Lecture: 28 TRANSAMINATION, DEAMINATION AND
... Protein metabolism is a key physiological process in all forms of life. Proteins are converted to amino acids and then catabolised. The complete hydrolysis of a polypeptide requires mixture of peptidases because individual peptidases do not cleave all peptide bonds. ...
... Protein metabolism is a key physiological process in all forms of life. Proteins are converted to amino acids and then catabolised. The complete hydrolysis of a polypeptide requires mixture of peptidases because individual peptidases do not cleave all peptide bonds. ...
Section: 9.1 2) 2) The molec
... 6) 7) Starting with one molecule of glucose, the energy-containing products of glycolysis are _____. Section: 9.2 7) 8) If you were to add one of the eight citric acid cycle intermediates to the culture medium of yeast growing in the laboratory, what do you think would happen to the rates of ATP and ...
... 6) 7) Starting with one molecule of glucose, the energy-containing products of glycolysis are _____. Section: 9.2 7) 8) If you were to add one of the eight citric acid cycle intermediates to the culture medium of yeast growing in the laboratory, what do you think would happen to the rates of ATP and ...
Brewing biochemistry
... The theoretical teaching is subdivided in two parts and supported by practicals: Biochemistry of malting and brewing: (1) barley an enzymatic reactions occurring during malting, (2) biochemical reactions during brewing. Biochemistry of fermentation: Focused on the utilization of Saccharomyces cerevi ...
... The theoretical teaching is subdivided in two parts and supported by practicals: Biochemistry of malting and brewing: (1) barley an enzymatic reactions occurring during malting, (2) biochemical reactions during brewing. Biochemistry of fermentation: Focused on the utilization of Saccharomyces cerevi ...
Allosteric enzymes
... Of note, many key digestive enzymes, such as α-amylase and lipase, are present in the pancreas in their active forms. Presumably, these enzymes would not cause pancreatic cellular damage if released into the pancreatic cell/tissue because there is no starch, glycogen or triglyceride substrate for t ...
... Of note, many key digestive enzymes, such as α-amylase and lipase, are present in the pancreas in their active forms. Presumably, these enzymes would not cause pancreatic cellular damage if released into the pancreatic cell/tissue because there is no starch, glycogen or triglyceride substrate for t ...
Review Evolution of the coordinate regulation of glycolytic enzyme
... synthesis, transcription, translation and their regulation, were established under strictly anaerobic conditions, and perhaps as a consequence have an absolute requirement for a reducing environment in order to function (Segerer et al., 1985). Likewise it may be expected that certain biological acti ...
... synthesis, transcription, translation and their regulation, were established under strictly anaerobic conditions, and perhaps as a consequence have an absolute requirement for a reducing environment in order to function (Segerer et al., 1985). Likewise it may be expected that certain biological acti ...
October 15 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... treats chronic alcoholism blocks enzyme that ...
... treats chronic alcoholism blocks enzyme that ...
Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, Peroxisomes - Beck-Shop
... his chapter considers three organelles formed by posttranslational import of proteins synthesized in the cytoplasm. Mitochondria and chloroplasts both arose from endosymbiotic bacteria, two singular events that occurred about one billion years apart. Both mitochondria and chloroplasts retain [besitz ...
... his chapter considers three organelles formed by posttranslational import of proteins synthesized in the cytoplasm. Mitochondria and chloroplasts both arose from endosymbiotic bacteria, two singular events that occurred about one billion years apart. Both mitochondria and chloroplasts retain [besitz ...
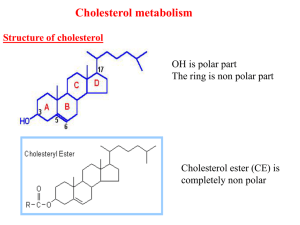
Lec4 Cholesterol met..
... 2- Drug inhibition: Statins such as atorvastatin (by Pfizer), lovastatin and simvastatin are drugs with a side chain structurally similar to HMG-CoA so competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase. They are used to decrease cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia. 3- Diet: its activity a ...
