File
... Hans Christian Oersted accidentally found that a currentcarrying wire induces a magnetic field. Similarly, a magnetic field can induce a current in a wire moving through it. This “new” are of study became known as electromagnetism. A straight current-carrying wire will have a magnetic field arou ...
... Hans Christian Oersted accidentally found that a currentcarrying wire induces a magnetic field. Similarly, a magnetic field can induce a current in a wire moving through it. This “new” are of study became known as electromagnetism. A straight current-carrying wire will have a magnetic field arou ...
Unit 3_electricity and magnetism_97
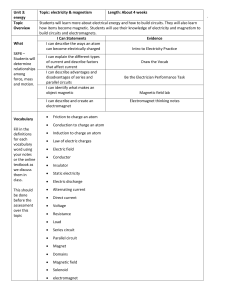
... how items become magnetic. Students will use their knowledge of electricity and magnetism to build circuits and electromagnets. I Can Statements Evidence I can describe the ways an atom can become electrically charged Intro to Electricity Practice I can explain the different types of current and des ...
... how items become magnetic. Students will use their knowledge of electricity and magnetism to build circuits and electromagnets. I Can Statements Evidence I can describe the ways an atom can become electrically charged Intro to Electricity Practice I can explain the different types of current and des ...
Magnetostriction vs. Magnetoelastic Effects
... all ferromagnetic materials. It couples elastic, electric, magnetic and in some situations also thermal fields and is of great industrial interest for use in sensors, actuators, adaptive or functional structures, robotics, transducers and MEMS. A magnetostrictive material develops large mechanical d ...
... all ferromagnetic materials. It couples elastic, electric, magnetic and in some situations also thermal fields and is of great industrial interest for use in sensors, actuators, adaptive or functional structures, robotics, transducers and MEMS. A magnetostrictive material develops large mechanical d ...
cp19
... (5) Two infinitely long wires carry equal currents of 8.0A running anti-parallel to each other. They are both parallel to the z-axis, and are located on the xaxis at x=3.0m and x=0.0m respectively. Find the magnetic field at the following points on the x-y ...
... (5) Two infinitely long wires carry equal currents of 8.0A running anti-parallel to each other. They are both parallel to the z-axis, and are located on the xaxis at x=3.0m and x=0.0m respectively. Find the magnetic field at the following points on the x-y ...
Magnetism Word List
... An object that attracts magnetic materials and attracts and repels other magnets Magnetic material A material that is attracted to a magnet Iron A magnetic element Cobalt A magnetic element Nickel A magnetic element Steel A material containing iron, which causes it to be a magnetic material Magnetis ...
... An object that attracts magnetic materials and attracts and repels other magnets Magnetic material A material that is attracted to a magnet Iron A magnetic element Cobalt A magnetic element Nickel A magnetic element Steel A material containing iron, which causes it to be a magnetic material Magnetis ...
Superconductors - Bryn Mawr College
... The Meissner effect in superconductors like this black ceramic yttrium based superconductor acts to exclude magnetic fields from the material. Since the electrical resistance is zero, supercurrents are generated in the material to exclude the magnetic fields from a magnet brought near it. The curren ...
... The Meissner effect in superconductors like this black ceramic yttrium based superconductor acts to exclude magnetic fields from the material. Since the electrical resistance is zero, supercurrents are generated in the material to exclude the magnetic fields from a magnet brought near it. The curren ...
Lecture_7_Magnets and Magnetism print
... – Lines indicating magnetic field – Direction from N to S – Density indicates strength ...
... – Lines indicating magnetic field – Direction from N to S – Density indicates strength ...
Oersted, Hans Christian
... While lecturing to his students at the University, he noticed that a nearby magnetized compass needle was disturbed when an electric current passed through a very thin platinum wire. In his own words, the experiment made no strong impression on his audience. He was also not sure that the effect was ...
... While lecturing to his students at the University, he noticed that a nearby magnetized compass needle was disturbed when an electric current passed through a very thin platinum wire. In his own words, the experiment made no strong impression on his audience. He was also not sure that the effect was ...
Lecture18
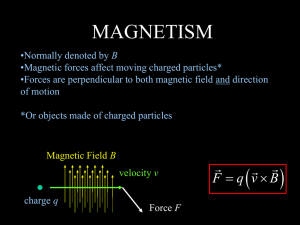
... •All magnets have a north and south pole! No such thing as an isolated north or south pole. (have magnetic dipoles, not monopoles) •Different force laws! ...
... •All magnets have a north and south pole! No such thing as an isolated north or south pole. (have magnetic dipoles, not monopoles) •Different force laws! ...
2.1.4 magnetic fields
... (North and & South). More correctly they should be referred to as the “North seeking pole” and “South seeking pole” Like poles repel each other Unlike poles attract each other ...
... (North and & South). More correctly they should be referred to as the “North seeking pole” and “South seeking pole” Like poles repel each other Unlike poles attract each other ...
Giant magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in thin-film structures composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR.The effect is observed as a significant change in the electrical resistance depending on whether the magnetization of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are in a parallel or an antiparallel alignment. The overall resistance is relatively low for parallel alignment and relatively high for antiparallel alignment. The magnetization direction can be controlled, for example, by applying an external magnetic field. The effect is based on the dependence of electron scattering on the spin orientation.The main application of GMR is magnetic field sensors, which are used to read data in hard disk drives, biosensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and other devices. GMR multilayer structures are also used in magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) as cells that store one bit of information.In literature, the term giant magnetoresistance is sometimes confused with colossal magnetoresistance of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic semiconductors, which is not related to the multilayer structure.