Syllabus - Randolph College
... would likely not survive. While early work in the field of learning simply strived to examine behavior in an objective, quantifiable manner, later learning theorists have worked to apply learning principles to our everyday lives. In this course, we will examine basic theories and phenomena in the fi ...
... would likely not survive. While early work in the field of learning simply strived to examine behavior in an objective, quantifiable manner, later learning theorists have worked to apply learning principles to our everyday lives. In this course, we will examine basic theories and phenomena in the fi ...
Long-term memory - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • How info is processed initially has impact on recall. • More likely to remember new material if you integrate it with information already stored in long-term memory. • 3 ways to facilitate this kind of integration: 1. Elaboration: add meaning to new info by connecting it to existing knowledge (app ...
... • How info is processed initially has impact on recall. • More likely to remember new material if you integrate it with information already stored in long-term memory. • 3 ways to facilitate this kind of integration: 1. Elaboration: add meaning to new info by connecting it to existing knowledge (app ...
No Slide Title
... • How info is processed initially has impact on recall. • More likely to remember new material if you integrate it with information already stored in long-term memory. • 3 ways to facilitate this kind of integration: 1. Elaboration: add meaning to new info by connecting it to existing knowledge (app ...
... • How info is processed initially has impact on recall. • More likely to remember new material if you integrate it with information already stored in long-term memory. • 3 ways to facilitate this kind of integration: 1. Elaboration: add meaning to new info by connecting it to existing knowledge (app ...
Review Chp - Central Magnet School
... they hear that song a lot when they are together. At the end of the summer, they have to return to their separate colleges, which are quite far apart. That fall, every time Sarah hears the tune “Buckets of Love,” she experiences the same feelings of relaxation and contentment that she felt when she ...
... they hear that song a lot when they are together. At the end of the summer, they have to return to their separate colleges, which are quite far apart. That fall, every time Sarah hears the tune “Buckets of Love,” she experiences the same feelings of relaxation and contentment that she felt when she ...
Table of Contents
... Aversions can have survival benefits How to protect sheep from coyotes without killing the coyotes ...
... Aversions can have survival benefits How to protect sheep from coyotes without killing the coyotes ...
A.P. Psychology 6 (F) - Learning By Observation
... Unit 6 (F): Learning By Observation Mr. McCormick A.P. Psychology ...
... Unit 6 (F): Learning By Observation Mr. McCormick A.P. Psychology ...
PowerPoint Presentation - National Mental Health Court Summit
... Positive punishment, sometimes referred to as punishment by application, involves the presentation of an unfavorable event or outcome in order to weaken the response it follows, e.g. community service or jail. Negative punishment, also known as punishment by removal, occurs when a favorable event or ...
... Positive punishment, sometimes referred to as punishment by application, involves the presentation of an unfavorable event or outcome in order to weaken the response it follows, e.g. community service or jail. Negative punishment, also known as punishment by removal, occurs when a favorable event or ...
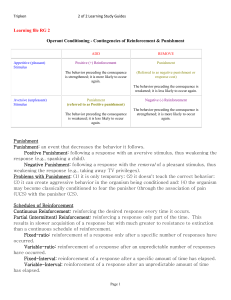
Learning file RG 2 Operant Conditioning
... Cognitive Map: a mental representation of the layout of one's environment. Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect: the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now s ...
... Cognitive Map: a mental representation of the layout of one's environment. Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect: the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now s ...
Chp 9
... People’s behaviors are largely the result of their experiences with environmental stimuli. › The “writing” of our behavior is called conditioning. Learning is the relationships among stimuli and responses. Learning involves a behavior change. › Note that this does not include mental events. Learning ...
... People’s behaviors are largely the result of their experiences with environmental stimuli. › The “writing” of our behavior is called conditioning. Learning is the relationships among stimuli and responses. Learning involves a behavior change. › Note that this does not include mental events. Learning ...
Chapter 1 Reading Questions Part II
... believed psychology should focus on the conscious mind of each individual. He asked, for example, why most people remember recent events better than things that happened in the distant past. 4. Discuss how Freud was different than the above ideas. Unlike Wundt and James, who concentrated their effor ...
... believed psychology should focus on the conscious mind of each individual. He asked, for example, why most people remember recent events better than things that happened in the distant past. 4. Discuss how Freud was different than the above ideas. Unlike Wundt and James, who concentrated their effor ...
The Behavioral And Brain Sciences (1984) 7:4, pp
... The other distinction that the target article appears to neglect is that between knowing propositions and having the ability to perform responses, or knowing that and "knowing" (in quotes, because, strictly speaking, only propositions can be known) how (Ryle 1949). The running together of this disti ...
... The other distinction that the target article appears to neglect is that between knowing propositions and having the ability to perform responses, or knowing that and "knowing" (in quotes, because, strictly speaking, only propositions can be known) how (Ryle 1949). The running together of this disti ...
The Story of Psychology
... through empiricism (by which we take in information through observation and through testing and measuring), and by rationalism (by which we think about what the results of our testing means and what conclusions we can draw about the things we can see and hear.) ...
... through empiricism (by which we take in information through observation and through testing and measuring), and by rationalism (by which we think about what the results of our testing means and what conclusions we can draw about the things we can see and hear.) ...
Jenkins “Defining Psychology” AP Psych Unit I: Thinking Critically
... based on unreliable personal beliefs, opinions, and emotions. In addition, scientists are characterized by skepticism. Skeptical people challenge whether a supposed fact is really true. Being skeptical can mean questioning what “everybody knows.” There was a time when “everybody knew” that women wer ...
