Chem 11 Spring 2012 Practice Final
... C) many α-helixes wound into fibrils. D) a braided triple helix. E) many glycoside links. 22) The fibrous protein responsible for the structure of hair and wool is A) keratin. B) collagen. C) endorphin. D) myosin. E) casein. 23) In the peptide Ser-Cys-Ala-Gly, the C-terminal end is A) serine. B) ser ...
... C) many α-helixes wound into fibrils. D) a braided triple helix. E) many glycoside links. 22) The fibrous protein responsible for the structure of hair and wool is A) keratin. B) collagen. C) endorphin. D) myosin. E) casein. 23) In the peptide Ser-Cys-Ala-Gly, the C-terminal end is A) serine. B) ser ...
CHE-120 Test 4
... E) the nonpolar tails of the salt dissolve in the grease and the polar salt ends dissolve in water. 15) Glycerophospholipids can interact both with other lipids and water because they contain A) saturated fatty acids. B) double bonds. C) polar regions and nonpolar regions. D) glycerol. E) cholestero ...
... E) the nonpolar tails of the salt dissolve in the grease and the polar salt ends dissolve in water. 15) Glycerophospholipids can interact both with other lipids and water because they contain A) saturated fatty acids. B) double bonds. C) polar regions and nonpolar regions. D) glycerol. E) cholestero ...
Supplementary Text - Overview of nutrition for endurance athletes
... effect when co-ingested with carbohydrate. Further contributing to this issue, Miller et al. [12] examined ...
... effect when co-ingested with carbohydrate. Further contributing to this issue, Miller et al. [12] examined ...
The Complex Role of Branched Chain Amino Acids
... with pancreas and liver cancer and more recent studies found increased incidence of endometrial, breast, colorectal, bladder and kidney cancers [2]. In fact, the conditions of overweight and obesity which are highly associated with type 2 diabetes are estimated to contribute to 15%–20% of all cancer ...
... with pancreas and liver cancer and more recent studies found increased incidence of endometrial, breast, colorectal, bladder and kidney cancers [2]. In fact, the conditions of overweight and obesity which are highly associated with type 2 diabetes are estimated to contribute to 15%–20% of all cancer ...
RED CELL MEMBRANE DEFECTS
... Structural & biochemical integrity of the RBC depends on: The normal function of more than 20 enzymes involved in these pathways The availability of five RBC substrates: Glucose, Glutathione, NAD, NAD phosphate & Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) ...
... Structural & biochemical integrity of the RBC depends on: The normal function of more than 20 enzymes involved in these pathways The availability of five RBC substrates: Glucose, Glutathione, NAD, NAD phosphate & Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) ...
Metabolism of “surplus” amino acids
... Robinson et al.(17) measured energy expenditure and whole body protein turnover for 9 hours in a group of men fed hourly with flavoured water (i.e. fasting) or iso-energetic liquid diets providing either 70 % carbohydrate or 70 % protein and 15 % fat. Compared with the fasting state, the high carboh ...
... Robinson et al.(17) measured energy expenditure and whole body protein turnover for 9 hours in a group of men fed hourly with flavoured water (i.e. fasting) or iso-energetic liquid diets providing either 70 % carbohydrate or 70 % protein and 15 % fat. Compared with the fasting state, the high carboh ...
Metabolism and Biotransformation of Pesticides
... In many cases males and females of the same species differ in levels (or even presence) of P450 isozymes. Examples: aromatase, which catalyzes conversion of testosterone to estradiol. In the rat, it is present in the male testes and the female adrenal glands. As sperm matures, it Apparently require ...
... In many cases males and females of the same species differ in levels (or even presence) of P450 isozymes. Examples: aromatase, which catalyzes conversion of testosterone to estradiol. In the rat, it is present in the male testes and the female adrenal glands. As sperm matures, it Apparently require ...
