Pathways of ethanol production from sucrose by a
... The rationale was that the pyruvate arising from glycolysis would then be diverted via pyruvate-formate lyase (PFL) to produce acetate, ethanol and formate in a 1: 1:2 ratio (per mol of hexose). The ethanol yield would still be uncompetitive with yeasts, but further physiological or genetic manipula ...
... The rationale was that the pyruvate arising from glycolysis would then be diverted via pyruvate-formate lyase (PFL) to produce acetate, ethanol and formate in a 1: 1:2 ratio (per mol of hexose). The ethanol yield would still be uncompetitive with yeasts, but further physiological or genetic manipula ...
Lactic Acidosis
... acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA then combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate, and so enters the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle of biochemical reactions then produces water, CO2 and most importantly, ATP, the primary cellular energy source. Under anaerobic conditions, or when the metabolic demands of the cel ...
... acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA then combines with oxaloacetate to form citrate, and so enters the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle of biochemical reactions then produces water, CO2 and most importantly, ATP, the primary cellular energy source. Under anaerobic conditions, or when the metabolic demands of the cel ...
Fitness: Physical Activity, Nutrients, and Body Adaptations
... – Muscles use glucose and stored glycogen • Muscle fatigue when glycogen is depleted ...
... – Muscles use glucose and stored glycogen • Muscle fatigue when glycogen is depleted ...
Dynamics of the cellular metabolome during human cytomegalovirus infection.
... the aldolase product, dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), increase roughly in parallel with those of FBP (if the increase in FBP were due to blockade of aldolase, DHAP levels should drop, not increase). It is confirmed by direct measurement of PFK activity from cell lysates, as described further below ...
... the aldolase product, dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), increase roughly in parallel with those of FBP (if the increase in FBP were due to blockade of aldolase, DHAP levels should drop, not increase). It is confirmed by direct measurement of PFK activity from cell lysates, as described further below ...
Methods of industrial production 1
... that are formed from the common precursor tripeptide isopenicillin N. • The β-lactam structure is formed by ring-closure reactions between Cys and Val,where (S)-Val is isomerized to ( R )-Val. • The β-lactam precursors of all penicillins and cephalosporins are produced by fermentation in fermentors ...
... that are formed from the common precursor tripeptide isopenicillin N. • The β-lactam structure is formed by ring-closure reactions between Cys and Val,where (S)-Val is isomerized to ( R )-Val. • The β-lactam precursors of all penicillins and cephalosporins are produced by fermentation in fermentors ...
Print - Stroke
... to 6 microvessels were obtained from each brain compartment of each dog under identical magnification and illumination conditions. Hence, 50 to 60 photographs of pial vessels could be compared with an identical number of microvessels of grey or white matter. After random pairing of photographs repre ...
... to 6 microvessels were obtained from each brain compartment of each dog under identical magnification and illumination conditions. Hence, 50 to 60 photographs of pial vessels could be compared with an identical number of microvessels of grey or white matter. After random pairing of photographs repre ...
Energy Metabolism in the Erythrocytes of Premature
... the Department of Pediatrics and Dirision of Human ...
... the Department of Pediatrics and Dirision of Human ...
1.4 enzymes 2014
... that speeds up chemical reactions. It is made of protein. Enzymes lower the energy needed for chemical reactions to take place. The enzyme is unchanged at the end of the reaction so can be used again. ...
... that speeds up chemical reactions. It is made of protein. Enzymes lower the energy needed for chemical reactions to take place. The enzyme is unchanged at the end of the reaction so can be used again. ...
LFT- GIT
... 1- Check certain enzymes & proteins levels in blood that if are higher or lower than normal can indicate liver problems (diagnosis) 2- Screen for liver infections, such as hepatitis 3- Monitor the progression of a liver disease, such as viral or alcoholic hepatitis & determine how well a treatment i ...
