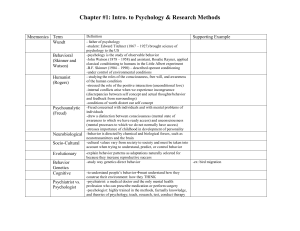
EDT610 project 2 - InstructionalDesign-EDT
... experimental model of learning, Classical Conditioning. Most of his research was gathered studying salivating dogs. Pavlov studied reflexes, automatic behavior that is caused by a stimulus from the environment. Some reflexes, such as blinking your eyes when a puff of air comes in it, or the sucking ...
... experimental model of learning, Classical Conditioning. Most of his research was gathered studying salivating dogs. Pavlov studied reflexes, automatic behavior that is caused by a stimulus from the environment. Some reflexes, such as blinking your eyes when a puff of air comes in it, or the sucking ...
Abnormal Psychology - PAWS - Western Carolina University
... • The core assumption of the psychoanalytic paradigm is that abnormal behavior reflects unconscious conflicts within the person • Drives such as sex and aggression come into conflict with laws, social rules, and moral codes. As we grow, we internalize these rules, so the conflicts are intrapsychic. ...
... • The core assumption of the psychoanalytic paradigm is that abnormal behavior reflects unconscious conflicts within the person • Drives such as sex and aggression come into conflict with laws, social rules, and moral codes. As we grow, we internalize these rules, so the conflicts are intrapsychic. ...
Name: For each of the examples below decide identify the
... For each of the examples below decide identify the unconditioned stimulus (US), unconditioned response (UR), conditioned stimulus (CS), and conditioned response (CR). Classical Conditioning Examples: 1. Every time someone flushes a toilet in the apartment building, the shower becomes very hot and ca ...
... For each of the examples below decide identify the unconditioned stimulus (US), unconditioned response (UR), conditioned stimulus (CS), and conditioned response (CR). Classical Conditioning Examples: 1. Every time someone flushes a toilet in the apartment building, the shower becomes very hot and ca ...
Click www.ondix.com to visit our student-to
... the bond between stimulus and response, then it supposes that whatever we do we do it because it brings some pleasant consequence. Applying this to human behavior, i.e. altruism/other aspects of self-sacrifice, then behavior theory might suggest that somehow this behaviorism are in fact producing pl ...
... the bond between stimulus and response, then it supposes that whatever we do we do it because it brings some pleasant consequence. Applying this to human behavior, i.e. altruism/other aspects of self-sacrifice, then behavior theory might suggest that somehow this behaviorism are in fact producing pl ...
Ability
... 1. Number Aptitude: Ability to do speedy and accurate arithmetic 2. Verbal Comprehension: Ability to understand what is read or heard and the relationship of words to each other. 3. Perceptual Speed: Ability to identify visual similarities and differences quickly and accurately. 4. Inductive Reasoni ...
... 1. Number Aptitude: Ability to do speedy and accurate arithmetic 2. Verbal Comprehension: Ability to understand what is read or heard and the relationship of words to each other. 3. Perceptual Speed: Ability to identify visual similarities and differences quickly and accurately. 4. Inductive Reasoni ...
Module 22 - operant conditioning
... 1. Immediate Reinforcer: A reinforcer that occurs closely to a behavior in time. Rat gets a food pellet for a bar press. 2. Delayed Reinforcer: A reinforcer that is delayed in time for a certain behavior. A paycheck that comes at the end of a week. ...
... 1. Immediate Reinforcer: A reinforcer that occurs closely to a behavior in time. Rat gets a food pellet for a bar press. 2. Delayed Reinforcer: A reinforcer that is delayed in time for a certain behavior. A paycheck that comes at the end of a week. ...
ppt_ch10
... Circular reasoning – labels rather than explains behavior Behavior may not be as stable across time and situations as assumed by trait theorists ...
... Circular reasoning – labels rather than explains behavior Behavior may not be as stable across time and situations as assumed by trait theorists ...
Term - Manhasset Schools
... awareness to which we have ready access) and unconsciousness (mental processes to which we do not normally have access) -stresses importance of childhood in development of personality -behavior is directed by chemical and biological forces, such as neurotransmitters and the brain -cultural values va ...
... awareness to which we have ready access) and unconsciousness (mental processes to which we do not normally have access) -stresses importance of childhood in development of personality -behavior is directed by chemical and biological forces, such as neurotransmitters and the brain -cultural values va ...
Cause
... • Studies have shown that exposure to media violence produces short-term increases in laboratory measures of aggressive thoughts and behavior. • Links between exposure to violent media and aggressive behavior both in and out of the classroom. • The American Psychological Association, the American Ac ...
... • Studies have shown that exposure to media violence produces short-term increases in laboratory measures of aggressive thoughts and behavior. • Links between exposure to violent media and aggressive behavior both in and out of the classroom. • The American Psychological Association, the American Ac ...
