Classical Conditioning 5.1 Introduction Classical conditioning
... The Rescorla- Wagner model argues that there is a limit to the amount of conditioning that can occur in the pairing of two stimuli. One determinant of this limit is the nature of the US. For example: pairing a bell with a juicy steak, is more likely to produce salivation than pairing a piece of dry ...
... The Rescorla- Wagner model argues that there is a limit to the amount of conditioning that can occur in the pairing of two stimuli. One determinant of this limit is the nature of the US. For example: pairing a bell with a juicy steak, is more likely to produce salivation than pairing a piece of dry ...
Redalyc.Transfer of latent inhibition of aversively conditioned
... members of an equivalence class, and the transformation of autonomic sexual responses in accordance with arbitrary relations other than equivalence (sameness and opposition), which extends the original findings by Dougher et al. (1994). Altogether these studies provide empirical data to explain how ...
... members of an equivalence class, and the transformation of autonomic sexual responses in accordance with arbitrary relations other than equivalence (sameness and opposition), which extends the original findings by Dougher et al. (1994). Altogether these studies provide empirical data to explain how ...
Learning and Memory Jeopardy
... BIV to remember the colors of the rainbow in the order of wavelength illustrates the use of this organizational system for ...
... BIV to remember the colors of the rainbow in the order of wavelength illustrates the use of this organizational system for ...
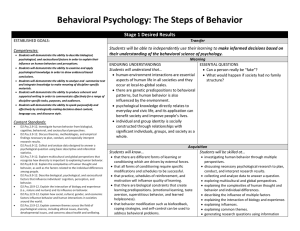
BEHAVIORAL PSYCH The Steps of Behavior
... • human-environment interactions are essential • What would happen if society had no family aspects of human life in all societies and they structure? occur at local-to-global scales. • there are genetic predispositions to behavioral patterns, but human behavior is also influenced by the environment ...
... • human-environment interactions are essential • What would happen if society had no family aspects of human life in all societies and they structure? occur at local-to-global scales. • there are genetic predispositions to behavioral patterns, but human behavior is also influenced by the environment ...
Behavior Modification
... Therapy and consultation cannot be effective unless the behaviors to be changed are understood within a specific context.[5][6] The process of understanding behavior in context is called functional behavioral assessment.[7] Therefore, a functional behavioral assessment is needed before performing be ...
... Therapy and consultation cannot be effective unless the behaviors to be changed are understood within a specific context.[5][6] The process of understanding behavior in context is called functional behavioral assessment.[7] Therefore, a functional behavioral assessment is needed before performing be ...
chapter outlines - Cengage Learning
... HERGENHAHN’S AN INTRODUCTION TO THE HISTORY OF PSYCHOLOGY, 6E ...
... HERGENHAHN’S AN INTRODUCTION TO THE HISTORY OF PSYCHOLOGY, 6E ...
Psychological Perspectives on Behavior: From Purposeful to
... humans) followed certain fundamental laws. The most well-known of these is his law of effect, stating that behaviors that are followed by “satisfaction to the animal” will most likely recur, while actions followed by “discomfort to the animal” will be less likely to recur. Thorndike was the first ps ...
... humans) followed certain fundamental laws. The most well-known of these is his law of effect, stating that behaviors that are followed by “satisfaction to the animal” will most likely recur, while actions followed by “discomfort to the animal” will be less likely to recur. Thorndike was the first ps ...
Intro to Motivation
... 1. Natural selection acts on genes expressed in particular circumstances 2. Selection takes place at the individual level; it is not “survival” in the literal sense 3. Behaviors adaptive in one time or place may not be adaptive to others (affluence and food choice) ...
... 1. Natural selection acts on genes expressed in particular circumstances 2. Selection takes place at the individual level; it is not “survival” in the literal sense 3. Behaviors adaptive in one time or place may not be adaptive to others (affluence and food choice) ...
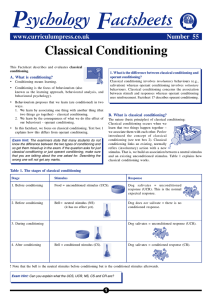
Classical Conditioning
... It has practical applications, such as in behavioural therapies (e.g., aversion therapy). It explains only behaviours which already exist (such as salivation), but it does not explain the appearance of entirely new behaviours. Learning also includes operant conditioning and observational learning. R ...
... It has practical applications, such as in behavioural therapies (e.g., aversion therapy). It explains only behaviours which already exist (such as salivation), but it does not explain the appearance of entirely new behaviours. Learning also includes operant conditioning and observational learning. R ...
Transfer of Latent Inhibition of Aversively Conditioned
... members of an equivalence class, and the transformation of autonomic sexual responses in accordance with arbitrary relations other than equivalence (sameness and opposition), which extends the original findings by Dougher et al. (1994). Altogether these studies provide empirical data to explain how ...
... members of an equivalence class, and the transformation of autonomic sexual responses in accordance with arbitrary relations other than equivalence (sameness and opposition), which extends the original findings by Dougher et al. (1994). Altogether these studies provide empirical data to explain how ...
B.F. Skinner Skinner`s Life Reinforcement, Cont`d.
... • It is objective and amenable to study. • Great deal of empirical support. ...