Lab Module 7 - philipdarrenjones.com
... and other alcoholic beverages, and even things like chocolate and coffee. Many organisms are capable of performing fermentation. Their by-products vary, depending on the organic molecule that is fermented and the enzyme system that the organism uses. In all cases, fermentation involves the breakdown ...
... and other alcoholic beverages, and even things like chocolate and coffee. Many organisms are capable of performing fermentation. Their by-products vary, depending on the organic molecule that is fermented and the enzyme system that the organism uses. In all cases, fermentation involves the breakdown ...
Amino acid metabolism II. Urea cycle
... Carbamoyl phosphate + ornithine → citrulline + Pi Citrulline + ATP + aspartate → argininosuccinate + AMP + PPi ...
... Carbamoyl phosphate + ornithine → citrulline + Pi Citrulline + ATP + aspartate → argininosuccinate + AMP + PPi ...
Muscle relaxants
... Sources of energy for muscle contraction • ATP – maintains contraction for 1 to 2 seconds • phosphocreatine – 5 times as great as ATP, sufficient for 7-8 s contraction • Anaerobic Glycolysis – Enzymatic breakdown of the glucose to pyruvate and lactate liberates energy that is used to convert ADP to ...
... Sources of energy for muscle contraction • ATP – maintains contraction for 1 to 2 seconds • phosphocreatine – 5 times as great as ATP, sufficient for 7-8 s contraction • Anaerobic Glycolysis – Enzymatic breakdown of the glucose to pyruvate and lactate liberates energy that is used to convert ADP to ...
Enzymes and pH Review Game with Answers 2013 2014
... B) Elevated body temperatures may denature enzymes. This would interfere with the cell's abilities to catalyze various reactions. C) Elevated body temperatures will increase the energy of activation needed to start various chemical reactions in the body. This will interfere with the ability of enzym ...
... B) Elevated body temperatures may denature enzymes. This would interfere with the cell's abilities to catalyze various reactions. C) Elevated body temperatures will increase the energy of activation needed to start various chemical reactions in the body. This will interfere with the ability of enzym ...
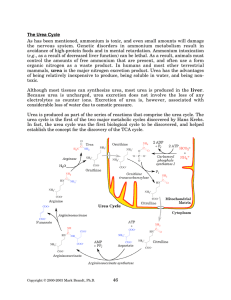
The Urea Cycle - Rose
... substrates for protein synthesis, or as the result of release following protein breakdown. Between meals (and especially during fasting), the muscle and liver are important in maintaining circulating levels of free amino acids. The liver is the site of the majority of amino acid synthesis, while the ...
... substrates for protein synthesis, or as the result of release following protein breakdown. Between meals (and especially during fasting), the muscle and liver are important in maintaining circulating levels of free amino acids. The liver is the site of the majority of amino acid synthesis, while the ...
Understanding fatty acid synthesis in developing - Shachar
... reducing equivalents in the form of NADH and NADPH. It was proposed that, in isolated plastids from heterotrophic tissues, reducing power could be generated via the conversion of imported malate into acetyl CoA; one mole of NADPH is liberated during the reaction catalyzed by plastidic NADP-dependent ...
... reducing equivalents in the form of NADH and NADPH. It was proposed that, in isolated plastids from heterotrophic tissues, reducing power could be generated via the conversion of imported malate into acetyl CoA; one mole of NADPH is liberated during the reaction catalyzed by plastidic NADP-dependent ...
Seminars in
... fatty acids to synthesize glucose and ketone bodies, the latter being exported to peripheral tissues and used preferentially to glucose as an alternative fuel; and (4) a normal endocrine system for integrating and modulating these processes. The major signals controlling the transition between fed a ...
... fatty acids to synthesize glucose and ketone bodies, the latter being exported to peripheral tissues and used preferentially to glucose as an alternative fuel; and (4) a normal endocrine system for integrating and modulating these processes. The major signals controlling the transition between fed a ...
Journal of Clinical Bioinformatics
... Among the total of 60 detected metabolites, our analysis revealed 5 key metabolites (lactate, alanine, glycine, and the two short-chain acyl carnitines C2 and C3) associated with physical exercise. These results are consistent with previous reports [19,22,23]. As is well known, anaerobic glycolysis ...
