Crash Course #11 Learning
... Behaviorism: an empirically rigorous science focused on ___________________ behaviors and not unobservable _______________________ mental processes. Learning: the process of ____________________, through _____________________, new and relatively enduring information or behaviors. What is a neutral s ...
... Behaviorism: an empirically rigorous science focused on ___________________ behaviors and not unobservable _______________________ mental processes. Learning: the process of ____________________, through _____________________, new and relatively enduring information or behaviors. What is a neutral s ...
classical conditioning
... Habituation is when an animal is presented with a stimulus and responds to this stimulus, but when the stimulus is presented repeatedly with only a few minutes or seconds between it soon stops responding to the stimulus because it has learnt that it will not harm or benefit the animal so it has lea ...
... Habituation is when an animal is presented with a stimulus and responds to this stimulus, but when the stimulus is presented repeatedly with only a few minutes or seconds between it soon stops responding to the stimulus because it has learnt that it will not harm or benefit the animal so it has lea ...
OperateConditioning
... • Something otherwise meaningless becomes linked to a meaningful experience and therefore causes same response as the original experience on it’s own. ...
... • Something otherwise meaningless becomes linked to a meaningful experience and therefore causes same response as the original experience on it’s own. ...
Motor Mechanisms and Behavior
... responsible for the coordination of body systems Studies support the idea that certain types of behavior have genetic basis ...
... responsible for the coordination of body systems Studies support the idea that certain types of behavior have genetic basis ...
social & group influences (cont.)
... • refers to explaining our successes by attributing them to our dispositions or personality traits and explaining our failures by attributing them to the situations ...
... • refers to explaining our successes by attributing them to our dispositions or personality traits and explaining our failures by attributing them to the situations ...
File
... response to a stimulus. Unconditioned stimulus (UCS) leads to unconditioned response (UR). A neutral, or Conditioned stimulus (CS) is presented repeatedly before the UCS. After repeated pairings, the CS itself leads to the Conditioned response (CR), usually the same behavior as the UCR. UCS (F ...
... response to a stimulus. Unconditioned stimulus (UCS) leads to unconditioned response (UR). A neutral, or Conditioned stimulus (CS) is presented repeatedly before the UCS. After repeated pairings, the CS itself leads to the Conditioned response (CR), usually the same behavior as the UCR. UCS (F ...
Unit 1: Motivation, Emotion and Stress - Ms. Anderson
... ■ A need creates a state of arousal called a drive. ■ Drive keeps us motivated and working to fulfill the need. ■ If we are driven by our need for achievement (money, fame, property), we keep working to fulfill this need. ...
... ■ A need creates a state of arousal called a drive. ■ Drive keeps us motivated and working to fulfill the need. ■ If we are driven by our need for achievement (money, fame, property), we keep working to fulfill this need. ...
Operant Conditioning
... of a behavior depends on the consequence that follows that behavior The frequency will increase if the consequence is reinforcing to the subject. The frequency will decrease if the consequence is not reinforcing or punishing to the subject. ...
... of a behavior depends on the consequence that follows that behavior The frequency will increase if the consequence is reinforcing to the subject. The frequency will decrease if the consequence is not reinforcing or punishing to the subject. ...
Important People #2 - Mr. Voigtschild
... norms for American children; tested group of young geniuses and followed in a longitudinal study that lasted beyond his own lifetime to show that high IQ does not necessarily lead to wonderful ...
... norms for American children; tested group of young geniuses and followed in a longitudinal study that lasted beyond his own lifetime to show that high IQ does not necessarily lead to wonderful ...
Science of Behavior Change
... abuse, overeating, and a sedentary lifestyle—contribute to negative health outcomes and common diseases. This type of behavior accounts for approximately 40 percent of the risk associated with preventable premature deaths in the United States. Unfortunately, it is extremely difficult to initiate and ...
... abuse, overeating, and a sedentary lifestyle—contribute to negative health outcomes and common diseases. This type of behavior accounts for approximately 40 percent of the risk associated with preventable premature deaths in the United States. Unfortunately, it is extremely difficult to initiate and ...
