Chap012 - Organizational Behavior
... Learning Objectives • Define the theoretical processes of learning: behavioristic, cognitive, and social. • Discuss the principle of reinforcement, with special attention given to the law of effect, positive and negative reinforcers, and punishment. • Analyze organizational reward systems, emphasiz ...
... Learning Objectives • Define the theoretical processes of learning: behavioristic, cognitive, and social. • Discuss the principle of reinforcement, with special attention given to the law of effect, positive and negative reinforcers, and punishment. • Analyze organizational reward systems, emphasiz ...
What is Organizational Behavior?
... A desired behavior is reinforced often enough to make the behavior worth repeating but not every time it is demonstrated Fixed interval schedule Variable interval schedule Fixed ratio schedule Variable ratio schedule ...
... A desired behavior is reinforced often enough to make the behavior worth repeating but not every time it is demonstrated Fixed interval schedule Variable interval schedule Fixed ratio schedule Variable ratio schedule ...
Classical Conditioning
... • When you get a consequence for a negative behavior so you stop doing the negative behavior – Ex: You get grounded for coming home after curfew. ...
... • When you get a consequence for a negative behavior so you stop doing the negative behavior – Ex: You get grounded for coming home after curfew. ...
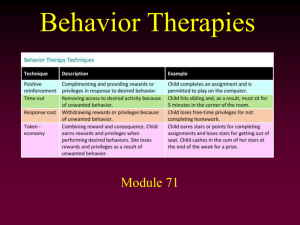
Module 71 - Behavioral Therapy
... unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior • The person is replacing a positive (relaxing) but harmful response with a negative/aversive response • Example with alcoholism: Lace a drink with a drug that makes the person becomes sick • Aversive conditioning is not very effective – Co ...
... unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior • The person is replacing a positive (relaxing) but harmful response with a negative/aversive response • Example with alcoholism: Lace a drink with a drug that makes the person becomes sick • Aversive conditioning is not very effective – Co ...
Albert Bandura - Personal Web Pages
... teacher is near or children who begin talking more at bedtime), 3. response facilitation (a function of the behavior of others - peer pressure), 4. environmental enhancement (children will fight more if they observe parents fighting). ...
... teacher is near or children who begin talking more at bedtime), 3. response facilitation (a function of the behavior of others - peer pressure), 4. environmental enhancement (children will fight more if they observe parents fighting). ...
ANIMAL BEHAVIORS
... A. Innate Behavior • Innate Behavior: behavior that is performed correctly the first time an animal does it – Animal does not have to be taught – “instincts” or “born” behaviors ...
... A. Innate Behavior • Innate Behavior: behavior that is performed correctly the first time an animal does it – Animal does not have to be taught – “instincts” or “born” behaviors ...
Chapter 1
... Behavioral Therapy Formulated at the beginning of the 20th century. Focused on how to reinforce, extinguish, or modify a broad range of behaviors. In its infancy (1900’s-1930’s), behaviorism was concerned almost entirely with outward observations. ...
... Behavioral Therapy Formulated at the beginning of the 20th century. Focused on how to reinforce, extinguish, or modify a broad range of behaviors. In its infancy (1900’s-1930’s), behaviorism was concerned almost entirely with outward observations. ...
Learning Theories
... especially when dealing with adults. For example, at United Independent School District in Laredo Tx. We have a time management device called the Kronos in order for the adult staff to successfully punch every morning they had to be trained repeatedly. Some of them understood the method rather quick ...
... especially when dealing with adults. For example, at United Independent School District in Laredo Tx. We have a time management device called the Kronos in order for the adult staff to successfully punch every morning they had to be trained repeatedly. Some of them understood the method rather quick ...
Animal Behavior
... Animals • Behavior could be studied among different animals and infer relationships • Injective knowledge ...
... Animals • Behavior could be studied among different animals and infer relationships • Injective knowledge ...
NEW DIRECTIONS: Autism, Mirror Neurons, and Applied Behavior
... visual discrimination training. The mirror system allows the observer to process information about self-performed actions and, using the same system, to understand the actions, emotions, and intentions of others (Oberman & Ramachandran, 2007). The integration of behavioral neuroscience with applied ...
... visual discrimination training. The mirror system allows the observer to process information about self-performed actions and, using the same system, to understand the actions, emotions, and intentions of others (Oberman & Ramachandran, 2007). The integration of behavioral neuroscience with applied ...
Noorudean tohmeh
... called radical behaviorism, and founded his own school of experimental research psychology. ...
... called radical behaviorism, and founded his own school of experimental research psychology. ...
The Tales of Operant Conditioning
... His idea was the Law of Effect which was a law for all the people of Thorn County and Skinnerian which stated: Behaviors with favorable consequences will occur more frequently and behaviors followed by less favorable consequences will occur less frequently. Here, the idea of operant conditioni ...
... His idea was the Law of Effect which was a law for all the people of Thorn County and Skinnerian which stated: Behaviors with favorable consequences will occur more frequently and behaviors followed by less favorable consequences will occur less frequently. Here, the idea of operant conditioni ...
Functionalistic and Associationistic Theories
... society should operate as a unit, that each part had its individuals function. If everyone functioned according to their role then everything should flow and things should remain in order. Functionalist theory defines the working of an organism affects another. Olsen, 2009 states 'The primary goal o ...