... Among the total of 60 detected metabolites, our analysis revealed 5 key metabolites (lactate, alanine, glycine, and the two short-chain acyl carnitines C2 and C3) associated with physical exercise. These results are consistent with previous reports [19,22,23]. As is well known, anaerobic glycolysis ...
1 ENZYME KINETICS [APPLICATION OF UV
... Prepare a HRP solution with a concentration of 25 Sigma units of HRP per mL. The Glucose oxidase stock solution should be about 5 Sigma units per mL. But this does not mean you should use this concentration. You should do a test run to see if this concentration gives an absorbance rate of change you ...
... Prepare a HRP solution with a concentration of 25 Sigma units of HRP per mL. The Glucose oxidase stock solution should be about 5 Sigma units per mL. But this does not mean you should use this concentration. You should do a test run to see if this concentration gives an absorbance rate of change you ...
Glucose Regulation in Diabetes
... When we eat a meal, our blood glucose level rises because we absorb sugar and carbohydrates into our blood via our digestive system. Consequently, blood glucose exceeds the set point of 90mg/100mL and the β-cells of the pancreas release insulin into the blood. Insulin then travels through the circul ...
... When we eat a meal, our blood glucose level rises because we absorb sugar and carbohydrates into our blood via our digestive system. Consequently, blood glucose exceeds the set point of 90mg/100mL and the β-cells of the pancreas release insulin into the blood. Insulin then travels through the circul ...
M01
... The end result of this oxidation is Acetyl CoA. Well fed state : Fasting, starvation, exercise: ...
... The end result of this oxidation is Acetyl CoA. Well fed state : Fasting, starvation, exercise: ...
Muscles
... raised and ready through the splitting of ATP. However it is not able to bind together with ease, because the actin molecule is physically blocked by a protein known as tropomyosin. For the muscle to contract the tropomyosin must be moved out of the bonding. For this to happen, Tropomyosin and tropo ...
... raised and ready through the splitting of ATP. However it is not able to bind together with ease, because the actin molecule is physically blocked by a protein known as tropomyosin. For the muscle to contract the tropomyosin must be moved out of the bonding. For this to happen, Tropomyosin and tropo ...
Biocatalysis - School of Chemical Sciences
... a biocatalyst is its high selectivity. This selectivity is often chiral (i.e., stereo-selectivity), positional (i.e., regio-selectivity), and functional group specific (i.e., chemo-selectivity). Such high selectivity is very desirable in chemical synthesis as it may offer several benefits such as redu ...
... a biocatalyst is its high selectivity. This selectivity is often chiral (i.e., stereo-selectivity), positional (i.e., regio-selectivity), and functional group specific (i.e., chemo-selectivity). Such high selectivity is very desirable in chemical synthesis as it may offer several benefits such as redu ...
Enzyme Complete ppt
... Induced fit model • More accurate model of enzyme action • 3-D structure of enzyme fits substrate • substrate binding cause enzyme to change shape leading to a tighter fit • “conformational change” • bring chemical groups in position to catalyze reaction ...
... Induced fit model • More accurate model of enzyme action • 3-D structure of enzyme fits substrate • substrate binding cause enzyme to change shape leading to a tighter fit • “conformational change” • bring chemical groups in position to catalyze reaction ...
1 ENZYME KINETICS [APPLICATION OF UV
... Prepare a HRP solution with a concentration of 25 Sigma units of HRP per mL. The Glucose oxidase stock solution should be about 5 Sigma units per mL. But this does not mean you should use this concentration. You should do a test run to see if this concentration gives an absorbance rate of change you ...
... Prepare a HRP solution with a concentration of 25 Sigma units of HRP per mL. The Glucose oxidase stock solution should be about 5 Sigma units per mL. But this does not mean you should use this concentration. You should do a test run to see if this concentration gives an absorbance rate of change you ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