... 1- Check certain enzymes & proteins levels in blood that if are higher or lower than normal can indicate liver problems (diagnosis) 2- Screen for liver infections, such as hepatitis 3- Monitor the progression of a liver disease, such as viral or alcoholic hepatitis & determine how well a treatment i ...
Oxidation - medscistudents
... acyl CoA. This contains a double bond at and position. 2. Enoyl CoA hydratase adds a molecule of water at the double bond position of ,- unsaturated fatty acyl CoA forming - hydroxy acyl CoA. 3. In the presence NAD+, -hydroxy acyl CoA dehydroegnase enzyme oxidises -hydroxy acyl CoA to form ...
... acyl CoA. This contains a double bond at and position. 2. Enoyl CoA hydratase adds a molecule of water at the double bond position of ,- unsaturated fatty acyl CoA forming - hydroxy acyl CoA. 3. In the presence NAD+, -hydroxy acyl CoA dehydroegnase enzyme oxidises -hydroxy acyl CoA to form ...
Reading materials 511/rumen microbes/rumen
... include the existence of a transmembrane pH gradient and an alkaline lumen. Free Ca2+ pools and calcium phosphate precipitates have also been detected in fungal hydrogenosomes suggesting that, like mitochondria, they accumulate this intracellular messenger (Biagini et al., 1997). Both organelles hav ...
... include the existence of a transmembrane pH gradient and an alkaline lumen. Free Ca2+ pools and calcium phosphate precipitates have also been detected in fungal hydrogenosomes suggesting that, like mitochondria, they accumulate this intracellular messenger (Biagini et al., 1997). Both organelles hav ...
Ariarad and Lindsay - Saddleback College
... muscles are fueled by aerobic and anaerobic metabolic processes. When a horse performs or exercises, they use their muscles to accomplish tasks. As lactic acid is produced in the muscles it leaks out into the blood and is then carried around the body. If this condition continues, the functioning of ...
... muscles are fueled by aerobic and anaerobic metabolic processes. When a horse performs or exercises, they use their muscles to accomplish tasks. As lactic acid is produced in the muscles it leaks out into the blood and is then carried around the body. If this condition continues, the functioning of ...
Test Example
... Name two functions of (a) proteins, (b) nucleic acids, (c) polysaccharides, (d) lipids. Ans: Many answers are possible including: (a) proteins function as enzymes, structural elements, signal carriers, transporters; (b) nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information and act as both structural ...
... Name two functions of (a) proteins, (b) nucleic acids, (c) polysaccharides, (d) lipids. Ans: Many answers are possible including: (a) proteins function as enzymes, structural elements, signal carriers, transporters; (b) nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information and act as both structural ...
of the fatty acid is oxidized. Fatty acid oxidation is divided into two
... complete degradation of saturated fatty acids having an even number of carbon atoms. Most fatty acids have such structures because of their mode of synthesis . The oxidation of fatty acids containing double bonds requires additional steps. Likewise, fatty acids containing an odd number of carbon ato ...
... complete degradation of saturated fatty acids having an even number of carbon atoms. Most fatty acids have such structures because of their mode of synthesis . The oxidation of fatty acids containing double bonds requires additional steps. Likewise, fatty acids containing an odd number of carbon ato ...
A Negative Feedback Mechanism Between Brain Catecholamines
... hormone decreases glucose uptake by peripheral tissues and induces a form of secondary diabetes mellitus. Decreasing of glucose uptake occurs as a result of desensitization of insulin receptors by growth hormone. Growth hormone decreases glucose uptake by peripheral tissues and induces a form of sec ...
... hormone decreases glucose uptake by peripheral tissues and induces a form of secondary diabetes mellitus. Decreasing of glucose uptake occurs as a result of desensitization of insulin receptors by growth hormone. Growth hormone decreases glucose uptake by peripheral tissues and induces a form of sec ...