... • It is objective and amenable to study. • Great deal of empirical support. ...
The Evolution of Interdisciplinary Research on Human Behavior
... behavior has been the development of new technologies for the assessment of brain function and physiological, molecular, and genetic processes as well as a much better understanding of the reciprocal interactions between brain, body, behavior (the 3 Bs), genes, and environment. In terms of theoretic ...
... behavior has been the development of new technologies for the assessment of brain function and physiological, molecular, and genetic processes as well as a much better understanding of the reciprocal interactions between brain, body, behavior (the 3 Bs), genes, and environment. In terms of theoretic ...
Learning - Net Texts
... and skills through experience. Looking back at our surfing scenario, Julian will have to spend much more time training with his surfboard before he learns how to ride the waves like his father. Learning to surf, as well as any complex learning process (e.g., learning about the discipline of psycholo ...
... and skills through experience. Looking back at our surfing scenario, Julian will have to spend much more time training with his surfboard before he learns how to ride the waves like his father. Learning to surf, as well as any complex learning process (e.g., learning about the discipline of psycholo ...
The History of Behaviorism designed by: Dylan Osborne
... How does Walden Two achieve this utopia? Through a science of behavior. Everything that is done at Walden Two is based on principles of behaviorism, the idea that human behavior can be controlled by manipulating contingencies of reward and, to a lesser extent, punishment (SparkNotes Editors, n.d.). ...
... How does Walden Two achieve this utopia? Through a science of behavior. Everything that is done at Walden Two is based on principles of behaviorism, the idea that human behavior can be controlled by manipulating contingencies of reward and, to a lesser extent, punishment (SparkNotes Editors, n.d.). ...
Allen Joel Neuringer Professor of Psychology
... Pigeons respond to produce periods in which rewards are independent of responding. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 1973, 19, 39-54. Extinction in the presence of free food. Psychonomic Science, 1972, 26, 267-269 (Enkema, S., Slavin, R., Spaeth, C. & Neuringer, A.). Responding under ...
... Pigeons respond to produce periods in which rewards are independent of responding. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 1973, 19, 39-54. Extinction in the presence of free food. Psychonomic Science, 1972, 26, 267-269 (Enkema, S., Slavin, R., Spaeth, C. & Neuringer, A.). Responding under ...
What is Cognitive Science?
... some serious problems for a natural science What representations are about is what matters But how can the fact that a belief is about some particular thing have an observable consequence? • e.g. How can the presence of “holy grail” in a belief determine behavior when the holy grail does not exist ...
... some serious problems for a natural science What representations are about is what matters But how can the fact that a belief is about some particular thing have an observable consequence? • e.g. How can the presence of “holy grail” in a belief determine behavior when the holy grail does not exist ...
Psychology 312-1 - Northwestern University
... knew that at the segment chosen (170190 ms post stimulus), the EP amplitude was typically variable, high to low values. He intuited that the variability was tied to some behavioral state which he hoped could be operantly conditioned. (The tricky, slippery part is identifying that state. We never hav ...
... knew that at the segment chosen (170190 ms post stimulus), the EP amplitude was typically variable, high to low values. He intuited that the variability was tied to some behavioral state which he hoped could be operantly conditioned. (The tricky, slippery part is identifying that state. We never hav ...
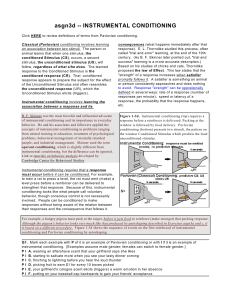
asgn3d -- INSTRUMENTAL CONDITIONING
... to train a rat to press a level, the rat m ust em it (m ake) a level press before a reinforcer can be delivered to strengthen that response. Because of this, instrum ental conditioning looks like what people call voluntary behavior, though conscious control is not necessarily involved. People can be ...
... to train a rat to press a level, the rat m ust em it (m ake) a level press before a reinforcer can be delivered to strengthen that response. Because of this, instrum ental conditioning looks like what people call voluntary behavior, though conscious control is not necessarily involved. People can be ...
A Behavioural Approach to Language Assessment and
... “Thirty points about motivation from Skinner’s book Verbal Behavior” (Sundberg, 2013) Jack Michael and colleagues have published various refinements and extensions of Skinner’s analysis (Laraway, Snycerski, Michael, & Poling, 2003; Michael, 1982, 1988, 1993, 2000, 2004, 2007) “Discriminative variabl ...
... “Thirty points about motivation from Skinner’s book Verbal Behavior” (Sundberg, 2013) Jack Michael and colleagues have published various refinements and extensions of Skinner’s analysis (Laraway, Snycerski, Michael, & Poling, 2003; Michael, 1982, 1988, 1993, 2000, 2004, 2007) “Discriminative variabl ...
Operant conditioning

Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is a learning process in which behavior is sensitive to, or controlled by its consequences. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the candy inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove. In contrast, classical conditioning causes a stimulus to signal a positive or negative consequence; the resulting behavior does not produce the consequence. For example, the sight of a colorful wrapper comes to signal ""candy"", causing a child to salivate, or the sound of a door slam comes to signal an angry parent, causing a child to tremble. The study of animal learning in the 20th century was dominated by the analysis of these two sorts of learning, and they are still at the core of behavior analysis.