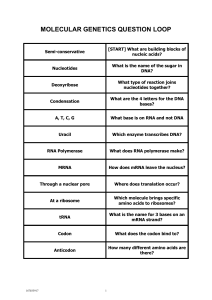
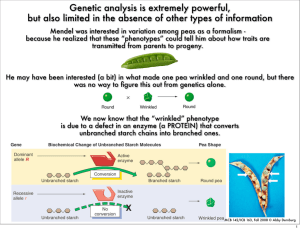
Bio 5924: Molecular Basis of Heredity
... Engineering), Barak Cohen (Genetics), Tim Ley (Internal Medicine), Jeff Gordon (Developmental Biology), and Robi Mitra (Genetics) Teaching Assistants: Taylor Cordonnier, Matthew Dothager, Stephen McDaniel, Andrew Nylander, Priya Srikanth ...
... Engineering), Barak Cohen (Genetics), Tim Ley (Internal Medicine), Jeff Gordon (Developmental Biology), and Robi Mitra (Genetics) Teaching Assistants: Taylor Cordonnier, Matthew Dothager, Stephen McDaniel, Andrew Nylander, Priya Srikanth ...
Basic DNA
... • The base adenine always bonds with thymine (A-T), and cytosine always bonds with guanine (C-G). ...
... • The base adenine always bonds with thymine (A-T), and cytosine always bonds with guanine (C-G). ...
Principles of genetic engineering
... What is genetic engineering • Genetic engineering, also known as recombinant DNA technology, means altering the genes in a living organism to produce a Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) with a new genotype. • Various kinds of genetic modification are possible: inserting a foreign gene from one sp ...
... What is genetic engineering • Genetic engineering, also known as recombinant DNA technology, means altering the genes in a living organism to produce a Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) with a new genotype. • Various kinds of genetic modification are possible: inserting a foreign gene from one sp ...
Chem*4570 Applied Biochemistry Lecture 11 Conjugation and
... species, but the transferred genes do not usually end up in their normal genomic context. Plasmids are small autonomously replicating DNA circles that lie outside the main chromosome, placing genes in an episomal context. Plasmids can be set up to express the genes they carry but represent an extra ...
... species, but the transferred genes do not usually end up in their normal genomic context. Plasmids are small autonomously replicating DNA circles that lie outside the main chromosome, placing genes in an episomal context. Plasmids can be set up to express the genes they carry but represent an extra ...
Handout on the Central Dogma
... A Codon is a triplet of base pairs. Each codon corresponds to one of twenty Amino acids -- it’s the amino acids that are the building-blocks of proteins, which do the work of the cell. A gene is a sequence of codons. Each gene corresponds to a particular protein that is used by the cell to do its wo ...
... A Codon is a triplet of base pairs. Each codon corresponds to one of twenty Amino acids -- it’s the amino acids that are the building-blocks of proteins, which do the work of the cell. A gene is a sequence of codons. Each gene corresponds to a particular protein that is used by the cell to do its wo ...
student notes protein synthesis mutation
... REALLY ITS _______________________________I N THE DNA DETERMINE THE CHARACTERISTIC. BUT SOMETIMES PROBLEMS ARISE…. ...
... REALLY ITS _______________________________I N THE DNA DETERMINE THE CHARACTERISTIC. BUT SOMETIMES PROBLEMS ARISE…. ...
Freeman 1e: How we got there
... • Biotechnology is the use of living organisms to carry out chemical processes for industrial or commercial application. • Much of genetic engineering is based on molecular cloning, in which a doublestranded DNA fragment from any source is recombined with a vector and introduced into a suitable hos ...
... • Biotechnology is the use of living organisms to carry out chemical processes for industrial or commercial application. • Much of genetic engineering is based on molecular cloning, in which a doublestranded DNA fragment from any source is recombined with a vector and introduced into a suitable hos ...
A Novel Framework for De Novo Protein Design and its Applications
... the sequences from stage one and to perform docking simulations [3] between the new sequences and the target protein. Finally, rotamerically-based ensembles of the structures for each new peptide, the target protein, and the peptide-protein complex are generated and used to calculate an approximate ...
... the sequences from stage one and to perform docking simulations [3] between the new sequences and the target protein. Finally, rotamerically-based ensembles of the structures for each new peptide, the target protein, and the peptide-protein complex are generated and used to calculate an approximate ...