02b Basic equations two substrates
... Often the enzyme is transiently covalently modified in order to transfer a functional group from one substrate to the other. Note: the substrates are not in contact with each other on the enzyme. This type of mechanism is seen in serine proteases and is common in aminotransferases and some flavoenzy ...
... Often the enzyme is transiently covalently modified in order to transfer a functional group from one substrate to the other. Note: the substrates are not in contact with each other on the enzyme. This type of mechanism is seen in serine proteases and is common in aminotransferases and some flavoenzy ...
CHAPTER 25
... a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the three statements are true. c) Only one of the statements is true. d) None of the statements is true. 25.40 c - TFF Statements: (1) The number of acetyl CoA molecules produced in the fatty acid spiral is equal to half the number of carbon atoms in the f ...
... a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the three statements are true. c) Only one of the statements is true. d) None of the statements is true. 25.40 c - TFF Statements: (1) The number of acetyl CoA molecules produced in the fatty acid spiral is equal to half the number of carbon atoms in the f ...
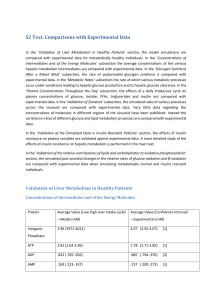
The model was provided with glucose and FFA inputs to
... The fold increase in the rate of non-oxidative glucose metabolism is well within one standard deviation of the experimental data at the moderate insulin concentration (Table 5). The very high insulin concentration had a smaller effect in the simulated data than is seen experimentally. However, one p ...
... The fold increase in the rate of non-oxidative glucose metabolism is well within one standard deviation of the experimental data at the moderate insulin concentration (Table 5). The very high insulin concentration had a smaller effect in the simulated data than is seen experimentally. However, one p ...
A Guide to Baking Enzymes
... flour and baked goods is governed by Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations. Malt and fungal alpha- amylase from Aspergillus o ryzae are permitted to standardize wheat flour under 21 CFR 137.105. Malt must be labeled as “malted wheat,” “malted wheat flour,” or “malted barley flour” in both the ...
... flour and baked goods is governed by Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations. Malt and fungal alpha- amylase from Aspergillus o ryzae are permitted to standardize wheat flour under 21 CFR 137.105. Malt must be labeled as “malted wheat,” “malted wheat flour,” or “malted barley flour” in both the ...
biochemistry - Louis Bolk Institute
... Biochemistry is the area in the life sciences which pre-eminently offers insight into the continuous and manifold changes that occur in organisms. It shows substances to be not static but ever changing, in structure as well as function. The cell, including the cell membrane, as well as tissues and o ...
... Biochemistry is the area in the life sciences which pre-eminently offers insight into the continuous and manifold changes that occur in organisms. It shows substances to be not static but ever changing, in structure as well as function. The cell, including the cell membrane, as well as tissues and o ...
Role of TCA cycle and glyoxylate shunt for succinic acid production
... extremely important role in the food and beverage industry. Because its ability to produce ethanol, via alcoholic fermentation of different sugars as carbon sources, it’s widely used for the industrial production of alcoholic beverages like beer, wine or sake. During the fermentation process CO2 is ...
... extremely important role in the food and beverage industry. Because its ability to produce ethanol, via alcoholic fermentation of different sugars as carbon sources, it’s widely used for the industrial production of alcoholic beverages like beer, wine or sake. During the fermentation process CO2 is ...
Urinalysis
... Reagent tablet – Coppe r sulfate, citric acid, sodium hydroxide and sodium carb onate. Add tablet to 5 drops of urine in a glass tube and look for a color cha nge in a spe cified time. Compare color change (blue to green to orange) to a chart for quantitation. ...
... Reagent tablet – Coppe r sulfate, citric acid, sodium hydroxide and sodium carb onate. Add tablet to 5 drops of urine in a glass tube and look for a color cha nge in a spe cified time. Compare color change (blue to green to orange) to a chart for quantitation. ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