today
... usually not all sites in a sequence are under selection all the time. PAML (and other programs) allow to either determine omega for each site over the whole tree, ...
... usually not all sites in a sequence are under selection all the time. PAML (and other programs) allow to either determine omega for each site over the whole tree, ...
Chapter 11 Notes
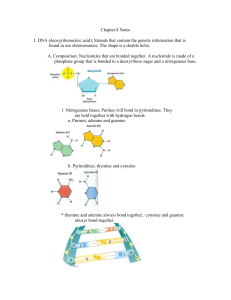
... occur. A complementary strand of m-RNA codons is formed using the DNA strand as a template. B. Translation; 1. m-RNA leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome. 2. The start codon (AUG) attracts a complementary anticodon of t-RNA that carries the amino acid methionine. This starts the protein syn ...
... occur. A complementary strand of m-RNA codons is formed using the DNA strand as a template. B. Translation; 1. m-RNA leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome. 2. The start codon (AUG) attracts a complementary anticodon of t-RNA that carries the amino acid methionine. This starts the protein syn ...
What Causes Mutations?
... during our lifetime, either through mistakes during DNA copying or cell division or, more often, because of damage from the environment. Bits of our DNA may be deleted, inserted, broken, or substituted. Most mutations affect only the parts of DNA that do not contain instructions for making a gene, s ...
... during our lifetime, either through mistakes during DNA copying or cell division or, more often, because of damage from the environment. Bits of our DNA may be deleted, inserted, broken, or substituted. Most mutations affect only the parts of DNA that do not contain instructions for making a gene, s ...
Study Guide
... 2. Chromosomes are rod-like bundles of coiled DNA. They contain a string of genes packaged in a single unit. Genes are located on chromosomes. 3. Genes are the structures that carry the information for the inheritance of traits. They contain the information that specify for the making of a particula ...
... 2. Chromosomes are rod-like bundles of coiled DNA. They contain a string of genes packaged in a single unit. Genes are located on chromosomes. 3. Genes are the structures that carry the information for the inheritance of traits. They contain the information that specify for the making of a particula ...
ucla1 - WEHI Bioinformatics
... The information content of various species in terms of the number of nucleotides in the genome. The complete genome sequences were determined in the years as designated. The increase of the GenBank nucleotide sequence database is also shown together with the release dates. (Bit s) ...
... The information content of various species in terms of the number of nucleotides in the genome. The complete genome sequences were determined in the years as designated. The increase of the GenBank nucleotide sequence database is also shown together with the release dates. (Bit s) ...
2.5 Changes to a cell`s DNA
... be altered in a way similar to how you might copy a word down wrong from the board. Also chemicals that we eat or come in contact with can alter our DNA. This is called a mutation. ...
... be altered in a way similar to how you might copy a word down wrong from the board. Also chemicals that we eat or come in contact with can alter our DNA. This is called a mutation. ...
Mitochondrial Genome Evolution
... Leblanc C, Richard O, Kloareg B et al. (1997) “Origin and evolution of mitochondria: what have we learnt from red algae?” Current Genetics 31: 193-207 Lang BF, Gray MW, Burger G (1999) “Mitochondrial genome evolution and the origin of eukaryotes” Annual Review of Genetics 33: 351-397 Turmel M, Otis ...
... Leblanc C, Richard O, Kloareg B et al. (1997) “Origin and evolution of mitochondria: what have we learnt from red algae?” Current Genetics 31: 193-207 Lang BF, Gray MW, Burger G (1999) “Mitochondrial genome evolution and the origin of eukaryotes” Annual Review of Genetics 33: 351-397 Turmel M, Otis ...
Gene Mutation, DNA Repair, and Transposition
... Base analogs can be incorporated into DNA molecules o Other chemicals can have other effects o Oxidative reactions can damage the DNA, causing chemical changes to the bases and leading to mutations o Intercalating agents are ring-containing molecules that are about the size of a base pair These pr ...
... Base analogs can be incorporated into DNA molecules o Other chemicals can have other effects o Oxidative reactions can damage the DNA, causing chemical changes to the bases and leading to mutations o Intercalating agents are ring-containing molecules that are about the size of a base pair These pr ...
(DNA and RNA).