... 2- Drug inhibition: Statins such as atorvastatin (by Pfizer), lovastatin and simvastatin are drugs with a side chain structurally similar to HMG-CoA so competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase. They are used to decrease cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia. 3- Diet: its activity a ...
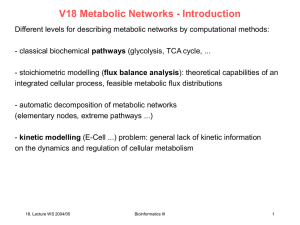
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... Conclusions about large-scale structure In a cell or microorganism, the processes that generate mass, energy, information transfer and cell-fate specification are seamlessly integrated through a complex network of cellular constituents and reactions. A systematic comparative mathematical analysis o ...
... Conclusions about large-scale structure In a cell or microorganism, the processes that generate mass, energy, information transfer and cell-fate specification are seamlessly integrated through a complex network of cellular constituents and reactions. A systematic comparative mathematical analysis o ...
The Skinny on Low-Carbohydrate Diets
... • “Carbohydrate restriction is one of several strategies for reducing body mass but even in the absence of weight loss or in comparison with low fat alternatives, CHO restriction is effective at ameliorating high fasting glucose and insulin, high plasma triglycerides, low HDL and high blood pressur ...
... • “Carbohydrate restriction is one of several strategies for reducing body mass but even in the absence of weight loss or in comparison with low fat alternatives, CHO restriction is effective at ameliorating high fasting glucose and insulin, high plasma triglycerides, low HDL and high blood pressur ...
8 - student.ahc.umn.edu
... spectrum. It absorbs light in the visible wavelength giving it a color which is visible to the human eye. That spectrum changes depending on whether the molecule is oxidized or reduced. Such changes in absorption are useful to biochemists because they provide a window through which investigators can ...
... spectrum. It absorbs light in the visible wavelength giving it a color which is visible to the human eye. That spectrum changes depending on whether the molecule is oxidized or reduced. Such changes in absorption are useful to biochemists because they provide a window through which investigators can ...
Dietary whey protein increases liver and skeletal muscle glycogen
... glucogenesis and glycolysis, and glucose release that is determined by glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis (Levine & Haft, 1970). Glycolysis also has a role in determining the activity of key enzymes of the opposing glycolytic and gluconeogenic pathways, which must be controlled and regulated in orde ...
... glucogenesis and glycolysis, and glucose release that is determined by glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis (Levine & Haft, 1970). Glycolysis also has a role in determining the activity of key enzymes of the opposing glycolytic and gluconeogenic pathways, which must be controlled and regulated in orde ...
Module 13 Enzymes and Vitamins Lecture 34 Enzymes
... but weak enough to allow the product to depart once it is produced. The amino acids present in the active site also assist in the reaction mechanism. For example, nucleophilic amino acid such as serine is commonly involved in enzymecatalyzed reaction mechanisms and will form covalent bond with the s ...
... but weak enough to allow the product to depart once it is produced. The amino acids present in the active site also assist in the reaction mechanism. For example, nucleophilic amino acid such as serine is commonly involved in enzymecatalyzed reaction mechanisms and will form covalent bond with the s ...
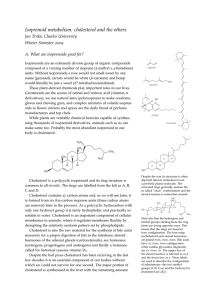
Isoprenoid metabolism: cholesterol and the others
... which is an essential electron carrier in the mitochondrial electron transport chain. It is important to bear in mind that the inhibition of the isoprenoid pathway does not only reduce the synthesis of cholesterol but also of these other important metabolites. Let’s come back to cholesterol. Two mol ...
... which is an essential electron carrier in the mitochondrial electron transport chain. It is important to bear in mind that the inhibition of the isoprenoid pathway does not only reduce the synthesis of cholesterol but also of these other important metabolites. Let’s come back to cholesterol. Two mol ...
