Chapter 13 Genetic Engineering Changing the living world
... only the largest seeds to be planted in the spring. This practice continued for thousands of years. The original plant is believed to be extinct, but the modern corn plant flourishes. ...
... only the largest seeds to be planted in the spring. This practice continued for thousands of years. The original plant is believed to be extinct, but the modern corn plant flourishes. ...
problem set
... derived by reverse transcription of mRNA. A genomic DNA library is a collection of cloned DNA fragments representing all of the DNA of an organism. This includes both protein-coding and non-protein-coding segments of DNA. To clone a gene expressed only in neurons, you could start with either of the ...
... derived by reverse transcription of mRNA. A genomic DNA library is a collection of cloned DNA fragments representing all of the DNA of an organism. This includes both protein-coding and non-protein-coding segments of DNA. To clone a gene expressed only in neurons, you could start with either of the ...
1 Evolution of Genome Size 1. The C
... why the Drosophila genome is small and has no pseudogenes – because pseudogenes are lost very rapidly by deletion mutations rendering them undetectable. Does this result extend to other taxa with larger genome sizes? The approach: Grasshoppers (genus Podisma) have even larger genomes (≈20 Gb) – over ...
... why the Drosophila genome is small and has no pseudogenes – because pseudogenes are lost very rapidly by deletion mutations rendering them undetectable. Does this result extend to other taxa with larger genome sizes? The approach: Grasshoppers (genus Podisma) have even larger genomes (≈20 Gb) – over ...
Ten Unifying Themes in Biology 1. Emergent properties
... inheritance of biological information in the form of DNA molecules. The genetic information is encoded in the nucleotide sequence of the DNA. ...
... inheritance of biological information in the form of DNA molecules. The genetic information is encoded in the nucleotide sequence of the DNA. ...
Genetics
... Incorporate desired gene into plasmid DNA Infect into bacteria DNA. Bacteria infect the plant with the plasmid and hopefully insert plasmid and desired DNA into ...
... Incorporate desired gene into plasmid DNA Infect into bacteria DNA. Bacteria infect the plant with the plasmid and hopefully insert plasmid and desired DNA into ...
Strings and Sequences in Biology
... • orientation (read from 5’ to 3’ end) • length measured in bp (base pairs) • double stranded, the two strands are antiparallel • A - T and C - G complementary (Watson-Crick pairs) ...
... • orientation (read from 5’ to 3’ end) • length measured in bp (base pairs) • double stranded, the two strands are antiparallel • A - T and C - G complementary (Watson-Crick pairs) ...
Genetic Code Review.cwk
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNAis transcribed from DNAin the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNAto bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it releases ...
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNAis transcribed from DNAin the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNAto bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it releases ...
Gene Testing: What Does It Mean for Producers?
... favorable gene variation. If it occurs with a frequency of 90% in a population, for example, the gene variation is almost fixed in the population, and it probably wouldn’t be worthwhile to test all of the animals to find those that do not carry it. Alternatively, if the gene is at very low frequency ...
... favorable gene variation. If it occurs with a frequency of 90% in a population, for example, the gene variation is almost fixed in the population, and it probably wouldn’t be worthwhile to test all of the animals to find those that do not carry it. Alternatively, if the gene is at very low frequency ...
stucture of DNA
... characteristics are inherited and he formulated a set of rules to explain that inheritance. It was proposed that genes that are resided on chromosomes made from proteins and they are responsible for genetic materials. Later on, techniques for gene mapping were developed and had produced a compre ...
... characteristics are inherited and he formulated a set of rules to explain that inheritance. It was proposed that genes that are resided on chromosomes made from proteins and they are responsible for genetic materials. Later on, techniques for gene mapping were developed and had produced a compre ...
Chapter 16 - variation Notes
... same species in a given area. • Because all members of a population can interbreed, they share a common group of genes, called a gene pool. Gene Pool – the combined genetic information of all the members of a particular population. ...
... same species in a given area. • Because all members of a population can interbreed, they share a common group of genes, called a gene pool. Gene Pool – the combined genetic information of all the members of a particular population. ...
