Recombinant DNA
... Recombinant DNA technology can be used to clone (make identical copies) genes. Transformation: Recombinant DNA is cloned by inserting it into host cells (transfection if host cells are from an animal). The altered host cell is called transgenic. ...
... Recombinant DNA technology can be used to clone (make identical copies) genes. Transformation: Recombinant DNA is cloned by inserting it into host cells (transfection if host cells are from an animal). The altered host cell is called transgenic. ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... uptake DNA by horizontal DNA transfer. However, some bacteria such as Pseudomonas species which are not naturally competent must use more complex strategies such as conjugation to uptake DNA. Bacterial conjugation (described Chapter 4) is very efficient in Pseudomonas but requires the presence of a ...
... uptake DNA by horizontal DNA transfer. However, some bacteria such as Pseudomonas species which are not naturally competent must use more complex strategies such as conjugation to uptake DNA. Bacterial conjugation (described Chapter 4) is very efficient in Pseudomonas but requires the presence of a ...
Transcription - SCIS Teachers
... Environmental changes and regulation of genes Another type of operon control involves activators, proteins that turn operons on by • binding to DNA and • making it easier for RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter. ...
... Environmental changes and regulation of genes Another type of operon control involves activators, proteins that turn operons on by • binding to DNA and • making it easier for RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter. ...
book ppt
... Recombinant DNA technology can be used to clone (make identical copies) genes. Transformation: Recombinant DNA is cloned by inserting it into host cells (transfection if host cells are from an animal). The altered host cell is called transgenic. ...
... Recombinant DNA technology can be used to clone (make identical copies) genes. Transformation: Recombinant DNA is cloned by inserting it into host cells (transfection if host cells are from an animal). The altered host cell is called transgenic. ...
Chapter 13 from book
... Recombinant DNA technology can be used to clone (make identical copies) genes. Transformation: Recombinant DNA is cloned by inserting it into host cells (transfection if host cells are from an animal). The altered host cell is called transgenic. ...
... Recombinant DNA technology can be used to clone (make identical copies) genes. Transformation: Recombinant DNA is cloned by inserting it into host cells (transfection if host cells are from an animal). The altered host cell is called transgenic. ...
Biology GENETICS Practice Test with Answer Key
... When a sperm and ovum combine to form a cell, what is this cell called? A. embryo B. fetus C. zygote D. baby 6. During translation, the tRNA anti-codon GGA codes for what amino acid? A. alanine B. tyrosine C. proline D. glutamic 7. Artificial selection is human intervention allowing only the best or ...
... When a sperm and ovum combine to form a cell, what is this cell called? A. embryo B. fetus C. zygote D. baby 6. During translation, the tRNA anti-codon GGA codes for what amino acid? A. alanine B. tyrosine C. proline D. glutamic 7. Artificial selection is human intervention allowing only the best or ...
Lecture 10
... transfer colonies from one plate to another. The original plate is called the Master Plate. It is pressed on a piece of velvet, transferring about 50% of the cells from each colony. A second plate, replica 1, is then pressed on the velvet, to leave an imprint. ...
... transfer colonies from one plate to another. The original plate is called the Master Plate. It is pressed on a piece of velvet, transferring about 50% of the cells from each colony. A second plate, replica 1, is then pressed on the velvet, to leave an imprint. ...
The origins of mouse strains and substrains - Last
... A gene symbol must i) be unique, ii) be short (normally 3-5 characters), iii) begin with an uppercase letter (not a number), followed by all lowercase letters / numbers, iv) be italicized, v) comprise only Roman letters and Arabic ...
... A gene symbol must i) be unique, ii) be short (normally 3-5 characters), iii) begin with an uppercase letter (not a number), followed by all lowercase letters / numbers, iv) be italicized, v) comprise only Roman letters and Arabic ...
What do we need DNA for?
... •A biotinylated oligo dT is added to guanidiniumtreated cells, and it anneals to the polyA tail of mRNAs •Biotin/streptavidin interactions permit isolation of the mRNA/oligo dT complexes ...
... •A biotinylated oligo dT is added to guanidiniumtreated cells, and it anneals to the polyA tail of mRNAs •Biotin/streptavidin interactions permit isolation of the mRNA/oligo dT complexes ...
Powerpoint for Lecture 12
... Identification of sensitive and specific molecular targets suitable for microbial identification, typing, and for use as markers of anti-microbial resistance Discovery of microbial molecular markers associated with substantial variance in the risk and severity of disease Selection of potential candi ...
... Identification of sensitive and specific molecular targets suitable for microbial identification, typing, and for use as markers of anti-microbial resistance Discovery of microbial molecular markers associated with substantial variance in the risk and severity of disease Selection of potential candi ...
File
... gene is a heritable factor / unit of inheritance gene is composed of DNA gene controls a specific characteristic / codes for a polypeptide / protein allele is a form of a gene alleles of a gene occupy the same gene locus / same position on chromosome alleles differ (from each other) by one / a small ...
... gene is a heritable factor / unit of inheritance gene is composed of DNA gene controls a specific characteristic / codes for a polypeptide / protein allele is a form of a gene alleles of a gene occupy the same gene locus / same position on chromosome alleles differ (from each other) by one / a small ...
Keystone Review Packet Selected Topics Winter 2015 #4 Keystone
... a. independent assortment – genes segregate independently and do not influence each other’s inheritance i. the principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes 12. some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, a ...
... a. independent assortment – genes segregate independently and do not influence each other’s inheritance i. the principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes 12. some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, a ...