Regulation of Primary Metabolism in Response to
... cycle also contribute to the production of key metabolic intermediates for use in many other fundamental biosynthetic processes elsewhere in the cell (Fernie et al., 2004; Sweetlove et al., 2010; van Dongen et al., 2011; Araújo et al., 2012). Nevertheless, the control and regulation of the carbon flu ...
... cycle also contribute to the production of key metabolic intermediates for use in many other fundamental biosynthetic processes elsewhere in the cell (Fernie et al., 2004; Sweetlove et al., 2010; van Dongen et al., 2011; Araújo et al., 2012). Nevertheless, the control and regulation of the carbon flu ...
23. electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation
... to turn, resulting in conformational changes in the β, subunits where ATP is synthesized. (Courtesy : Drs. Peter L. Pedersen, Young Hee Ko, and Sangjin Hong) ...
... to turn, resulting in conformational changes in the β, subunits where ATP is synthesized. (Courtesy : Drs. Peter L. Pedersen, Young Hee Ko, and Sangjin Hong) ...
PAGES 1-41 INCL. 1. Overview (a) discovery of enzymes (b
... "Enzyme"--means "in yeast" (Greek) -used by man--fermentation of alcohol and cheese 1.(a) discovery of enzymes - enzyme first used in 1878 by Kühne to indicate yeast were organized systems capable of fermentation - shown by Büchner in 1897 that yeast extracts could also ferment sugar to alcohol; nev ...
... "Enzyme"--means "in yeast" (Greek) -used by man--fermentation of alcohol and cheese 1.(a) discovery of enzymes - enzyme first used in 1878 by Kühne to indicate yeast were organized systems capable of fermentation - shown by Büchner in 1897 that yeast extracts could also ferment sugar to alcohol; nev ...
anabolic and catabolic reactions. Energetics of bacterial growth
... in energy transduction of living cells was first recognized by Harden and Young in 1906 (41), but it was not until the 1940s that the significance of phosphate esters was more fully appreciated. Lipmann (56) used the term ‘‘energy rich’’ to describe ATP and other phosphorylated intermediates, and wi ...
... in energy transduction of living cells was first recognized by Harden and Young in 1906 (41), but it was not until the 1940s that the significance of phosphate esters was more fully appreciated. Lipmann (56) used the term ‘‘energy rich’’ to describe ATP and other phosphorylated intermediates, and wi ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Inducible Genes
... (a) Lactose present, glucose scarce (cAMP level high): abundant lac mRNA synthesized. If glucose is scarce, the high level of cAMP activates CAP, and the lac operon produces large amounts of mRNA for the lactose pathway. ...
... (a) Lactose present, glucose scarce (cAMP level high): abundant lac mRNA synthesized. If glucose is scarce, the high level of cAMP activates CAP, and the lac operon produces large amounts of mRNA for the lactose pathway. ...
МИНИСТЕРСТВО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ И НАУКИ
... Attendance is strictly necessary. If for any reason a student cannot attend, then a student is responsible for all the material. Control tasks are required to perform and should be given on time. The work carried out with a delay, will automatically be assessed below. The results of the Midterm Exam ...
... Attendance is strictly necessary. If for any reason a student cannot attend, then a student is responsible for all the material. Control tasks are required to perform and should be given on time. The work carried out with a delay, will automatically be assessed below. The results of the Midterm Exam ...
1 - u.arizona.edu
... with increased Vmax; another variant has an increased affinity (low Km) for ribose-5-P leading to overproduction of PRPP - 3rd defect associated with loss of feedback inhibition of this enzyme by purine nucleotides; when purine nucleotides reach excessive concentration no signal for shutting off ...
... with increased Vmax; another variant has an increased affinity (low Km) for ribose-5-P leading to overproduction of PRPP - 3rd defect associated with loss of feedback inhibition of this enzyme by purine nucleotides; when purine nucleotides reach excessive concentration no signal for shutting off ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