9 Genomics and Beyond
... (1) Genome is cut into small, overlapping fragments with a restriction enzyme, and each piece is cloned, forming a DNA library. (2) The DNA fragments must overlap other fragments, so the restriction enzyme is not allowed to cut at every possible restriction site. (3) Computers assemble the fragments ...
... (1) Genome is cut into small, overlapping fragments with a restriction enzyme, and each piece is cloned, forming a DNA library. (2) The DNA fragments must overlap other fragments, so the restriction enzyme is not allowed to cut at every possible restriction site. (3) Computers assemble the fragments ...
Comparative Genomics
... are transcribed simultaneously. These genes were shown to share a promoter, much like prokaryotes control gene expression. ...
... are transcribed simultaneously. These genes were shown to share a promoter, much like prokaryotes control gene expression. ...
pptx - Central Web Server 2
... Paralogs: “deepest” bifurcation in molecular tree reflects gene duplication. The study of paralogs and their distribution in genomes provides clues on the way genomes evolved. Gen and genome duplication have emerged as the most important pathway to molecular innovation, including the evolution of de ...
... Paralogs: “deepest” bifurcation in molecular tree reflects gene duplication. The study of paralogs and their distribution in genomes provides clues on the way genomes evolved. Gen and genome duplication have emerged as the most important pathway to molecular innovation, including the evolution of de ...
Does your DNA define you Qu
... genome on and off at specific times and places so that different genes are expressed at different times; this is achieved through the addition of chemical tags to DNA itself or to the proteins DNA is associated with. Epigenetics is the study of these reactions and the factors that influence them. Ep ...
... genome on and off at specific times and places so that different genes are expressed at different times; this is achieved through the addition of chemical tags to DNA itself or to the proteins DNA is associated with. Epigenetics is the study of these reactions and the factors that influence them. Ep ...
Lecture 1: Overview of bioinformatics
... A phylogenetic tree depicts the evolutionary history of a group of species. By observing similarities and differences between species, we may be able to reconstruct their phylogeny. Classically, the degree of similarity between two species has been assessed from morphological characters. By comparin ...
... A phylogenetic tree depicts the evolutionary history of a group of species. By observing similarities and differences between species, we may be able to reconstruct their phylogeny. Classically, the degree of similarity between two species has been assessed from morphological characters. By comparin ...
Welkin`s Presentation on Assigning and Correctly
... number. – Most of these will be supported by HHpred and BLAST on NCBI. ...
... number. – Most of these will be supported by HHpred and BLAST on NCBI. ...
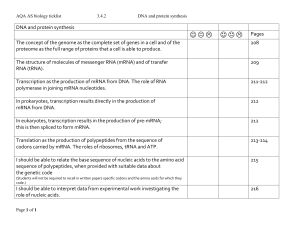
doc 3.4.2 protein synthesis checklist
... Transcription as the production of mRNA from DNA. The role of RNA polymerase in joining mRNA nucleotides. ...
... Transcription as the production of mRNA from DNA. The role of RNA polymerase in joining mRNA nucleotides. ...
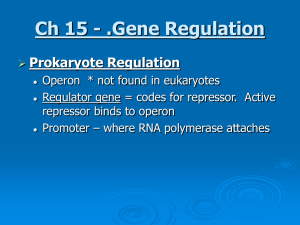
Ch 15 - .Gene Regulation
... Point Mutations- Change a single base→ change codon Frame shift mutations- deletion or addition result in a completely new amino acid sequence. Mutations in proto-oncogenes or tumor suppressor →cancer ...
... Point Mutations- Change a single base→ change codon Frame shift mutations- deletion or addition result in a completely new amino acid sequence. Mutations in proto-oncogenes or tumor suppressor →cancer ...
genome
... particular organism; its size is generally given as its total number of base pairs. • Genomics: the study of genes and their function. Recent advances in genomics are bringing about a revolution in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of disease, including the complex interplay of genetic a ...
... particular organism; its size is generally given as its total number of base pairs. • Genomics: the study of genes and their function. Recent advances in genomics are bringing about a revolution in our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of disease, including the complex interplay of genetic a ...