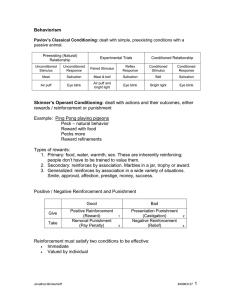
Best Review Sheet Ever - Mr. Voigtschild
... V CS – Originally neutral stimulus that, S after association with UCS, comes to trigger a conditioned response – the condition needed to elicit response V CR – Learned response to previously S neutral stimulus– need conditions for a response – same as UCR after conditioning occurs V Discrimination – ...
... V CS – Originally neutral stimulus that, S after association with UCS, comes to trigger a conditioned response – the condition needed to elicit response V CR – Learned response to previously S neutral stimulus– need conditions for a response – same as UCR after conditioning occurs V Discrimination – ...
Unit 6 Study Guide - PSYCHOLOGY
... being provoked. b. a change in the behavior of an organism. c. a relatively permanent change in the behavior of an organism due to experience. d. behavior based on operant rather than respondent conditioning. 2. Which of the following is a form of associative learning? a. classical conditioning b. o ...
... being provoked. b. a change in the behavior of an organism. c. a relatively permanent change in the behavior of an organism due to experience. d. behavior based on operant rather than respondent conditioning. 2. Which of the following is a form of associative learning? a. classical conditioning b. o ...
Organizational Behaviour
... individuals react and interact with others. It is defined in terms of measurable traits. Traits are the enduring characteristics that describe an individual’s behaviour. Personality is influenced by the following: ...
... individuals react and interact with others. It is defined in terms of measurable traits. Traits are the enduring characteristics that describe an individual’s behaviour. Personality is influenced by the following: ...
Chapter 8 pt. 2: Operant Conditioning and Social Learning
... Cognition’s Effect on Operant Conditioning Cognitive map: a mental representation of one’s environment that is developed without the aid of reinforcement. Latent learning: learning that occurs (like cognitive map) that is not apparent until there is an incentive to justify it. Ex: rats that wer ...
... Cognition’s Effect on Operant Conditioning Cognitive map: a mental representation of one’s environment that is developed without the aid of reinforcement. Latent learning: learning that occurs (like cognitive map) that is not apparent until there is an incentive to justify it. Ex: rats that wer ...
IB Psychology: Summer Assignment 2016
... situation” experimental design; described secure and insecure attachment. Neuroscientist who has a region of the brain responsible for understanding language named after him. Neo-Freudian psychologist who developed the idea of archetypes and the collective unconscious; famous for his work on dream i ...
... situation” experimental design; described secure and insecure attachment. Neuroscientist who has a region of the brain responsible for understanding language named after him. Neo-Freudian psychologist who developed the idea of archetypes and the collective unconscious; famous for his work on dream i ...
1. Complete index cards
... situation” experimental design; described secure and insecure attachment. Neuroscientist who has a region of the brain responsible for understanding language named after him. Neo-Freudian psychologist who developed the idea of archetypes and the collective unconscious; famous for his work on dream i ...
... situation” experimental design; described secure and insecure attachment. Neuroscientist who has a region of the brain responsible for understanding language named after him. Neo-Freudian psychologist who developed the idea of archetypes and the collective unconscious; famous for his work on dream i ...
Junior IB Psychology Summer Assignment
... situation” experimental design; described secure and insecure attachment. Neuroscientist who has a region of the brain responsible for understanding language named after him. Neo-Freudian psychologist who developed the idea of archetypes and the collective unconscious; famous for his work on dream i ...
... situation” experimental design; described secure and insecure attachment. Neuroscientist who has a region of the brain responsible for understanding language named after him. Neo-Freudian psychologist who developed the idea of archetypes and the collective unconscious; famous for his work on dream i ...
Lesson 1: Attributes of Learning and Classical Conditioning
... opportunity to explore a maze will develop a cognitive map, even when there is neither reward nor motivation for learning. Later, when reward is available, rats that have had the opportunity to explore will perform better than those that have not had that opportunity C. Observational learning, descr ...
... opportunity to explore a maze will develop a cognitive map, even when there is neither reward nor motivation for learning. Later, when reward is available, rats that have had the opportunity to explore will perform better than those that have not had that opportunity C. Observational learning, descr ...
Psy101 Learning.lst
... Differentiate between primary and secondary reinforcers and give an example of each as they relate to you. ...
... Differentiate between primary and secondary reinforcers and give an example of each as they relate to you. ...
Biological Influences on Learning
... According to Timberlake, an animal possesses instinctive behaviors such as feeding, mating, social bonding, care of young, and defense. ...
... According to Timberlake, an animal possesses instinctive behaviors such as feeding, mating, social bonding, care of young, and defense. ...
Learning - WordPress.com
... The approach to the study of learning that focuses on the thought process that underlie learning. Types of Learning 1. Latent Learning 2. Observational Learning ...
... The approach to the study of learning that focuses on the thought process that underlie learning. Types of Learning 1. Latent Learning 2. Observational Learning ...
Operant Conditioning
... Operant Conditioning Form of learning based on the consequences of actions People and animals learn to do things (and not to do others) because of the results of what they do. Learning from the consequences. In operant conditioning, behaviors that people and animals have control over are conditione ...
