Reviewing Key Concepts Chapter 12 DNA and RNA Section Review 12-3
... 4. During the process of carried by mRNA is used to produce proteins. ...
... 4. During the process of carried by mRNA is used to produce proteins. ...
Genetic Engineering
... it to the gene structure of a bacterial cell, and replacing the recombinant DNA into the bacterial cell. The bacteria then have the capability to produce the chemical produced by the original animal or plant cell. ...
... it to the gene structure of a bacterial cell, and replacing the recombinant DNA into the bacterial cell. The bacteria then have the capability to produce the chemical produced by the original animal or plant cell. ...
DNA - Valhalla High School
... transfer of genetic information from one generation to the next. You inherited half of your DNA (your genes) from Mom, and the other half from Dad. DNA is the molecule that allows this to ...
... transfer of genetic information from one generation to the next. You inherited half of your DNA (your genes) from Mom, and the other half from Dad. DNA is the molecule that allows this to ...
Previously in Bio308
... How do you get a protein where it needs to be? Biaxial Model of bipolar affective disorders: Combination of neuroelectrical and neurochemical phenotypes Determines the range and tonicity of an individuals affect ...
... How do you get a protein where it needs to be? Biaxial Model of bipolar affective disorders: Combination of neuroelectrical and neurochemical phenotypes Determines the range and tonicity of an individuals affect ...
Recombinant DNA
... two DNA sequences from two different organisms are cut with the same RE, their sticky ends can be matched and they can be permanently bonded Resulting molecules called recombinant DNA (recombinant DNA technology) ...
... two DNA sequences from two different organisms are cut with the same RE, their sticky ends can be matched and they can be permanently bonded Resulting molecules called recombinant DNA (recombinant DNA technology) ...
Biochemistry Review Worksheet - CHS Science Department Mrs
... time forming a complex folded polypeptide (protein). The ribosome will continue translating the protein until it reads one of the three stop codons. Modifying the mRNA Transcript Genes are made of parts represented in the mRNA (exons) and parts that are transcribed but not present in the mRNA (intro ...
... time forming a complex folded polypeptide (protein). The ribosome will continue translating the protein until it reads one of the three stop codons. Modifying the mRNA Transcript Genes are made of parts represented in the mRNA (exons) and parts that are transcribed but not present in the mRNA (intro ...
The Human Genome Project - Institute of Life Sciences
... 545 genes, 134 pseudogenes and 200 to 300 additional ones. Size of a gene - 1,000 to 583,000 bases of DNA. 39% of the chromosome is copied into RNA (exons and introns). 247 genes were revealed to be identical to previously identified genes. There are families of genes that are distributed over large ...
... 545 genes, 134 pseudogenes and 200 to 300 additional ones. Size of a gene - 1,000 to 583,000 bases of DNA. 39% of the chromosome is copied into RNA (exons and introns). 247 genes were revealed to be identical to previously identified genes. There are families of genes that are distributed over large ...
Glossary of genetics terms
... due to gains or losses of around one thousand to several million base-pairs. These have been discovered by comparing genomes between people using comparative genomic hybridization arrays. Copy number variations which include coding regions, and thus alter the number of copies of a gene present, are ...
... due to gains or losses of around one thousand to several million base-pairs. These have been discovered by comparing genomes between people using comparative genomic hybridization arrays. Copy number variations which include coding regions, and thus alter the number of copies of a gene present, are ...
DNA Review
... only 61 of the 64 codons code for an amino acid; the other 3 codons are stop codons and signal the end of the protein steps in translation: o the large and small subunits of a ribosome attach to a strand of mRNA o the first codon in a mRNA strand is AUG; this is known as a start codon o the firs ...
... only 61 of the 64 codons code for an amino acid; the other 3 codons are stop codons and signal the end of the protein steps in translation: o the large and small subunits of a ribosome attach to a strand of mRNA o the first codon in a mRNA strand is AUG; this is known as a start codon o the firs ...
here
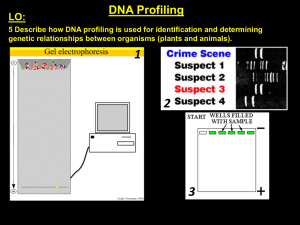
... DNA profiling is a technique that allows an individual’s genes to be visualised, this allows someone's genetic makeup to be compared to known genes to see if they too have it. This technique can be used to identify genetic disorders in individuals or match DNA samples to individuals. We usually sam ...
... DNA profiling is a technique that allows an individual’s genes to be visualised, this allows someone's genetic makeup to be compared to known genes to see if they too have it. This technique can be used to identify genetic disorders in individuals or match DNA samples to individuals. We usually sam ...
Introduction to Medical Genetics
... SNPs appear at least once per 0.3-1-kb average intervals. Considering the size of entire human genome (3.2X109 bp), the total number of SNPs is around to 5-10 million ...
... SNPs appear at least once per 0.3-1-kb average intervals. Considering the size of entire human genome (3.2X109 bp), the total number of SNPs is around to 5-10 million ...
Athena, Jen and Natalie`s Powerpt
... Upstream from a gene, template strand of DNA, This enzyme is called RNA polymerase It binds to a site packed with adenine and thymine It’s not transcribed but unwinding is very easy Between these bases are only 2 hydrogen bonds; This promoter region’s bonds are not as strong RNA polymerase unwinds t ...
... Upstream from a gene, template strand of DNA, This enzyme is called RNA polymerase It binds to a site packed with adenine and thymine It’s not transcribed but unwinding is very easy Between these bases are only 2 hydrogen bonds; This promoter region’s bonds are not as strong RNA polymerase unwinds t ...
BIO201_1
... evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junction diversity. Mutation can result in many different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations ca ...
... evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junction diversity. Mutation can result in many different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations ca ...
Biology Standards (For the Year) *DO NOT LOSE THIS!* CST
... increases the chances that at least some organisms can survive changes in an environment. 8c) Genetic drift through the Bottleneck Effect or the Founder Effect decreases the size of a gene pool and its diversity. This can decrease the chances of survival of the species. 8d) Speciation can occur due ...
... increases the chances that at least some organisms can survive changes in an environment. 8c) Genetic drift through the Bottleneck Effect or the Founder Effect decreases the size of a gene pool and its diversity. This can decrease the chances of survival of the species. 8d) Speciation can occur due ...
2.2 Sequencing learning grid File
... What is the maximum length of DNA that can be sequenced in one reaction? How do scientists reduce errors when carrying out sequencing? What is referred to as the shotgun approach? Why are the sections of genome transferred into E. coli? Why are different restriction enzymes used when sequencing BAC ...
... What is the maximum length of DNA that can be sequenced in one reaction? How do scientists reduce errors when carrying out sequencing? What is referred to as the shotgun approach? Why are the sections of genome transferred into E. coli? Why are different restriction enzymes used when sequencing BAC ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Instructions for making proteins with the correct sequence of amino acids are encoded in DNA. DNA is found in chromosomes. In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes always remain in the nucleus, but proteins are made at ribosomes in the cytoplasm. How do the ...
... sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Instructions for making proteins with the correct sequence of amino acids are encoded in DNA. DNA is found in chromosomes. In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes always remain in the nucleus, but proteins are made at ribosomes in the cytoplasm. How do the ...