... based on unreliable personal beliefs, opinions, and emotions. In addition, scientists are characterized by skepticism. Skeptical people challenge whether a supposed fact is really true. Being skeptical can mean questioning what “everybody knows.” There was a time when “everybody knew” that women wer ...
FREE Sample Here
... Prepare three decks of flashcards. The first deck contains Spanish words on one side and its English counterpart on the reverse side. A second deck contains the same Spanish* words as the first deck; however, this deck also has illustrations with its respective Spanish words. Also include the corres ...
... Prepare three decks of flashcards. The first deck contains Spanish words on one side and its English counterpart on the reverse side. A second deck contains the same Spanish* words as the first deck; however, this deck also has illustrations with its respective Spanish words. Also include the corres ...
Sample Lecture: "Feedback Reinforcement and Intrinsic Motivation"
... Influential approach in psychology – Operant conditioning (A) Antecedents or environmental stimuli; (B) behaviors in which the person engages; and (C) Consequences that follow the behaviors. ...
... Influential approach in psychology – Operant conditioning (A) Antecedents or environmental stimuli; (B) behaviors in which the person engages; and (C) Consequences that follow the behaviors. ...
Test Bank 1
... such as therapy groups, rather than traditional insight therapies? Ask students this question. They will often focus on the practical reasons such as "It's faster," "It's cheaper," or "There are too many clients and not enough counselors." Although these answers are often true, research demonstrates ...
... such as therapy groups, rather than traditional insight therapies? Ask students this question. They will often focus on the practical reasons such as "It's faster," "It's cheaper," or "There are too many clients and not enough counselors." Although these answers are often true, research demonstrates ...
history of psychology
... He placed little credence in the unconscious because it was not observable. There must be observable and measurable behavior to be scientific. “Scientific Inquiry” Little Albert and Classical Conditioning Phobias: Fear is learned All behavior is the result of a stimulus / response relationship ...
... He placed little credence in the unconscious because it was not observable. There must be observable and measurable behavior to be scientific. “Scientific Inquiry” Little Albert and Classical Conditioning Phobias: Fear is learned All behavior is the result of a stimulus / response relationship ...
File - IISWBM EVE Website
... are accompanied or closely followed by satisfaction (reinforcement) will be more likely to recur, those which are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort (punishment) will be less likely to occur. • In other-words desirable or reinforcing consequences will increase the strength of a response & ...
... are accompanied or closely followed by satisfaction (reinforcement) will be more likely to recur, those which are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort (punishment) will be less likely to occur. • In other-words desirable or reinforcing consequences will increase the strength of a response & ...
SP ED 5022/6022-001 | Applied Behavior Analysis Powerpoint
... Piaget also had some theories about why individuals engage in certain behaviors, and he had some developmental explanations as well. His stages were not like Freud's stages. He had sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operations, formal operations. And so he said that individuals go through these ...
... Piaget also had some theories about why individuals engage in certain behaviors, and he had some developmental explanations as well. His stages were not like Freud's stages. He had sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operations, formal operations. And so he said that individuals go through these ...
Clark Leonard Hull
... hope if a bell sounds just prior to food or of disappointment if the bell sounds just prior to the removal of ...
... hope if a bell sounds just prior to food or of disappointment if the bell sounds just prior to the removal of ...
Cognitive Learning
... on subsequent trials. Their Performance was better than Group A. • Rats in Group C had been learning the maze all along, just as much as the rats in group A, BUT they had no motivation to demonstrate this learning until a reward was introduced. ...
... on subsequent trials. Their Performance was better than Group A. • Rats in Group C had been learning the maze all along, just as much as the rats in group A, BUT they had no motivation to demonstrate this learning until a reward was introduced. ...
M_5_Glossary Learning - user.meduni
... Locus of control. A personality trait that concerns whether people attribute responsibility for their own failure or success to internal factors or to external factors. Long-term memory. Components of memory where large amounts of information can be stored for long periods of time (see Module 2). Ma ...
... Locus of control. A personality trait that concerns whether people attribute responsibility for their own failure or success to internal factors or to external factors. Long-term memory. Components of memory where large amounts of information can be stored for long periods of time (see Module 2). Ma ...
tablesection1-teacher-website-ch8
... Type of counterconditioning which associates an unpleasant feeling with an unwanted behavior ...
... Type of counterconditioning which associates an unpleasant feeling with an unwanted behavior ...
ABC`s of ABA - Ventura County SELPA
... reinforcing stimuli, have become reinforcing. Social praise, tokens Conditioned reinforcers are typically more convenient to use than primary. Secondary reinforcement lessens the need for proximity to a child. Secondary reinforcement can be used to broaden the interests of the child Using a to ...
... reinforcing stimuli, have become reinforcing. Social praise, tokens Conditioned reinforcers are typically more convenient to use than primary. Secondary reinforcement lessens the need for proximity to a child. Secondary reinforcement can be used to broaden the interests of the child Using a to ...
Learning Chapter Preview
... Little Albert generalized his fear to other things like white beards – Generalization ...
... Little Albert generalized his fear to other things like white beards – Generalization ...
Operant conditioning

Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is a learning process in which behavior is sensitive to, or controlled by its consequences. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the candy inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove. In contrast, classical conditioning causes a stimulus to signal a positive or negative consequence; the resulting behavior does not produce the consequence. For example, the sight of a colorful wrapper comes to signal ""candy"", causing a child to salivate, or the sound of a door slam comes to signal an angry parent, causing a child to tremble. The study of animal learning in the 20th century was dominated by the analysis of these two sorts of learning, and they are still at the core of behavior analysis.