... Operant Conditioning Form of learning based on the consequences of actions People and animals learn to do things (and not to do others) because of the results of what they do. Learning from the consequences. In operant conditioning, behaviors that people and animals have control over are conditione ...
behaviorism
... Behaviorism-focuses on observable behavior and actual conditions that lead to behavior; deals with the relationship between stimuli and responses and among stimuli. Learning is defined as a change in the behavior of the learner Stimulus response principle Known as associative learning All beha ...
... Behaviorism-focuses on observable behavior and actual conditions that lead to behavior; deals with the relationship between stimuli and responses and among stimuli. Learning is defined as a change in the behavior of the learner Stimulus response principle Known as associative learning All beha ...
Animal Behavior_05
... 1. Natural Selection An animal that successfully completes a helpful behavior survives to pass on the behavior to offspring E.g. lion infanticide (new alpha male kills all former alpha’s get) Why would this be beneficial to the species? 2. Innate Behavior Appear in fully functional form when f ...
... 1. Natural Selection An animal that successfully completes a helpful behavior survives to pass on the behavior to offspring E.g. lion infanticide (new alpha male kills all former alpha’s get) Why would this be beneficial to the species? 2. Innate Behavior Appear in fully functional form when f ...
Examination Subject Course Number Course Title Full Marks M.Sc
... learning. The history of learning theory; major issues of controversy in learning theory. 2. Basic principles and background of Pavlovian conditioning: processes and concepts of classical conditioning; physiological basis of classical conditioning; Basic types of conditioning Pavlov’s contribution a ...
... learning. The history of learning theory; major issues of controversy in learning theory. 2. Basic principles and background of Pavlovian conditioning: processes and concepts of classical conditioning; physiological basis of classical conditioning; Basic types of conditioning Pavlov’s contribution a ...
Behaviorism
... 1. Punishment suppresses rather than eliminates behaviors. The behavior may reappear when punishment is absent. 2. Punishment can lead to an increase in punished behavior. “Punishment” can be reinforcing. Some kids crave attention so badly that they misbehave to get any kind of attention – even puni ...
... 1. Punishment suppresses rather than eliminates behaviors. The behavior may reappear when punishment is absent. 2. Punishment can lead to an increase in punished behavior. “Punishment” can be reinforcing. Some kids crave attention so badly that they misbehave to get any kind of attention – even puni ...
Operant Conditioning - Little Miami Schools
... Learning in which a certain action is reinforced or punished, resulting in behavioral change ...
... Learning in which a certain action is reinforced or punished, resulting in behavioral change ...
Modules 19-20
... she cries. If Ken is spanked immediately before his baby sister cries, he is not likely to become fearful when she cries. What do the different reactions of George and Ken suggest about the role of cognitive processes in associative learning? 4. Mr. Byrne can't understand why scolding his seventh-gr ...
... she cries. If Ken is spanked immediately before his baby sister cries, he is not likely to become fearful when she cries. What do the different reactions of George and Ken suggest about the role of cognitive processes in associative learning? 4. Mr. Byrne can't understand why scolding his seventh-gr ...
Learning ppt
... Bobo doll experiment • Albert Bandura allowed children to watch an adult play with a bobo doll. • The experimental group watched a video of an adult playing violently with the doll • The control group watched a boring video. • The experimental group children imitated the violent behavior. ...
... Bobo doll experiment • Albert Bandura allowed children to watch an adult play with a bobo doll. • The experimental group watched a video of an adult playing violently with the doll • The control group watched a boring video. • The experimental group children imitated the violent behavior. ...
Behaviorism - pgt201e2009
... theories of John Locke (1632-1704) who believed that knowledge came to the child only through experience and learning. The children were the products of their environment and upbringing. Watson´s new approach to psychology was called behaviourism, a theory of psychology that says that human developm ...
... theories of John Locke (1632-1704) who believed that knowledge came to the child only through experience and learning. The children were the products of their environment and upbringing. Watson´s new approach to psychology was called behaviourism, a theory of psychology that says that human developm ...
2) Operant conditioning where there is reinforcement
... theories of John Locke (1632-1704) who believed that knowledge came to the child only through experience and learning. The children were the products of their environment and upbringing. Watson´s new approach to psychology was called behaviourism, a theory of psychology that says that human developm ...
... theories of John Locke (1632-1704) who believed that knowledge came to the child only through experience and learning. The children were the products of their environment and upbringing. Watson´s new approach to psychology was called behaviourism, a theory of psychology that says that human developm ...
Organized-Crime-9th-Edition-Howard-Abadinsky-Test
... 28. Central to the psychoanalytic explanation for crime is the __________, a consciencelike mechanism whose function is to restrain the person from antisocial behavior. (b) – LO 7, p. 36 a. id b. superego c. ego d. superid 29. Persons with ________________ have a poorly developed superego—they are p ...
... 28. Central to the psychoanalytic explanation for crime is the __________, a consciencelike mechanism whose function is to restrain the person from antisocial behavior. (b) – LO 7, p. 36 a. id b. superego c. ego d. superid 29. Persons with ________________ have a poorly developed superego—they are p ...