... society should operate as a unit, that each part had its individuals function. If everyone functioned according to their role then everything should flow and things should remain in order. Functionalist theory defines the working of an organism affects another. Olsen, 2009 states 'The primary goal o ...
No Slide Title
... Habituation: simple type: progressive decrease in response. Classical conditioning: classic S-R connective associations. Operant conditioning: associations between response and reinforcement. Observational learning: see and (may) do; Reinforcement secondary to learning. ...
... Habituation: simple type: progressive decrease in response. Classical conditioning: classic S-R connective associations. Operant conditioning: associations between response and reinforcement. Observational learning: see and (may) do; Reinforcement secondary to learning. ...
Operant Conditioning Notes (teacher version)
... consequences becomes more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely. Skinner Box – a chamber containing a bar that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; devices are attached to record the animal’s rate of bar pressing. ...
... consequences becomes more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely. Skinner Box – a chamber containing a bar that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; devices are attached to record the animal’s rate of bar pressing. ...
Conditioning
... • Stimulus – something that produces a reaction or response. • Unconditioned stimulus • Unconditioned response • Neutral stimulus • Conditioned stimulus ...
... • Stimulus – something that produces a reaction or response. • Unconditioned stimulus • Unconditioned response • Neutral stimulus • Conditioned stimulus ...
Operant Conditioning
... for pecking a key while a vertical line (S+) was projected on the key. Extinction was in effect when S+ was absent. Tests were conducted in extinction while lines of various angle were projected on the key. ...
... for pecking a key while a vertical line (S+) was projected on the key. Extinction was in effect when S+ was absent. Tests were conducted in extinction while lines of various angle were projected on the key. ...
Observational Learning
... • Antisocial models- in one’s family or neighborhood, or on TV- may have antisocial effects. – “Copycat” threats or incidents in every state after Columbine High School massacre – Abusive parents might have aggressive children – Many men who beat their wives had wife-battering fathers • Intergenerat ...
... • Antisocial models- in one’s family or neighborhood, or on TV- may have antisocial effects. – “Copycat” threats or incidents in every state after Columbine High School massacre – Abusive parents might have aggressive children – Many men who beat their wives had wife-battering fathers • Intergenerat ...
Operant Conditioning
... or a multitude of chains: eating, getting dressed, using the computer, counting, brushing your teeth, riding a bike, walking to school and so on. Behavior chains are very important to all of us; as is the procedure for building chains, which is called chaining. Instinctive Drift - Although humans, a ...
... or a multitude of chains: eating, getting dressed, using the computer, counting, brushing your teeth, riding a bike, walking to school and so on. Behavior chains are very important to all of us; as is the procedure for building chains, which is called chaining. Instinctive Drift - Although humans, a ...
Principles of Learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning, and
... • Copying what other’s are doing, although no real learning takes place (We see, so we do.) • Imitation after watching someone do something, that the observer couldn’t do before. • Disinhibition occurs when an observer sees a someone engage in a threatening activity without being punished, then enga ...
... • Copying what other’s are doing, although no real learning takes place (We see, so we do.) • Imitation after watching someone do something, that the observer couldn’t do before. • Disinhibition occurs when an observer sees a someone engage in a threatening activity without being punished, then enga ...
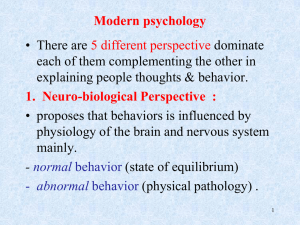
1. Neuro-biological Perspective
... - Behaviors are learned depending on whether they are rewarded or not. ** scientific approach to study behavior, (differ from psychoanalytic theory). ...
... - Behaviors are learned depending on whether they are rewarded or not. ** scientific approach to study behavior, (differ from psychoanalytic theory). ...
Abnormal Behavior
... Panic Disorder - Anxiety that strikes suddenly wreaks havoc and then disappears - a panic attack is a minutes long episode that includes the belief that something terrible is going to happen - Can cause heart palpitations, shortness of breath, trembling or dizziness - 1 in 75 people has this disord ...
... Panic Disorder - Anxiety that strikes suddenly wreaks havoc and then disappears - a panic attack is a minutes long episode that includes the belief that something terrible is going to happen - Can cause heart palpitations, shortness of breath, trembling or dizziness - 1 in 75 people has this disord ...
6AnimalBehavior
... 2. How does the animal’s experience during growth and development influence the response? (proximate) 3. How does the behavior aid survival and reproduction? (ultimate) 4. What is the behavior’s evolutionary history? (ultimate) ...
... 2. How does the animal’s experience during growth and development influence the response? (proximate) 3. How does the behavior aid survival and reproduction? (ultimate) 4. What is the behavior’s evolutionary history? (ultimate) ...
Learning Theory Theorists (Alphabetical) Year Ideals Classroom
... whatever mental maps they have mental “maps, for understanding and constructed. responding to physical experiences within Teachers must develop appropriate curriculum their own environment. Over time a child’s that enhances their students’ logical and mental structure increases in sophistication con ...
... whatever mental maps they have mental “maps, for understanding and constructed. responding to physical experiences within Teachers must develop appropriate curriculum their own environment. Over time a child’s that enhances their students’ logical and mental structure increases in sophistication con ...