Glossary Algae: Unicellular or simple multicellular photosynthetic
... industrial, medical and research purposes. Genome: The genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA. Genomics: The study of genomes as opposed to individual genes. Haploid: (Gr. haploos, single+ploion, vessel). Hav ...
... industrial, medical and research purposes. Genome: The genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA. Genomics: The study of genomes as opposed to individual genes. Haploid: (Gr. haploos, single+ploion, vessel). Hav ...
doc14873 - Mrothery.co.uk
... What word is used to describe the fact that several codon codes are used for the same amino acid? ...
... What word is used to describe the fact that several codon codes are used for the same amino acid? ...
Central Dogma - We Heart Science
... incorrectly matched (e.g., A bonded to C rather than A bonded to T) and can, but usually do not, improve the product coded by the gene. • Inserting or deleting base pairs in an existing gene can cause a mutation by changing the codon reading frame used by a ribosome. ...
... incorrectly matched (e.g., A bonded to C rather than A bonded to T) and can, but usually do not, improve the product coded by the gene. • Inserting or deleting base pairs in an existing gene can cause a mutation by changing the codon reading frame used by a ribosome. ...
Pre – AP Biology
... this new inserted DNA and thus make that protein. This has been done for numerous human medicines such as Insulin or Human Growth Hormone. – Eukaryotes DO have introns. This allows them to take out the introns and rearrange the important exon pieces to make an almost unlimited number of different pr ...
... this new inserted DNA and thus make that protein. This has been done for numerous human medicines such as Insulin or Human Growth Hormone. – Eukaryotes DO have introns. This allows them to take out the introns and rearrange the important exon pieces to make an almost unlimited number of different pr ...
Lecture Slides - Computer Science
... Think of AUGCCGGGAGUAUAG as AUGCCG-GGA-GUA-UAG. Each triplet (codon) maps to an amino acid. ...
... Think of AUGCCGGGAGUAUAG as AUGCCG-GGA-GUA-UAG. Each triplet (codon) maps to an amino acid. ...
Gene Mutations
... Both of these are sentences. One works perfectly, the other does not. The point mutation leaves a sentence with words, but it does not make sense. ...
... Both of these are sentences. One works perfectly, the other does not. The point mutation leaves a sentence with words, but it does not make sense. ...
comparative genomics
... understanding genome structure. Second, within a given species most individuals are genetically distinct in a number of ways. What does it actually mean, for example, to "sequence a human genome"? The genomes of two individuals who are genetically distinct ...
... understanding genome structure. Second, within a given species most individuals are genetically distinct in a number of ways. What does it actually mean, for example, to "sequence a human genome"? The genomes of two individuals who are genetically distinct ...
GENES, GENOMES, AND CODES
... process of translation from a text written in nucleotide sequences to one written in amino acid sequences. Incidentally, he was also careful to distinguish the sequence hypothesis from what he called the central dogma: the hypothesis that «Once information has got into a protein it can’t get out aga ...
... process of translation from a text written in nucleotide sequences to one written in amino acid sequences. Incidentally, he was also careful to distinguish the sequence hypothesis from what he called the central dogma: the hypothesis that «Once information has got into a protein it can’t get out aga ...
Key
... 18. Mismatch repair depends on the recognition of the old DNA strand by virtue of its: a. phosphorylation b. restriction c. methylation d. acetylation e. glycosylation 19. Fragile X syndrome is caused by a. trinucleotide repeats b. free radicals c. microdeletions d. 5-bromouracil e. transversions 20 ...
... 18. Mismatch repair depends on the recognition of the old DNA strand by virtue of its: a. phosphorylation b. restriction c. methylation d. acetylation e. glycosylation 19. Fragile X syndrome is caused by a. trinucleotide repeats b. free radicals c. microdeletions d. 5-bromouracil e. transversions 20 ...
Gene Editing - Royal Society of New Zealand
... editing, or natural mutation. Gene editing technology is getting cheaper and easier, so is being used more frequently. While it can make more precise changes to genetic material than earlier techniques, there can still be unintended effects. As a result, while the technology offers exciting new oppo ...
... editing, or natural mutation. Gene editing technology is getting cheaper and easier, so is being used more frequently. While it can make more precise changes to genetic material than earlier techniques, there can still be unintended effects. As a result, while the technology offers exciting new oppo ...