AUG)—acts as the starting point for the translation of any mRNA into a chain of amino acids. There are three different codons that are rea ...
DNA Worksheet
... 12. DNA must “unzip” to replicate. Describe how DNA “unzips”. Include the name of the enzyme involved. ...
... 12. DNA must “unzip” to replicate. Describe how DNA “unzips”. Include the name of the enzyme involved. ...
Dr Asmat Salim MM 707 Molecular biology
... Purity and amount of DNA required depends on intended application. Tissue typing for organ transplant Detection of pathogens Human identity testing Genetic research ...
... Purity and amount of DNA required depends on intended application. Tissue typing for organ transplant Detection of pathogens Human identity testing Genetic research ...
protein synthesis fill-in
... Three Types of RNA • _________ ____ (mRNA) copies DNA’s code & carries the genetic information to the ribosomes • _________ ____ (rRNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes • _________ ____ (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are copyright cmassengale ...
... Three Types of RNA • _________ ____ (mRNA) copies DNA’s code & carries the genetic information to the ribosomes • _________ ____ (rRNA), along with protein, makes up the ribosomes • _________ ____ (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes where proteins are copyright cmassengale ...
Chapter 26 - RNA Metabolism
... • Pause sites - regions of the gene where the rate of elongation slows down (10 to 100-fold) or stops temporarily • Transcription termination often occurs here • G-C- rich regions are more difficult to separate than A-T rich regions and may be pause sites • Pause is exaggerated when newly transcribe ...
... • Pause sites - regions of the gene where the rate of elongation slows down (10 to 100-fold) or stops temporarily • Transcription termination often occurs here • G-C- rich regions are more difficult to separate than A-T rich regions and may be pause sites • Pause is exaggerated when newly transcribe ...
Chapter-Translation (Prokaryotes)
... by aminoacyl tRNA synthetases, to form aminoacyl-tRNA. In prokaryotes, this sequence (CCA) is generally added during processing of tRNA. It is an important sequence for the correct recognition of tRNA by enzymes and plays an important role in translation. c) The acceptor stem that consists of 7- to ...
... by aminoacyl tRNA synthetases, to form aminoacyl-tRNA. In prokaryotes, this sequence (CCA) is generally added during processing of tRNA. It is an important sequence for the correct recognition of tRNA by enzymes and plays an important role in translation. c) The acceptor stem that consists of 7- to ...
PASS MOCK EXAM
... D) differs slightly between eukaryotes and prokaryotes E) has at least 2 codons coding for each Amino Acid. ...
... D) differs slightly between eukaryotes and prokaryotes E) has at least 2 codons coding for each Amino Acid. ...
Where do pumpkins come from?
... • Translational regulatory proteins – recognize sequences in mRNA and inhibit translation (sometimes at the start codon) • Antisense RNA – a RNA strand that is complementary to mRNA binds to the mRNA and keeps it from being translated ...
... • Translational regulatory proteins – recognize sequences in mRNA and inhibit translation (sometimes at the start codon) • Antisense RNA – a RNA strand that is complementary to mRNA binds to the mRNA and keeps it from being translated ...
A - Alanine (Ala)
... To the left is shown twenty amino acids with their one and three-letter abbreviations. 1. Choose a partner at another table and write a short message to that partner using only the letters included in the single letter abbreviations for amino acids (no B, J, O, U, X, or Z). Write your message here: ...
... To the left is shown twenty amino acids with their one and three-letter abbreviations. 1. Choose a partner at another table and write a short message to that partner using only the letters included in the single letter abbreviations for amino acids (no B, J, O, U, X, or Z). Write your message here: ...
DNA Replication, Translation, Transcription, & Protein
... • DNA uses a method know as TRANSCRIPTION to transfer the information from DNA into another molecule called RNA • Transcription doesn’t change the DNA, only reads it to create the RNA • RNA uses nucleotides as well… but one change…A-U-G-C Adenine-Uracil Guanine-Cytosine • The RNA is then read to mak ...
... • DNA uses a method know as TRANSCRIPTION to transfer the information from DNA into another molecule called RNA • Transcription doesn’t change the DNA, only reads it to create the RNA • RNA uses nucleotides as well… but one change…A-U-G-C Adenine-Uracil Guanine-Cytosine • The RNA is then read to mak ...
GENETICS
... before it completes translation of that gene, another ribosome may attach itself and begin translation of the same mRNA strand • Several ribosomes moving simultaneously in tandem along the same mRNA molecule permit the translation of a single mRNA strand into several identical proteins simultaneousl ...
... before it completes translation of that gene, another ribosome may attach itself and begin translation of the same mRNA strand • Several ribosomes moving simultaneously in tandem along the same mRNA molecule permit the translation of a single mRNA strand into several identical proteins simultaneousl ...
Dr Ishtiaq Transcription
... Shortly after the discovery of splicing came the realization that the exons in some genes were not utilized in the same way in every cell or stage of development. In other words exons could be skipped or added. This means that variations of a protein (called isoforms) can be produced from the same g ...
... Shortly after the discovery of splicing came the realization that the exons in some genes were not utilized in the same way in every cell or stage of development. In other words exons could be skipped or added. This means that variations of a protein (called isoforms) can be produced from the same g ...
Chapter 31
... The length of the inactive region varies from cell to cell. o As a result, inactivation of genes in this vicinity causes position effect variegation. Similar spreading effects occur at telomeres and at the silent cassettes in yeast mating type. ...
... The length of the inactive region varies from cell to cell. o As a result, inactivation of genes in this vicinity causes position effect variegation. Similar spreading effects occur at telomeres and at the silent cassettes in yeast mating type. ...