Viruses - Studyclix
... type of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) - obligate parasites = can only multiply inside a living cell cause disease. Are they living or non-living? Examples of diseases caused by viruses are influenza (flu), HIV (causes AIDS), chicken pox, measles, mumps, rubella. ...
... type of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) - obligate parasites = can only multiply inside a living cell cause disease. Are they living or non-living? Examples of diseases caused by viruses are influenza (flu), HIV (causes AIDS), chicken pox, measles, mumps, rubella. ...
... whole genome allele homozygosity. Truly balanced chromosome alterations will not be detected by this analysis, although cryptic imbalance associated with some translocations are readily detected due to the dense whole genome probe coverage. The threshold for mosaicism is variable, depending on the s ...
Document
... • Mutation: Mutagens cause mutations that might result in a microbe with a desirable trait • Site-directed mutagenesis: Change a specific DNA code to change a protein • Select and culture microbe with the desired mutation ...
... • Mutation: Mutagens cause mutations that might result in a microbe with a desirable trait • Site-directed mutagenesis: Change a specific DNA code to change a protein • Select and culture microbe with the desired mutation ...
NEW Topic 2 Genes and Health Objectives
... of RNA polymerase, translation, messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomes and the role of start and stop codons. 12. Understand the roles of the DNA template (antisense) strand in transcription, codons on messenger RNA and anticodons on transfer RNA. 13. Understand the nature of the genetic code (tripl ...
... of RNA polymerase, translation, messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomes and the role of start and stop codons. 12. Understand the roles of the DNA template (antisense) strand in transcription, codons on messenger RNA and anticodons on transfer RNA. 13. Understand the nature of the genetic code (tripl ...
Module B Keystone Practice Problems answers File
... a. independent assortment – genes segregate independently and do not influence each other’s inheritance i. the principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes 12. some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, a ...
... a. independent assortment – genes segregate independently and do not influence each other’s inheritance i. the principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes 12. some alleles are neither dominant nor recessive, a ...
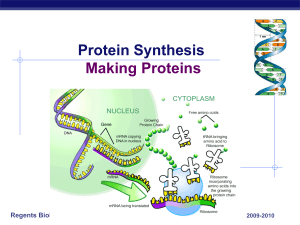
Protein Synthesis
... DNA contains the information that a cell needs to carry out all of its functions. In a way, DNA is like the cell’s encyclopedia. Suppose that you go to the library to do research for a science project. You find the information in an encyclopedia. You go to the desk to sign out the book, but the libr ...
... DNA contains the information that a cell needs to carry out all of its functions. In a way, DNA is like the cell’s encyclopedia. Suppose that you go to the library to do research for a science project. You find the information in an encyclopedia. You go to the desk to sign out the book, but the libr ...
Introduction to
... a. They are acellular, that is, they contain no cytoplasm or cellular organelles. b. No metabolic enzymes but must replicate using the host cell's metabolic machinery. In other words, viruses don't grow and divide. Instead, new viral components are synthesized and assembled within the infected host ...
... a. They are acellular, that is, they contain no cytoplasm or cellular organelles. b. No metabolic enzymes but must replicate using the host cell's metabolic machinery. In other words, viruses don't grow and divide. Instead, new viral components are synthesized and assembled within the infected host ...
slides
... picture below represents a piece of double-stranded DNA from daffodil. This DNA includ This DNA sequence can beThe cut by 4 differentrestriction enzymes phytoene synthase gene (psy), as well as additional sequences of DNA. E=Eco RI ...
... picture below represents a piece of double-stranded DNA from daffodil. This DNA includ This DNA sequence can beThe cut by 4 differentrestriction enzymes phytoene synthase gene (psy), as well as additional sequences of DNA. E=Eco RI ...
15.2 Regulation of Transcription & Translation
... In order to produce these molecules, what process did we establish had to occur? ...
... In order to produce these molecules, what process did we establish had to occur? ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... Mammalian genomes contain much fewer (only 20-25 %) of the CpG dinucleotide than is expected by the G+C content. This is typically explained in the following way: As most CpGs serve as targets of DNA methyltransferases, they are usually methylated. 5-Methylcytosine, whose occurrence is almost comple ...
... Mammalian genomes contain much fewer (only 20-25 %) of the CpG dinucleotide than is expected by the G+C content. This is typically explained in the following way: As most CpGs serve as targets of DNA methyltransferases, they are usually methylated. 5-Methylcytosine, whose occurrence is almost comple ...
Description
... The chimeric plasmid are introduced into bacterial host cell the process of introducing foreign DNA into bacteria is termed “transformation”, Alternatively, introducing foreign (recombinant DNA) into viral genome is termed “Transfection” ,i.e. the virus is infected and then infects the host cells, i ...
... The chimeric plasmid are introduced into bacterial host cell the process of introducing foreign DNA into bacteria is termed “transformation”, Alternatively, introducing foreign (recombinant DNA) into viral genome is termed “Transfection” ,i.e. the virus is infected and then infects the host cells, i ...
Large-Scale Purification Of Plasmids pRIT4501 and - RIT
... Density Gradient Centrifugation Now that you have identified your two recombinant plasmids, you need to produce large-scale preparations of each so that you can study them further. To do this, you will prepare lysates of 500 ml cultures and purify the DNA by density gradient centrifugation. Although ...
... Density Gradient Centrifugation Now that you have identified your two recombinant plasmids, you need to produce large-scale preparations of each so that you can study them further. To do this, you will prepare lysates of 500 ml cultures and purify the DNA by density gradient centrifugation. Although ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.