STUDY OF PERSONALITY FINAL REVIEW
... 12.) This man is one of the most famous psychologists because he founded the idea of psychoanalysis and discovered the importance of unconscious motives in human behavior. He also used mainly case studies for his experiments. His name is __________. 13.) Three cognitive psychologists are: a. b. c. ...
... 12.) This man is one of the most famous psychologists because he founded the idea of psychoanalysis and discovered the importance of unconscious motives in human behavior. He also used mainly case studies for his experiments. His name is __________. 13.) Three cognitive psychologists are: a. b. c. ...
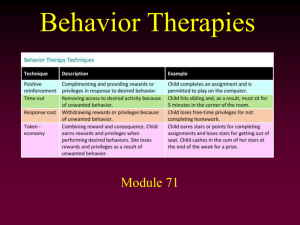
Module 71 - Behavioral Therapy
... • A type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior • The person is replacing a positive (relaxing) but harmful response with a negative/aversive response • Example with alcoholism: Lace a drink with a drug that makes the person becomes sick ...
... • A type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior • The person is replacing a positive (relaxing) but harmful response with a negative/aversive response • Example with alcoholism: Lace a drink with a drug that makes the person becomes sick ...
History of Animal Behavior
... • De humani corporis fabrica libri septem (On the fabric of the human body in seven books) • Paul Broca (1861) • Speech Production ...
... • De humani corporis fabrica libri septem (On the fabric of the human body in seven books) • Paul Broca (1861) • Speech Production ...
Learning Theory Theorists (Alphabetical) Year Ideals Classroom
... Watson did not believe that people had a positive emotional experiences with learning ng Psychology consciousness, instead he believed that and school. as the patterns of behavior were learned from Example: Getting nervous when you see the Behaviorists experiences. teacher holding out papers for a p ...
... Watson did not believe that people had a positive emotional experiences with learning ng Psychology consciousness, instead he believed that and school. as the patterns of behavior were learned from Example: Getting nervous when you see the Behaviorists experiences. teacher holding out papers for a p ...
Operant Conditioning
... your teeth, riding a bike, walking to school and so on. Behavior chains are very important to all of us; as is the procedure for building chains, which is called chaining. Instinctive Drift - Although humans, animals, etc., can learn to perform different behaviors, there are times when they stop per ...
... your teeth, riding a bike, walking to school and so on. Behavior chains are very important to all of us; as is the procedure for building chains, which is called chaining. Instinctive Drift - Although humans, animals, etc., can learn to perform different behaviors, there are times when they stop per ...
First approaches to Psychology, the study of mental
... Uncomfortable with ignoring mental processes that might be important to fully understand behavior Computers enabled psychologists to measure mental activity and to study the biological bases of mental processes. Cognitive and biological factors are influential Commitment to empiricism and scientific ...
... Uncomfortable with ignoring mental processes that might be important to fully understand behavior Computers enabled psychologists to measure mental activity and to study the biological bases of mental processes. Cognitive and biological factors are influential Commitment to empiricism and scientific ...
Chapter 1: The Science of Psychology Module 1: Psychology`s
... Physiological: Finding biological reasons for behavior ...
... Physiological: Finding biological reasons for behavior ...
Chapter 1
... Behavior—observable actions of a person or animal Mind—thoughts, feelings, sensations, perceptions, memories, dreams, motives and other subjective experiences Science—an objective way to answer questions based on observable facts/data and well-described methods ...
... Behavior—observable actions of a person or animal Mind—thoughts, feelings, sensations, perceptions, memories, dreams, motives and other subjective experiences Science—an objective way to answer questions based on observable facts/data and well-described methods ...
introduction to psychology and key people
... His social learning theory stressed the importance of observational learning, imitation, and modeling. "Learning would be exceedingly laborious, not to mention hazardous, if people had to rely solely on the effects of their own actions to inform them what to do," Bandura explained in his 1977 book ...
... His social learning theory stressed the importance of observational learning, imitation, and modeling. "Learning would be exceedingly laborious, not to mention hazardous, if people had to rely solely on the effects of their own actions to inform them what to do," Bandura explained in his 1977 book ...