Operant Conditioning
... A grade school principal has 1 week to try out a new fire-alarm system for the school. He decides to test the system three times during the week. The first time the alarm is sounded, all of the students leave the school within 5 minutes. The second time, it takes the students 15 minutes to leave th ...
... A grade school principal has 1 week to try out a new fire-alarm system for the school. He decides to test the system three times during the week. The first time the alarm is sounded, all of the students leave the school within 5 minutes. The second time, it takes the students 15 minutes to leave th ...
The Physiological approach:
... The behavioral approach observes a change as a result of experience, that is to look at the learning process. According to John B. Watson, in behavioral approach, there isn't a difference between other animals and humans because psychology is only concerned with behavior and not the reasoning behind ...
... The behavioral approach observes a change as a result of experience, that is to look at the learning process. According to John B. Watson, in behavioral approach, there isn't a difference between other animals and humans because psychology is only concerned with behavior and not the reasoning behind ...
Running head: BEHAVIOR MODIFICATION THROUGH OPERANT
... modification through positive reinforcement. Don was able to learn a new association between successfully using the restroom and receiving a drink of water. Therefore, Don viewed the behavior of using the restroom more enjoyable than before the implementation of positive reinforcement strategies. Wh ...
... modification through positive reinforcement. Don was able to learn a new association between successfully using the restroom and receiving a drink of water. Therefore, Don viewed the behavior of using the restroom more enjoyable than before the implementation of positive reinforcement strategies. Wh ...
Cognition and Operant Conditioning
... by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely ...
... by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely ...
Powerpoint for Module 21
... justifiable than manipulation of others. Humanity improves through free choice guided by wisdom, conscience, and responsibility. ...
... justifiable than manipulation of others. Humanity improves through free choice guided by wisdom, conscience, and responsibility. ...
ch03
... An alternative to punishing undesirable behaviour – the attempt to weaken behavior by attaching no consequences (either positive or negative) to it. It is equivalent to ignoring the behavior. ...
... An alternative to punishing undesirable behaviour – the attempt to weaken behavior by attaching no consequences (either positive or negative) to it. It is equivalent to ignoring the behavior. ...
Crash Course Study Guide for AP Psychology Exam
... b. Population: a group of people about whom the researcher wants to make conclusions. A sample should be representative of the population 2. Random assignment: random placement of subjects into experimental or control groups a. Control group: a group not subject to experimental manipulation 3. Varia ...
... b. Population: a group of people about whom the researcher wants to make conclusions. A sample should be representative of the population 2. Random assignment: random placement of subjects into experimental or control groups a. Control group: a group not subject to experimental manipulation 3. Varia ...
The philosophical position that every behavior has a cause is known
... approach, revised in 1989 (MMPI-2) and has 567 T/F items – Most widely used inventory in clinical settings – items generally lack face validity (not obvious) – 3 validity scales (lying, defensiveness, infrequency) – Assesses m/f, Si, Hs, Pa, etc. (psychopathology= personality) ...
... approach, revised in 1989 (MMPI-2) and has 567 T/F items – Most widely used inventory in clinical settings – items generally lack face validity (not obvious) – 3 validity scales (lying, defensiveness, infrequency) – Assesses m/f, Si, Hs, Pa, etc. (psychopathology= personality) ...
APPsynotesch9-learning
... Cognitive maps-mental representations people rely on to understand complex patterns Latent learning-learning that may not be displayed until a later time, it is not always immediately observable and may lie hidden until a circumstance arises that requires this prior learning to be displayed. It is ...
... Cognitive maps-mental representations people rely on to understand complex patterns Latent learning-learning that may not be displayed until a later time, it is not always immediately observable and may lie hidden until a circumstance arises that requires this prior learning to be displayed. It is ...
Unit 4 - Learning and Cognitive Processes
... Apply motivational concepts to the behavior of humans and other animals. Investigate the role of biology and learning in motivation and emotion Describe the theories of motivation, such as expectancy value, cognitive dissonance, arousal, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, and drive reduction. Discuss cult ...
... Apply motivational concepts to the behavior of humans and other animals. Investigate the role of biology and learning in motivation and emotion Describe the theories of motivation, such as expectancy value, cognitive dissonance, arousal, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, and drive reduction. Discuss cult ...
Module 21 Operant Conditioning
... gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. Eg: money. Immediate reinforcers are innately satisfying rewards (food & sex); most humans need to learn delayed reinforcement as a big step to maturity. (Logue, 1998). ...
... gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer. Eg: money. Immediate reinforcers are innately satisfying rewards (food & sex); most humans need to learn delayed reinforcement as a big step to maturity. (Logue, 1998). ...
Operantmine
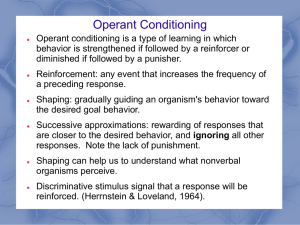
... • A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. ...
... • A type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. ...