... acteristics of living organisms. GENOME: A complete, haploid set of all the single chromosomes that determine the physical makeup of an organism. GUANINE: A base compound in DNA and RNA molecules. HAPLOID: A cell containing a set of single chromosomes, or an organism composed of haploid cells. Gamet ...
... acteristics of living organisms. GENOME: A complete, haploid set of all the single chromosomes that determine the physical makeup of an organism. GUANINE: A base compound in DNA and RNA molecules. HAPLOID: A cell containing a set of single chromosomes, or an organism composed of haploid cells. Gamet ...
wave genetics verbatim
... The wave emitting genes of this “fine field” level are called the “super-gene-continuum”, but there is no sharp distinction between genes and super-genes. There is a fundamental similarity, or unity, between fractal (replicating itself on increasing or decreasing scales) sequence structures of DNA ...
... The wave emitting genes of this “fine field” level are called the “super-gene-continuum”, but there is no sharp distinction between genes and super-genes. There is a fundamental similarity, or unity, between fractal (replicating itself on increasing or decreasing scales) sequence structures of DNA ...
Evolution Review
... One is listed below. Name the other four. a) Natural Selection b) Mutation c) Gene flow d) Genetic drift e) Sexual selection (non-random mating) ...
... One is listed below. Name the other four. a) Natural Selection b) Mutation c) Gene flow d) Genetic drift e) Sexual selection (non-random mating) ...
FAQ of Module 7
... genes. Genes hold the information to build and maintain an organism's cells and pass genetic traits to offspring. Genome is the sum total of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding se ...
... genes. Genes hold the information to build and maintain an organism's cells and pass genetic traits to offspring. Genome is the sum total of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding se ...
protein synthesis
... early in the history of life • The genetic code is nearly universal, shared by organisms from the simplest bacteria to the most complex plants and animals. • In laboratory experiments, genes can be transcribed and translated after they are transplanted from one species to another - biotechnology • T ...
... early in the history of life • The genetic code is nearly universal, shared by organisms from the simplest bacteria to the most complex plants and animals. • In laboratory experiments, genes can be transcribed and translated after they are transplanted from one species to another - biotechnology • T ...
Genetic Engineering
... Leaves single stranded “sticky” ends that can become incorporated into other DNA sequences with COMPLIMENTARY BASES ...
... Leaves single stranded “sticky” ends that can become incorporated into other DNA sequences with COMPLIMENTARY BASES ...
file
... low as possible, limited only by the cost of error-avoidance and error-correction mechanisms. But up to one per cent of natural bacterial isolates are 'mutator' clones that have high mutation rates. We consider here whether high mutation rates might play an important role in adaptive evolution. Mode ...
... low as possible, limited only by the cost of error-avoidance and error-correction mechanisms. But up to one per cent of natural bacterial isolates are 'mutator' clones that have high mutation rates. We consider here whether high mutation rates might play an important role in adaptive evolution. Mode ...
Ch. 15
... The extracted DNA can be cut into fragments of manageable size using restriction enzymes. These restriction fragments can then be separated according to size, using gel electrophoresis or another similar technique. ...
... The extracted DNA can be cut into fragments of manageable size using restriction enzymes. These restriction fragments can then be separated according to size, using gel electrophoresis or another similar technique. ...
Does your DNA define you Ans
... human body is controlled by sets of chemical reactions that switch parts of the genome on and off at specific times and places so that different genes are expressed at different times; this is achieved through the addition of chemical tags or marks to DNA itself or to the proteins DNA is associated ...
... human body is controlled by sets of chemical reactions that switch parts of the genome on and off at specific times and places so that different genes are expressed at different times; this is achieved through the addition of chemical tags or marks to DNA itself or to the proteins DNA is associated ...
No Slide Title
... Plants, animals, fungi, protistas. Often multicellular. DNA contained within a membrane-bound nucleus. linear chromosomes (usually more than 1) careful division of chromosomes in cell division: mitosis and meiosis • transcription separated from translation • sexual reproduction: 2 partners contribut ...
... Plants, animals, fungi, protistas. Often multicellular. DNA contained within a membrane-bound nucleus. linear chromosomes (usually more than 1) careful division of chromosomes in cell division: mitosis and meiosis • transcription separated from translation • sexual reproduction: 2 partners contribut ...